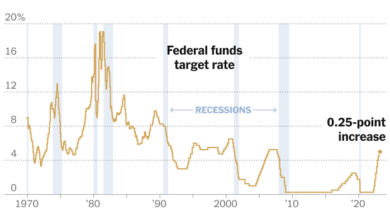
Federal Reserve Report: SVB Collapse Exposes Mismanagement and Oversight Failures
Federal reserve report on svb collapse highlights mismanagement and supervisory failures – Federal Reserve Report: SVB Collapse Exposes Mismanagement and Oversight Failures – The recent collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) sent shockwaves through the financial world, prompting a thorough investigation by the Federal Reserve. The resulting report paints a stark picture of mismanagement and supervisory failures that contributed to the bank’s demise.
The report delves into the bank’s risky investment strategies, inadequate risk management practices, and a lack of effective oversight from regulators. It also sheds light on the vulnerabilities within the financial system that were exposed by SVB’s collapse, highlighting the need for improved regulatory frameworks and enhanced oversight of financial institutions.
The report details how SVB’s management, driven by a desire for rapid growth, engaged in risky investments and failed to adequately assess and manage the associated risks. The report also identifies significant shortcomings in the Federal Reserve’s supervision of SVB, including a failure to adequately monitor the bank’s activities and identify emerging risks.
These failures have far-reaching implications for the financial industry, raising questions about the effectiveness of existing regulatory mechanisms and the need for stronger oversight of financial institutions.
Overview of the SVB Collapse
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) in March 2023 sent shockwaves through the financial world, highlighting the vulnerabilities of the banking system and raising concerns about the potential for contagion. The bank’s failure was a culmination of several factors, including risky investment strategies, a rapid rise in interest rates, and a lack of effective oversight.
The Federal Reserve’s report on the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank is a stark reminder of the importance of sound risk management and effective oversight. It highlights the dangers of unchecked growth and the need for robust regulatory frameworks. It’s also interesting to see how the crypto world is evolving, with platforms like Ethereum offering more than just a store of value, as explained in this article on how Ethereum is different from Bitcoin.
The SVB report underscores the importance of understanding the risks associated with both traditional and emerging financial systems, and the need for constant vigilance in the face of evolving market dynamics.
The Role of the Federal Reserve in Overseeing SVB
The Federal Reserve (Fed) plays a crucial role in regulating and overseeing banks, including SVB. The Fed is responsible for ensuring the safety and soundness of the financial system and for protecting depositors. In the case of SVB, the Fed had supervisory oversight of the bank and was responsible for monitoring its risk management practices and financial condition.
Timeline of Events
- February 2023:SVB announces a $1.8 billion loss on its investment portfolio, primarily due to rising interest rates. The bank also announces plans to raise capital to offset the losses.
- March 8, 2023:SVB announces a $2.25 billion capital raise, but investors are skeptical, and the bank’s stock price plummets.
- March 9, 2023:SVB announces it will sell a portion of its investment portfolio to raise capital. The announcement further spooks investors, and a run on the bank begins.
- March 10, 2023:SVB is seized by California regulators and placed into receivership. The FDIC is appointed as the receiver and begins the process of winding down the bank’s operations.
- March 12, 2023:The Fed announces a new lending program to help banks with liquidity issues, including those that may be affected by the SVB collapse.
- March 13, 2023:The FDIC announces that all depositors at SVB will have full access to their funds, including those exceeding the $250,000 FDIC insurance limit.
Key Findings of the Federal Reserve Report
The Federal Reserve’s report on the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) provides a comprehensive analysis of the events leading to the bank’s failure, identifying critical management practices and supervisory shortcomings. The report highlights significant lapses in risk management, internal controls, and communication, contributing to the rapid deterioration of SVB’s financial position.
Management Practices
The report identifies several instances of mismanagement that contributed to SVB’s downfall. These include:
- Concentration Risk:SVB’s significant concentration in the venture capital and technology sectors exposed the bank to significant risks. The report notes that SVB’s loan portfolio was highly concentrated, with a large portion of loans extended to companies in the technology sector.
This concentration meant that a downturn in the tech industry could have a significant impact on the bank’s financial health.
- Interest Rate Risk:SVB’s investment portfolio was heavily weighted towards long-duration assets, making it vulnerable to rising interest rates. As interest rates increased in 2022, the value of SVB’s bond portfolio declined, leading to significant losses.
The Federal Reserve’s report on the SVB collapse is a stark reminder of the importance of sound financial management and effective regulatory oversight. It’s a sobering reminder that even seemingly stable institutions can falter when risk management practices are lax.
In times of economic uncertainty, understanding inflation and its impact on our finances is crucial. The inflation guide tips to understand and manage rising prices can provide valuable insights into navigating these challenges. The SVB collapse underscores the need for vigilance, both on the part of financial institutions and regulators, to prevent similar disasters from occurring in the future.
- Aggressive Growth Strategy:SVB’s aggressive growth strategy, which involved expanding its loan portfolio rapidly, contributed to its risk profile. The bank’s focus on growth led to a decline in its capital adequacy, making it more vulnerable to financial shocks.
- Inadequate Risk Management Practices:The report identifies several weaknesses in SVB’s risk management practices.
The bank’s risk management framework was not sufficiently robust to address the risks associated with its business model. Additionally, the bank’s risk management team lacked the necessary experience and expertise to effectively manage the bank’s risks.
- Lack of Transparency:The report criticizes SVB’s lack of transparency with regulators and investors about its risk exposures.
The bank failed to disclose the full extent of its concentration risk and interest rate risk, which contributed to the market’s perception of the bank’s financial health.
Risk Management Practices
The report highlights several shortcomings in SVB’s risk management practices, contributing to the bank’s failure. These include:
- Inadequate Stress Testing:The report states that SVB’s stress testing practices were not sufficiently rigorous to identify the bank’s vulnerabilities to a downturn in the tech sector or rising interest rates.
- Limited Risk Appetite:The report finds that SVB’s risk appetite was not adequately defined or monitored.
The Federal Reserve report on the SVB collapse paints a stark picture of mismanagement and supervisory failures, highlighting the need for a comprehensive review of banking practices. While the financial world grapples with the implications of this report, the market seems to be taking a breather today, with the Nifty crossing 17650 as reported in these live updates on share market movement.
It’s crucial to remember that the SVB collapse serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of the financial system and the need for robust oversight to prevent similar crises in the future.
This led to a lack of clear guidance for risk-taking decisions and an increase in the bank’s risk profile.
- Weak Internal Controls:The report identifies several weaknesses in SVB’s internal controls. These included a lack of independent oversight of risk management activities and a lack of effective communication between risk management and senior management.
- Lack of a Comprehensive Risk Culture:The report finds that SVB lacked a comprehensive risk culture. This meant that employees were not adequately trained on risk management principles and did not feel empowered to raise concerns about potential risks.
Supervisory Failures Identified in the Report
The Federal Reserve’s report on the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) identifies several supervisory failures that contributed to the bank’s demise. The report provides a critical assessment of the Federal Reserve’s oversight of SVB and Artikels recommendations for improving bank supervision in the future.
Supervisory Failures Identified in the Report
The report details various supervisory failures that allowed SVB’s risks to grow unchecked, including:
- Inadequate risk management framework:The report found that SVB’s risk management framework was inadequate, particularly regarding its concentration in venture capital-backed companies and its reliance on uninsured deposits. This lack of a robust framework allowed SVB to take on excessive risks, leading to its downfall.
- Insufficient monitoring of interest rate risk:The report highlighted that the Federal Reserve did not adequately monitor SVB’s exposure to interest rate risk. As interest rates rose, SVB’s large portfolio of long-duration assets became increasingly vulnerable to losses, ultimately contributing to its collapse.
- Delayed response to early warning signs:The report indicates that the Federal Reserve was slow to respond to early warning signs of SVB’s financial vulnerabilities. Despite the bank’s growing concentration risk and reliance on uninsured deposits, the Federal Reserve did not take timely action to address these issues.
- Limited communication and coordination:The report criticizes the Federal Reserve’s communication and coordination with other regulators. This lack of collaboration hindered the timely identification and response to SVB’s growing risks.
Assessment of the Federal Reserve’s Supervision of SVB
The report provides a critical assessment of the Federal Reserve’s supervision of SVB, highlighting the following key issues:
- Insufficient focus on concentration risk:The report acknowledges that the Federal Reserve did not sufficiently focus on SVB’s concentration risk in venture capital-backed companies. This oversight allowed SVB to build a highly concentrated portfolio, making it vulnerable to sudden changes in market conditions.
- Inadequate understanding of SVB’s business model:The report suggests that the Federal Reserve did not fully understand SVB’s business model, particularly its reliance on uninsured deposits. This lack of understanding hindered the Federal Reserve’s ability to assess and manage the risks associated with SVB’s operations.
- Limited use of supervisory tools:The report indicates that the Federal Reserve did not fully utilize available supervisory tools to monitor and address SVB’s risks. This included a lack of timely use of stress tests and other tools to assess the bank’s resilience to potential shocks.
Recommendations for Improving Bank Supervision, Federal reserve report on svb collapse highlights mismanagement and supervisory failures
The report offers several recommendations for improving bank supervision, including:
- Strengthening risk management frameworks:The report recommends strengthening risk management frameworks for banks, including increased focus on concentration risk, interest rate risk, and reliance on uninsured deposits. This will help banks better identify and manage potential risks.
- Improving communication and coordination:The report emphasizes the need for improved communication and coordination among regulators. This will facilitate timely identification and response to potential risks across the financial system.
- Enhancing supervisory tools and practices:The report recommends enhancing supervisory tools and practices, including more frequent stress tests and enhanced data collection and analysis. This will allow regulators to better monitor and assess the risks faced by banks.
- Increasing focus on systemic risk:The report calls for a greater focus on systemic risk, recognizing that the failure of a single institution can have cascading effects on the broader financial system. This will help regulators identify and mitigate potential threats to financial stability.
Impact of the SVB Collapse: Federal Reserve Report On Svb Collapse Highlights Mismanagement And Supervisory Failures
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) sent shockwaves through the financial system, raising concerns about the stability of the broader banking sector and the potential for a wider financial crisis. The Federal Reserve’s report on the SVB collapse provides insights into the impact of the event and its implications for the financial landscape.
Impact on the Broader Financial System
The SVB collapse had a significant impact on the broader financial system, causing widespread uncertainty and volatility in the markets.
- Market Volatility:The collapse triggered a sell-off in bank stocks, with the KBW Bank Index falling by over 20% in a single day. This volatility spread to other asset classes, including bonds and equities.
- Investor Confidence:The failure of a major bank like SVB eroded investor confidence in the banking sector, leading to concerns about the health of other institutions.
- Liquidity Concerns:The collapse raised concerns about the availability of liquidity in the banking system, as banks became more cautious about lending and investors sought safe haven assets.
Potential Implications for Other Banks and Financial Institutions
The SVB collapse highlighted the risks associated with concentrated lending and asset bubbles, particularly in sectors like technology.
- Risk of Contagion:The failure of SVB raised concerns about the possibility of contagion, where the collapse of one bank could trigger a domino effect and lead to failures in other institutions.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny:The collapse prompted regulators to increase scrutiny of banks with similar business models and risk profiles as SVB. This includes heightened attention to concentration risk, asset valuations, and stress testing.
- Changes in Lending Practices:Banks may become more cautious in their lending practices, particularly to high-growth companies and sectors that are perceived as more risky.
Assessment of Systemic Risk
The Federal Reserve’s report acknowledges the systemic risk posed by SVB’s failure, highlighting the bank’s significant role in the technology sector and its interconnectedness with other financial institutions.
- Concentration Risk:SVB’s concentration of lending in the technology sector created a significant vulnerability to shocks in that industry. The bank’s failure demonstrated the potential for a rapid and severe decline in asset values, which could have a ripple effect on other institutions.
- Interconnectedness:SVB’s collapse also highlighted the interconnectedness of the financial system. The bank’s failure had a cascading effect, leading to losses for other institutions that had invested in SVB or had exposure to its clients.
- Regulatory Response:The Federal Reserve’s swift response to the SVB collapse, including the guarantee of deposits and the provision of liquidity to the banking system, helped to mitigate the systemic risk.
Lessons Learned from the SVB Collapse
![]()
The collapse of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB) in March 2023 sent shockwaves through the financial system and highlighted the need for a comprehensive review of bank regulation and supervision. The Federal Reserve’s report on the SVB collapse identified several key lessons that need to be addressed to prevent similar failures in the future.
These lessons are crucial for strengthening the resilience of the financial system and protecting depositors.The Federal Reserve’s report on the SVB collapse provides a comprehensive analysis of the factors that contributed to the bank’s failure. The report identifies several key lessons that need to be addressed to prevent similar failures in the future.
These lessons are crucial for strengthening the resilience of the financial system and protecting depositors.
Supervisory Practices and Risk Management
The report highlights several shortcomings in SVB’s risk management practices and the Federal Reserve’s supervisory oversight. The report identifies several shortcomings in SVB’s risk management practices and the Federal Reserve’s supervisory oversight. These shortcomings contributed to the bank’s vulnerability to a sudden loss of confidence and liquidity.
The report highlights several shortcomings in SVB’s risk management practices and the Federal Reserve’s supervisory oversight. These shortcomings contributed to the bank’s vulnerability to a sudden loss of confidence and liquidity.
- Inadequate Risk Management:SVB’s concentration of its loan portfolio in the technology sector, combined with its lack of diversification, exposed the bank to significant risks. The bank’s reliance on a single sector also made it vulnerable to changes in interest rates and economic conditions.
The report highlights the importance of diversifying loan portfolios and managing interest rate risk effectively.
- Insufficient Stress Testing:SVB’s stress testing practices were inadequate in assessing the bank’s resilience to potential shocks. The report emphasizes the need for banks to conduct rigorous stress testing that accounts for a wide range of potential risks.
- Lack of Effective Supervision:The report highlights the need for more robust supervisory oversight of banks, particularly those with concentrated exposures to specific industries or sectors. The report emphasizes the need for regulators to proactively identify and address potential risks, rather than relying solely on reactive measures.