US Manufacturing Dips in October, Says ISM
Us manufacturing takes a dip in october says ism – US Manufacturing Dips in October, Says ISM – a headline that sent ripples through the economic landscape. The Institute for Supply Management (ISM) reported a contraction in October, signaling a potential slowdown in the manufacturing sector. This dip comes after months of fluctuating growth, raising concerns about the health of the US economy.
The ISM Manufacturing Index, a key indicator of manufacturing activity, fell to 49.1 in October, down from 50.9 in September. A reading below 50 indicates contraction, and this decline marks the first time the index has dipped below the growth threshold since January 2023.
This downturn highlights the challenges facing US manufacturers, including persistent supply chain disruptions, rising interest rates, and persistent inflation.
ISM Manufacturing Index Decline
The ISM Manufacturing Index is a crucial indicator of the health of the U.S. manufacturing sector. It provides insights into the current state of the industry and its potential for future growth. A decline in the index suggests a contraction in manufacturing activity, raising concerns about the overall economy.The ISM Manufacturing Index declined to 49.1 in October 2023, signaling a contraction in the manufacturing sector.
This decline followed a reading of 50.9 in September, indicating that the sector had been expanding. The index has now been below the 50-point threshold for two consecutive months, which is considered the dividing line between expansion and contraction.
Historical Context of the Decline
The decline in the ISM Manufacturing Index in October is part of a broader trend of slowing manufacturing activity in the U.S. The index has been fluctuating in recent months, indicating a period of uncertainty in the manufacturing sector. The index has declined significantly from its peak of 64.7 in March 2022.
This decline reflects the impact of various factors, including rising interest rates, supply chain disruptions, and the ongoing global economic slowdown. The October decline is similar to the decline observed in May 2023, when the index fell to 49.2. However, the decline in October is more significant than the decline in May, indicating a more pronounced contraction in manufacturing activity.
The ISM Manufacturing Index dipping in October highlights the challenges facing the US economy, with factors like inflation and supply chain issues continuing to play a role. Meanwhile, on the environmental front, California has taken a bold step by taking legal action against oil giants for their role in the climate crisis.
While the focus may be on manufacturing and energy, the interconnectedness of these issues underscores the need for a comprehensive approach to economic and environmental sustainability.
The ISM Manufacturing Index is a widely followed indicator of the health of the U.S. manufacturing sector.
The ISM Manufacturing Index reported a dip in October, signaling a potential slowdown in the sector. This news comes as Wall Street grapples with mixed earnings reports and anxiously awaits the Federal Reserve’s interest rate decision, which could have a significant impact on the economy.
The Fed’s decision, covered live on sites like thevenomblog.com , will likely influence the direction of the US manufacturing sector in the coming months.
Factors Contributing to the Decline

The recent dip in the ISM Manufacturing Index for October reflects a confluence of factors impacting the US manufacturing sector. While the index has been trending downwards for several months, the October reading signaled a more pronounced decline. This downturn can be attributed to several factors, including persistent supply chain disruptions, rising interest rates, and ongoing inflationary pressures.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions have been a major challenge for manufacturers throughout the pandemic and its aftermath. These disruptions have led to delays in production, increased costs, and reduced output. While some supply chain issues have begun to ease, ongoing geopolitical tensions, such as the war in Ukraine, continue to exacerbate these problems.
The ISM Manufacturing Index reported a dip in October, highlighting a slowdown in the US manufacturing sector. This decline comes amidst broader economic uncertainty, and it’s worth noting that this trend is reflected in other sectors, too. For example, airline stocks experience volatility leading to year to date losses , indicating that investors are cautious about the overall economic outlook.
The ISM report suggests that the manufacturing sector may be facing headwinds, which could ripple through other parts of the economy.
For example, the ongoing semiconductor shortage, a key component in many manufactured goods, has hampered production across various industries. This shortage has been driven by factors like factory closures in Southeast Asia due to COVID-19 lockdowns and the ongoing war in Ukraine, which has disrupted supply chains for critical materials.
Rising Interest Rates and Inflation
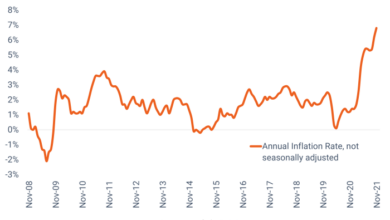
The Federal Reserve’s aggressive monetary tightening policy, aimed at curbing inflation, has had a significant impact on manufacturing activity. Rising interest rates increase borrowing costs for businesses, making it more expensive to finance investments and expansion. Moreover, inflation has driven up the cost of raw materials, energy, and labor, further squeezing profit margins for manufacturers.
The rising cost of borrowing and input materials has led to reduced investment and a slowdown in production, contributing to the decline in the ISM Manufacturing Index. For instance, the cost of steel, a key input for many manufactured goods, has risen sharply in recent months due to inflation and supply chain disruptions, making it more expensive for manufacturers to produce their goods.
This has led to a decline in manufacturing output as businesses are forced to cut back on production to maintain profitability.
Impact on the US Economy

The decline in the ISM Manufacturing Index signals a potential slowdown in the US economy. This contraction in manufacturing activity could have significant ripple effects throughout the economy, impacting growth, employment, and other industries.
Impact on Economic Growth
The manufacturing sector plays a crucial role in the US economy, contributing significantly to overall economic output and growth. A decline in manufacturing activity can directly impact GDP growth. The ISM Manufacturing Index is a leading indicator of economic activity, and its decline suggests that the US economy may be headed for slower growth in the coming months.
For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, the manufacturing sector experienced a sharp decline, contributing to the overall economic recession.
Industry-Specific Trends: Us Manufacturing Takes A Dip In October Says Ism
The decline in the ISM Manufacturing Index in October 2023 was not uniform across all manufacturing sub-sectors. Some industries experienced a more pronounced downturn than others, reflecting the diverse nature of the manufacturing landscape and the unique challenges faced by different sectors.
This section delves into the performance of key manufacturing sub-sectors during the decline, highlighting the varying impacts and potential for recovery.
Performance of Different Manufacturing Sub-Sectors
The decline in the ISM Manufacturing Index in October 2023 was not uniform across all manufacturing sub-sectors. Some industries experienced a more pronounced downturn than others, reflecting the diverse nature of the manufacturing landscape and the unique challenges faced by different sectors.
This section delves into the performance of key manufacturing sub-sectors during the decline, highlighting the varying impacts and potential for recovery.
- Automotive:The automotive sector faced significant challenges in October, with production hampered by ongoing supply chain disruptions and weakening demand. The decline in new orders and production was particularly pronounced, reflecting the ongoing global chip shortage and the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, which require different components and manufacturing processes.
- Electronics:The electronics sector also experienced a decline in October, although it was less severe than in the automotive sector. The decline was primarily driven by weakening consumer demand for electronic devices, particularly smartphones and computers. However, the sector remains optimistic about future growth, driven by the continued expansion of the internet of things (IoT) and the adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing.
- Chemicals:The chemicals sector experienced a mixed performance in October, with some segments showing resilience while others faced challenges. The decline in new orders and production was largely attributed to the slowdown in global economic activity and the rising costs of raw materials.
However, the sector remains optimistic about future growth, driven by the increasing demand for chemicals in industries such as agriculture, construction, and energy.
Impact on Different Industries, Us manufacturing takes a dip in october says ism
The decline in the ISM Manufacturing Index had a varying impact on different industries, reflecting the diverse nature of the manufacturing landscape and the unique challenges faced by different sectors. This section explores the impact of the decline on key industries, highlighting the varying impacts and potential for recovery.
- Automotive:The automotive sector was particularly hard hit by the decline in the ISM Manufacturing Index, with production hampered by ongoing supply chain disruptions and weakening demand. The decline in new orders and production was particularly pronounced, reflecting the ongoing global chip shortage and the increasing adoption of electric vehicles, which require different components and manufacturing processes.
- Electronics:The electronics sector also experienced a decline in October, although it was less severe than in the automotive sector. The decline was primarily driven by weakening consumer demand for electronic devices, particularly smartphones and computers. However, the sector remains optimistic about future growth, driven by the continued expansion of the internet of things (IoT) and the adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing.
- Chemicals:The chemicals sector experienced a mixed performance in October, with some segments showing resilience while others faced challenges. The decline in new orders and production was largely attributed to the slowdown in global economic activity and the rising costs of raw materials.
However, the sector remains optimistic about future growth, driven by the increasing demand for chemicals in industries such as agriculture, construction, and energy.
Potential for Recovery in Different Industries
The potential for recovery in different industries varies depending on the specific challenges faced by each sector and the broader economic outlook. This section explores the potential for recovery in key industries, highlighting the factors that will influence the pace and extent of recovery.
- Automotive:The automotive sector is expected to recover gradually, driven by the easing of supply chain disruptions and the continued growth in demand for new vehicles. However, the transition to electric vehicles will continue to pose challenges for the industry, requiring significant investments in new technologies and manufacturing processes.
- Electronics:The electronics sector is expected to recover more quickly than the automotive sector, driven by the continued expansion of the internet of things (IoT) and the adoption of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and cloud computing. However, the sector will need to navigate the challenges posed by the ongoing trade tensions between the United States and China, which could impact supply chains and costs.
- Chemicals:The chemicals sector is expected to recover gradually, driven by the increasing demand for chemicals in industries such as agriculture, construction, and energy. However, the sector will need to address the challenges posed by the rising costs of raw materials and the growing environmental regulations.