US Dollar Strengthens as Fed Hints at Rate Hikes, Yen Weakens
Us dollar strengthens as federal reserve hints at rate hikes japanese yen weakened – US Dollar Strengthens as Fed Hints at Rate Hikes, Yen Weakens: The global currency landscape is shifting, with the US dollar surging in value as the Federal Reserve signals its intention to raise interest rates. Meanwhile, the Japanese yen has weakened, reflecting the Bank of Japan’s commitment to a loose monetary policy.
This dynamic interplay between these two major currencies is having a significant impact on global markets, trade, and investment flows.
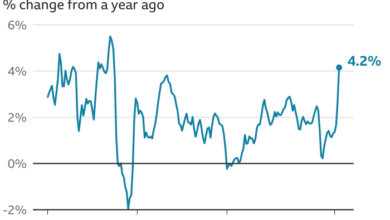
The Federal Reserve’s rate hike plans are aimed at combating inflation, which has been a major concern in the US and globally. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive, which can help to slow down economic activity and cool down inflation.
However, these rate hikes also make the US dollar more attractive to investors seeking higher returns, leading to its appreciation. On the other hand, the Bank of Japan has maintained its ultra-loose monetary policy, keeping interest rates low to stimulate the Japanese economy.
This has led to a weaker yen, making Japanese exports more competitive but also increasing the cost of imports.
US Dollar Strengthens
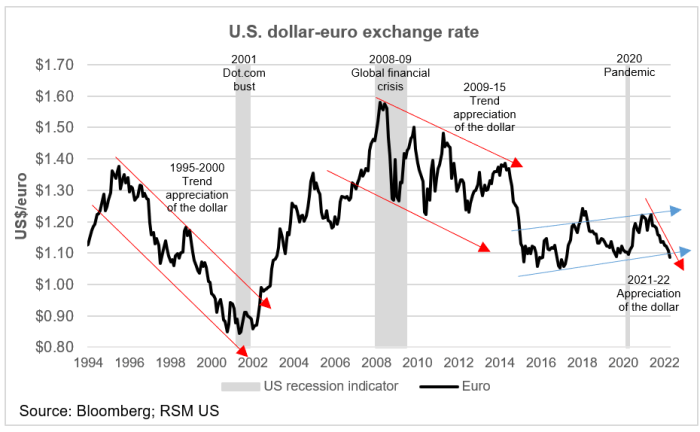
The US dollar has recently strengthened against other major currencies, driven by a combination of factors, including the Federal Reserve’s hawkish stance on interest rates and a flight to safety amidst global economic uncertainty.
Historical Overview of US Dollar Strength and Weakness
The US dollar’s strength and weakness have historically been influenced by various economic and geopolitical factors.
- During periods of economic growth and stability, the US dollar tends to strengthen as investors seek safe-haven assets. For instance, during the 1990s, the US dollar appreciated significantly as the US economy experienced a period of sustained growth.
- Conversely, during periods of economic recession or geopolitical turmoil, the US dollar may weaken as investors seek alternative currencies or assets. The 2008 financial crisis led to a significant decline in the US dollar’s value.
- The US dollar’s value is also influenced by interest rate differentials between the US and other major economies. When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it attracts foreign investors seeking higher returns, increasing demand for the US dollar and pushing its value higher.
The US dollar’s recent surge, fueled by the Federal Reserve’s hints of upcoming rate hikes, has sent the Japanese yen tumbling. This dynamic is reflected in the global markets, with the Nifty index hovering near the 17,650 mark. For a detailed look at the live updates on share market movements, check out this article on live updates share market movement flat nifty crosses 17650 focus on hcl tech and tata motors.
Keep an eye on how the strengthening dollar and the Fed’s actions will continue to impact the global financial landscape.
Conversely, lower interest rates in the US can lead to a weaker dollar.
Impact of Federal Reserve Rate Hikes on US Dollar
The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy plays a significant role in determining the US dollar’s strength.
- When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it makes US assets more attractive to foreign investors, increasing demand for the US dollar and pushing its value higher.
- The Fed’s recent hawkish stance on interest rates, signaling multiple rate hikes in the coming months, has contributed to the recent strengthening of the US dollar.
- The anticipation of higher interest rates in the US has led to a widening interest rate differential between the US and other major economies, further boosting demand for the US dollar.
Implications of a Strong US Dollar on Global Markets
A strong US dollar can have both positive and negative implications for global markets.
- For US exporters, a strong dollar can make their goods more expensive in foreign markets, potentially reducing demand and hurting profits.
- Conversely, a strong dollar can benefit US importers, as they can purchase goods from overseas at lower prices.
- A strong dollar can also have implications for emerging market economies, as it can make their debt repayments more expensive and potentially lead to currency depreciation.
- For example, during the 2013 “taper tantrum,” when the Federal Reserve hinted at reducing its asset purchases, the US dollar strengthened significantly, leading to capital outflows from emerging markets and currency depreciations.
Federal Reserve’s Rate Hike Hints
The Federal Reserve’s recent statements have sent ripples through the financial markets, signaling a potential shift towards a more hawkish monetary policy stance. The central bank’s hints at upcoming interest rate hikes have fueled speculation about the future trajectory of economic growth and inflation.
Potential Economic Consequences of Rate Hikes, Us dollar strengthens as federal reserve hints at rate hikes japanese yen weakened
The Federal Reserve’s rate hikes are designed to curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive, thereby slowing down economic activity. This can have a range of consequences for different sectors of the economy.
- Impact on Borrowing Costs:Higher interest rates will increase borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, potentially leading to reduced investment and spending. This can dampen economic growth, particularly in sectors that rely heavily on credit, such as housing and automobiles.
- Effect on Inflation:Rate hikes aim to reduce demand and cool down the economy, thereby putting downward pressure on inflation. However, the effectiveness of this strategy depends on various factors, including the magnitude of the rate hikes, the state of the economy, and consumer confidence.
- Currency Appreciation:Higher interest rates can attract foreign investment, leading to an appreciation of the US dollar. This can make US exports less competitive in global markets and impact industries reliant on international trade.
Comparison with Previous Periods of Rate Hikes
The current economic landscape presents a unique context for the Federal Reserve’s decision-making. Comparing the situation to previous periods of rate hikes can provide valuable insights.
- Post-2008 Recession:Following the 2008 financial crisis, the Federal Reserve implemented a policy of near-zero interest rates to stimulate economic recovery. As the economy gradually strengthened, the central bank began a gradual process of raising rates. However, this period was characterized by a relatively low inflation environment, which differs from the current situation of elevated inflation.
- Volatility and Uncertainty:The current economic environment is marked by heightened volatility and uncertainty, driven by factors such as the ongoing war in Ukraine, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions. This makes it challenging for the Federal Reserve to predict the impact of rate hikes on the economy.
While the US dollar strengthens as the Federal Reserve hints at rate hikes, and the Japanese yen weakens, it’s important to remember that a sustainable future hinges on smart investments. The rise of renewable energy commodities offers a compelling investment opportunity, and this blog explores the potential for growth in this sector.
As global markets shift towards a greener future, it’s wise to consider the long-term impact of economic decisions, even amidst short-term fluctuations in currency values.
Key Factors Influencing the Federal Reserve’s Decision-Making
The Federal Reserve’s decision to raise interest rates is influenced by a complex interplay of factors.
- Inflation Rate:The primary objective of the Federal Reserve is to maintain price stability. The central bank closely monitors inflation data to gauge the effectiveness of its monetary policy.
- Economic Growth:The Federal Reserve aims to achieve sustainable economic growth without fueling inflation. The central bank considers indicators such as GDP growth, employment, and consumer spending.
- Financial Market Conditions:The Federal Reserve monitors financial market conditions to assess potential risks to the economy. This includes factors such as asset prices, credit spreads, and investor sentiment.
- Global Economic Outlook:The Federal Reserve takes into account global economic developments and their potential impact on the US economy. This includes factors such as international trade, foreign exchange rates, and global inflation.
Japanese Yen Weakens
The Japanese yen has been weakening against the US dollar in recent months, driven by a confluence of factors, including the widening interest rate differential between the two countries and the Bank of Japan’s (BOJ) continued adherence to its ultra-loose monetary policy.
This trend has raised concerns about the potential impact on the Japanese economy.
Historical Context of Yen Fluctuations
The Japanese yen’s value has historically been subject to significant fluctuations. Its weakness in recent times is not an isolated event, but rather a continuation of a long-term trend. The yen’s value has been influenced by various factors, including:
- Global economic conditions:The yen tends to appreciate during periods of global economic uncertainty, as investors seek safe-haven assets. Conversely, it depreciates during periods of economic growth, as investors seek higher returns in riskier assets.
- Japan’s trade balance:A trade surplus typically strengthens the yen, as it reflects a higher demand for Japanese goods and services. Conversely, a trade deficit weakens the yen.
- Monetary policy:The BOJ’s monetary policy has a significant impact on the yen’s value. Loose monetary policy, such as low interest rates and quantitative easing, tends to weaken the yen, as it makes it less attractive to foreign investors.
- Political factors:Political instability or uncertainty in Japan can also affect the yen’s value. For example, the yen weakened significantly in the aftermath of the 2011 earthquake and tsunami.
Impact of the Bank of Japan’s Monetary Policy
The BOJ’s monetary policy has been a key driver of the yen’s weakness. The BOJ has maintained an ultra-loose monetary policy for several years, keeping interest rates near zero and engaging in quantitative easing. This policy aims to stimulate economic growth and inflation, but it has also weakened the yen by making it less attractive to foreign investors.
The BOJ’s continued adherence to this policy, despite rising inflation in other countries, has further exacerbated the yen’s decline.
The US dollar’s recent strength, fueled by the Federal Reserve’s hints at future rate hikes, has put pressure on other currencies like the Japanese yen. This shift in the global market seems to be attracting attention from some unexpected corners, like the tech industry, as evidenced by the recent news that Daniel Baldwin has joined iShook, a company that’s been making waves in the tech space.
daniel baldwin joins ishook 202879 This move could signal a growing interest in the tech sector as a safe haven during times of economic uncertainty, mirroring the trend of investors seeking stability amidst the fluctuating currency markets.
Potential Consequences of a Weak Yen
A weak yen can have both positive and negative consequences for the Japanese economy.
- Positive consequences:A weak yen can boost exports by making Japanese goods and services more competitive in global markets. This can lead to increased economic growth and employment. For example, Japanese car manufacturers have benefited from a weak yen in recent years, as their cars have become more affordable in overseas markets.
- Negative consequences:A weak yen can also lead to higher import prices, which can increase inflation and erode consumer purchasing power. It can also make it more expensive for Japanese companies to import raw materials and components, potentially impacting their profitability.
Additionally, a weak yen can discourage foreign investment in Japan, as investors may perceive the currency as being at risk of further depreciation.
Currency Pair Dynamics
The recent strengthening of the US dollar against the Japanese yen has been a significant development in the global currency markets. This dynamic reflects the interplay of several factors, including interest rate differentials, economic growth prospects, and global risk sentiment.
The Relationship Between the US Dollar and the Japanese Yen
The US dollar and the Japanese yen are among the most actively traded currency pairs globally. Their relationship is influenced by a complex interplay of economic, political, and financial factors. When the US dollar strengthens, the Japanese yen typically weakens, and vice versa.
This inverse relationship is often attributed to the “carry trade,” where investors borrow in low-yielding currencies like the yen and invest in higher-yielding assets like US Treasury bonds. As interest rate differentials widen, the carry trade becomes more attractive, leading to increased demand for US dollars and a weakening of the yen.
The Impact of the Federal Reserve’s Actions on the Yen
The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions have a significant impact on the US dollar and, consequently, the Japanese yen. When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it makes US dollar assets more attractive to foreign investors, increasing demand for the US dollar and pushing the yen lower.
Conversely, when the Federal Reserve lowers interest rates, it can lead to a weakening of the US dollar and a strengthening of the yen.
The Federal Reserve’s recent hints at further rate hikes have contributed to the recent strengthening of the US dollar and the weakening of the Japanese yen.
The Implications for Global Trade and Investment
The US dollar-yen exchange rate has significant implications for global trade and investment. A stronger US dollar makes US exports more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially hurting US businesses. Conversely, a weaker yen makes Japanese exports more competitive, potentially benefiting Japanese businesses.
For investors, a strong US dollar can make investments in US assets more attractive, while a weak yen can make investments in Japanese assets less attractive. The currency pair dynamic can also influence the value of investments held in foreign currencies.
For example, a US investor holding Japanese yen-denominated assets would see the value of their investment decline as the yen weakens against the US dollar.
Economic Implications: Us Dollar Strengthens As Federal Reserve Hints At Rate Hikes Japanese Yen Weakened
A strengthening US dollar and a weakening Japanese yen have significant implications for global trade, investment flows, and economic growth. This dynamic creates winners and losers, influencing the economic landscape across the world.
Impact on Global Trade
The relative value of currencies plays a crucial role in international trade. A stronger US dollar makes US exports more expensive for foreign buyers, potentially hindering demand. Conversely, a weaker yen makes Japanese exports more competitive in global markets, potentially boosting their sales.
This dynamic can lead to trade imbalances, as one country experiences a surge in exports while the other faces a decline.
- For instance, a stronger US dollar could make American automobiles less attractive to Japanese consumers, while Japanese electronics might become more affordable in the US market.
Impact on International Investment Flows
Currency fluctuations influence international investment flows. A strong US dollar can attract foreign investors seeking higher returns in US assets, leading to increased capital inflows. Conversely, a weak yen might deter foreign investment in Japan, as investors anticipate potential losses due to currency depreciation.
This dynamic can impact the availability of capital for businesses and governments in both countries.
- For example, a strong US dollar might encourage Japanese investors to allocate funds to US stocks and bonds, while a weak yen might discourage foreign investors from investing in Japanese real estate.
Winners and Losers
The currency scenario creates winners and losers in different sectors and countries.
- US exporters might face challenges due to higher prices, while US importers might benefit from cheaper imports.
- Japanese exporters might experience increased demand, while Japanese importers might face higher costs for imported goods.
- Investors holding US dollar-denominated assets might benefit from appreciation, while those holding yen-denominated assets might face losses.
Implications for Economic Growth and Stability
The currency dynamics can impact economic growth and stability in various ways.
- A strong US dollar can contribute to deflationary pressures in the US, as imported goods become cheaper, potentially slowing down economic growth.
- A weak yen can lead to inflation in Japan, as imported goods become more expensive, potentially impacting consumer spending and economic activity.
- Currency fluctuations can create uncertainty and volatility in financial markets, potentially impacting investor confidence and economic stability.