
Gavin Wood: Chain Mergers & Acquisitions
Gavin wood chain mergers and acquisitions – Gavin Wood, a prominent figure in the blockchain space, is making waves with his innovative approach to chain mergers and acquisitions. His vision for interoperability and seamless integration of blockchain networks is shaping the future of this rapidly evolving industry.
This blog delves into the world of Gavin Wood’s chain mergers and acquisitions, exploring his key projects, the impact on the blockchain ecosystem, and the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
The concept of chain mergers and acquisitions is not simply about merging different blockchains; it’s about creating a unified and interconnected network that leverages the strengths of each individual chain. Wood’s vision is to break down the silos between different blockchains, fostering collaboration and interoperability.
This vision has fueled the development of groundbreaking projects, like Polkadot, that are revolutionizing the blockchain landscape.
Gavin Wood’s Role in Chain Mergers and Acquisitions
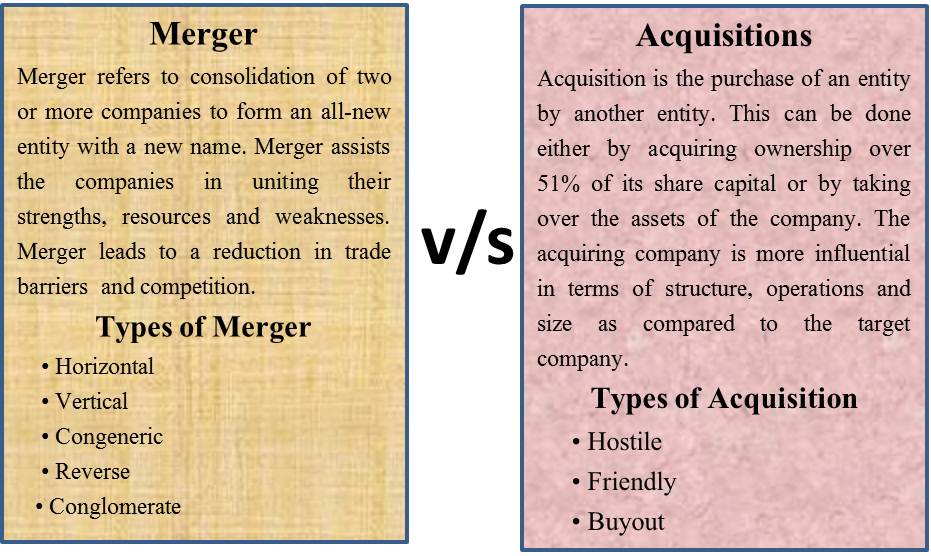
Gavin Wood, a prominent figure in the blockchain industry, is renowned for his visionary approach and pioneering contributions. His involvement in projects related to chain mergers and acquisitions (M&A) reflects his belief in the potential for interoperability and collaboration within the blockchain ecosystem.
This blog post explores Gavin Wood’s role in chain M&A, examining his vision for interoperability, the benefits and challenges of such mergers, and his insights into their potential impact on the future of blockchain technology.
Gavin Wood’s Vision for Interoperability
Gavin Wood’s vision for interoperability is central to his approach to chain mergers and acquisitions. He recognizes that the blockchain industry is currently fragmented, with numerous independent blockchains operating in isolation. This fragmentation hinders the development of a truly interconnected and scalable blockchain ecosystem.
Wood believes that interoperability is essential for unlocking the full potential of blockchain technology, enabling seamless communication and data exchange between different chains. He envisions a future where blockchains can work together harmoniously, forming a unified network that facilitates cross-chain transactions, data sharing, and application development.
Benefits and Challenges of Chain Mergers and Acquisitions
Chain mergers and acquisitions present both opportunities and challenges for the blockchain industry.
Benefits of Chain Mergers and Acquisitions
- Increased Interoperability:Mergers and acquisitions can foster interoperability by connecting different blockchains, enabling cross-chain communication and data exchange. This can create a more unified and interconnected blockchain ecosystem, facilitating the development of cross-chain applications and services.
- Enhanced Scalability:By combining resources and technologies, chain mergers can enhance scalability, allowing blockchains to handle larger transaction volumes and accommodate a growing user base. This can lead to improved performance and reduced transaction fees.
- Synergy and Innovation:Mergers can bring together complementary technologies, expertise, and communities, fostering innovation and accelerating the development of new blockchain solutions. This can lead to the emergence of more sophisticated and powerful applications.
Challenges of Chain Mergers and Acquisitions
- Technical Integration:Integrating different blockchain technologies can be technically challenging, requiring significant expertise and resources. Ensuring seamless communication and data exchange between disparate systems can be complex and time-consuming.
- Regulatory and Legal Considerations:Chain mergers and acquisitions may raise regulatory and legal issues, especially in jurisdictions with evolving blockchain regulations. Compliance with relevant laws and regulations can be complex and require careful consideration.
- Community Acceptance:Merging blockchains can be met with resistance from communities that value their autonomy and independence. Building consensus and ensuring community acceptance can be crucial for the success of such mergers.
Key Projects and Initiatives: Gavin Wood Chain Mergers And Acquisitions
Gavin Wood’s involvement in chain mergers and acquisitions has been marked by a series of projects and initiatives aimed at facilitating interoperability and collaboration between blockchain networks. These initiatives, often driven by his teams at Parity Technologies and Web3 Foundation, explore various approaches to chain mergers and acquisitions, with a focus on addressing the challenges and opportunities presented by this emerging field.
Chain Mergers and Acquisitions: A Technical Overview
Chain mergers and acquisitions encompass various strategies for combining or integrating blockchain networks. This can involve merging two or more chains into a single entity, acquiring one chain by another, or establishing bridges and interoperability protocols to connect separate chains.
The primary goal is to enhance scalability, security, and interoperability between different blockchain ecosystems.
Key Projects and Initiatives:
- Polkadot:Polkadot, a project founded by Gavin Wood, aims to create a heterogeneous multi-chain network where independent blockchains can interact and share information. It facilitates interoperability through a relay chain that connects parachains, which are independent blockchains that can leverage Polkadot’s security and scalability.
This approach allows for the merging of functionality and assets across different blockchains without compromising individual chain autonomy.
- Substrate:Substrate is an open-source framework developed by Parity Technologies, which enables developers to build custom blockchains. This framework facilitates the creation of interoperable blockchains that can potentially be merged or integrated with other Substrate-based chains. The modular design of Substrate allows for flexibility in chain design and integration, making it a suitable platform for exploring various chain merger and acquisition strategies.
- Parity Ethereum:Parity Technologies has also developed Parity Ethereum, a client implementation of the Ethereum blockchain. This implementation is known for its focus on scalability and interoperability. Parity Ethereum is used as a foundation for exploring chain mergers and acquisitions within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Impact on the Blockchain Ecosystem
The potential impact of chain mergers and acquisitions on the broader blockchain ecosystem is significant and multifaceted. These strategic moves can reshape the landscape of blockchain technology, influencing interoperability, scalability, and security, while potentially accelerating adoption and innovation.
Interoperability Enhancement
Chain mergers and acquisitions can foster interoperability between different blockchain networks. By combining technologies and resources, these mergers can facilitate seamless communication and data transfer between previously isolated blockchains. This enhanced interoperability can lead to:
- Cross-chain communication:Enabling the transfer of assets, data, and value between different blockchain networks, fostering a more interconnected and collaborative ecosystem.
- Increased liquidity:Facilitating the movement of assets across multiple blockchains, leading to greater liquidity and market efficiency.
- Expanded application possibilities:Opening up new avenues for decentralized applications (dApps) and services to leverage the unique strengths of various blockchains.
For example, the integration of Polkadot and Kusama, two blockchain networks with strong interoperability features, could create a robust ecosystem where different blockchains can interact and exchange information seamlessly.
Scalability Improvements
Mergers and acquisitions can address the scalability limitations of individual blockchain networks by combining resources and expertise. By leveraging complementary technologies and infrastructure, these mergers can create more efficient and scalable blockchain networks. This can lead to:
- Increased transaction throughput:Enabling faster and more efficient processing of transactions, reducing congestion and delays.
- Enhanced network capacity:Expanding the capacity of blockchain networks to handle a larger volume of transactions and users.
- Improved performance:Optimizing network performance by combining resources and expertise, leading to faster transaction confirmation times and lower latency.
A notable example is the merger of Ethereum and Zcash, which could potentially combine the robust smart contract functionality of Ethereum with the privacy features of Zcash, resulting in a more scalable and privacy-enhancing blockchain.
Security Enhancement
Chain mergers and acquisitions can enhance the security of blockchain networks by pooling resources and expertise. By integrating security protocols and best practices from different networks, these mergers can create more resilient and secure blockchain ecosystems. This can lead to:
- Improved resistance to attacks:Combining security measures and expertise can create a more robust defense against malicious attacks, such as 51% attacks and hacking attempts.
- Enhanced fault tolerance:Integrating diverse technologies and infrastructure can improve the resilience of blockchain networks, ensuring continued operation even in the face of disruptions.
- Reduced risk of vulnerabilities:By combining resources and expertise, mergers can help identify and address security vulnerabilities more effectively.
For instance, the acquisition of a blockchain security firm by a major cryptocurrency exchange could significantly strengthen the security posture of the exchange and its underlying blockchain network.
Increased Adoption and Innovation
Chain mergers and acquisitions can accelerate the adoption and innovation within the blockchain industry by:
- Creating larger and more influential networks:Mergers can combine user bases, resources, and market share, leading to increased adoption and broader market reach.
- Promoting industry consolidation:Mergers can help streamline the fragmented blockchain landscape, leading to greater clarity and focus for developers and investors.
- Facilitating the development of new applications and services:Mergers can bring together complementary technologies and expertise, fostering the creation of innovative blockchain applications and services.
The acquisition of a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform by a traditional financial institution could accelerate the adoption of DeFi services and introduce them to a wider audience.
Challenges and Opportunities
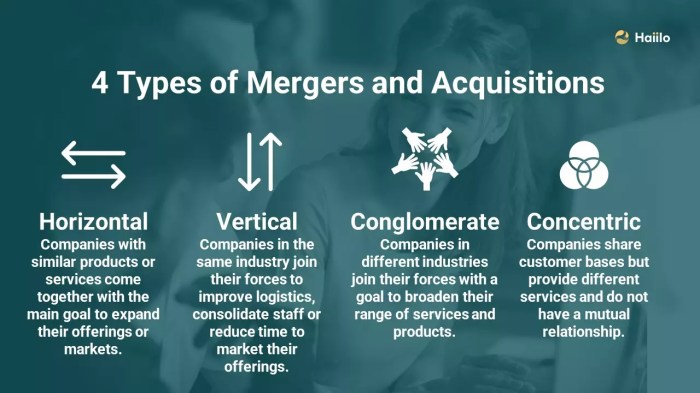
The landscape of blockchain mergers and acquisitions (M&A) is evolving rapidly, driven by the increasing adoption of blockchain technology and the emergence of new use cases. While M&A presents significant opportunities for growth and innovation, it also comes with its share of challenges.
Understanding these challenges and opportunities is crucial for stakeholders involved in blockchain M&A.
Challenges of Chain Mergers and Acquisitions
The technical, regulatory, and social complexities of blockchain technology pose unique challenges to M&A activities. These challenges can hinder the smooth integration of acquired chains and impact the overall success of the merger.
- Technical Challenges:
- Interoperability: Integrating different blockchain platforms with varying consensus mechanisms, data structures, and programming languages can be technically challenging. For example, merging a Proof-of-Work (PoW) chain with a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) chain requires careful consideration of how to reconcile their different consensus models.
- Security: Ensuring the security of merged chains is paramount, as any vulnerabilities could expose the entire network to attacks. This requires thorough security audits and risk assessments to identify and mitigate potential weaknesses.
- Scalability: Integrating chains with different transaction throughput capacities can lead to scalability issues. Merged chains must be able to handle the combined volume of transactions without compromising performance.
- Regulatory Challenges:
- Legal Framework: The lack of clear regulatory frameworks for blockchain technology, particularly in the context of M&A, can create uncertainty and legal risks for participating parties. For instance, the ownership and transfer of digital assets, as well as the implications of tokenized securities, need to be addressed by legal frameworks.
- Compliance: Merged chains must comply with applicable regulations, such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) rules. This can involve significant efforts to implement and maintain compliance systems.
- Jurisdictional Differences: Navigating varying regulatory landscapes across different jurisdictions can be complex, as each jurisdiction may have different rules governing blockchain technology.
- Social Challenges:
- Community Acceptance: Mergers and acquisitions can impact the communities surrounding the involved chains. It is crucial to ensure that the merger process is transparent and that the communities are adequately informed and engaged to minimize potential resistance or backlash.
- Tokenomics: Integrating different token economies can be challenging, as it involves balancing the interests of token holders from both chains. For example, determining the exchange rate between tokens and managing token distribution post-merger requires careful consideration.
- Governance: Establishing a fair and transparent governance model for the merged chain is essential to ensure community participation and decision-making. This involves considering how to represent the interests of both pre-merger communities.
Opportunities of Chain Mergers and Acquisitions, Gavin wood chain mergers and acquisitions
Despite the challenges, blockchain M&A presents significant opportunities for growth, innovation, and expansion into new markets. By strategically merging chains, stakeholders can unlock synergies and create value for all involved.
- Expansion of Market Reach: Merging chains can expand the reach of the combined network, accessing new markets and user bases. For example, merging a chain focused on supply chain management with a chain focused on digital identity could create a comprehensive platform for secure and transparent supply chains.
- Development of Innovative Solutions: Combining the strengths of different chains can lead to the development of innovative solutions that address specific industry needs. For instance, merging a chain with strong DeFi capabilities with a chain specializing in healthcare could create a platform for decentralized healthcare financing and data management.
- Increased Efficiency and Cost Savings: Merging chains can streamline operations, reduce redundancies, and achieve cost savings through shared resources and infrastructure. For example, merging two chains with overlapping functionalities could eliminate the need for duplicate infrastructure and development efforts.
- Enhanced Security and Reliability: Merging chains with complementary security features can enhance the overall security and reliability of the combined network. For example, merging a chain with strong consensus mechanisms with a chain with advanced cryptography could create a highly secure and robust platform.
- Faster Time to Market: Merging chains can accelerate the development and deployment of new products and services by leveraging existing infrastructure and resources. This can enable faster time to market and increased competitiveness in the rapidly evolving blockchain space.
Future Trends and Predictions

The landscape of blockchain mergers and acquisitions is poised for significant transformation, driven by technological advancements and evolving regulatory frameworks. This dynamic environment will see increased consolidation, innovative partnerships, and a greater emphasis on interoperability, all while navigating the complexities of legal and regulatory landscapes.
The Role of Gavin Wood and His Teams
Gavin Wood’s expertise in blockchain technology and his vision for a decentralized future will likely play a crucial role in shaping the future of chain mergers and acquisitions. His teams at Parity Technologies and Web3 Foundation are actively developing tools and infrastructure that can facilitate seamless integration and interoperability between different blockchains.
This includes projects like Substrate, a framework for building custom blockchains, and Polkadot, a network designed to connect diverse blockchains.
A Hypothetical Scenario of Chain Mergers and Acquisitions
Imagine a future where blockchain technology has become ubiquitous, with diverse blockchains serving specific industries and use cases. In this scenario, chain mergers and acquisitions become commonplace, driven by a desire for greater efficiency, interoperability, and market share.For instance, a leading supply chain management blockchain might merge with a prominent financial services blockchain, creating a comprehensive platform that streamlines trade finance and logistics.
This merger would unlock significant value by combining complementary technologies and expanding reach across different sectors.Similarly, smaller, specialized blockchains could be acquired by larger, more established platforms to expand their functionalities and gain access to new markets. This would lead to the emergence of powerful blockchain ecosystems, each catering to specific needs and industries.The success of these mergers and acquisitions would depend on several factors, including the ability to integrate different technologies seamlessly, address regulatory concerns, and ensure the security and stability of the combined platform.
“The future of blockchain lies in interoperability and collaboration, not in isolation. Mergers and acquisitions will play a crucial role in achieving this vision.”Gavin Wood

