Federal Reserve Chief Powell Discusses Interest Rate Changes Due to Inflation
Federal reserve chief powell talks about possible changes in interest rates due to inflation – Federal Reserve Chief Powell Discusses Interest Rate Changes Due to Inflation, a topic that has been on the minds of many Americans as inflation continues to rise. In a recent speech, Powell addressed the current economic landscape and the Federal Reserve’s role in managing inflation.
He Artikeld potential scenarios for interest rate adjustments, and discussed the potential impact of these changes on various aspects of the economy, including consumer spending, investment, and the housing market.
Powell’s speech highlighted the complex trade-offs the Federal Reserve faces in balancing inflation and economic growth. He acknowledged the potential risks associated with different interest rate strategies, and shared various perspectives on the appropriate course of action. The speech sparked discussions about the future of the economy and the role of the Federal Reserve in navigating these challenging times.
Powell’s Speech Context
Jerome Powell, the Chair of the Federal Reserve, delivered a speech addressing the current economic landscape and the potential adjustments to interest rates. His remarks came amidst heightened concerns about inflation, a key factor influencing the Fed’s monetary policy decisions.
The speech provided insights into the Fed’s thinking on inflation and its commitment to maintaining price stability.
The Current Economic Landscape and Inflation Concerns
The current economic landscape is characterized by a persistent inflationary environment. Consumer prices have risen significantly, driven by factors such as supply chain disruptions, strong consumer demand, and the war in Ukraine. Inflation has eroded purchasing power and posed challenges for households and businesses.
The Fed’s primary objective is to control inflation and maintain price stability, which is crucial for a healthy and sustainable economy.
The Federal Reserve’s Mandate and Its Role in Managing Inflation, Federal reserve chief powell talks about possible changes in interest rates due to inflation
The Federal Reserve’s mandate is to promote maximum employment and stable prices. The Fed uses various tools to achieve these objectives, including setting interest rates, buying and selling government securities, and regulating banks. When inflation is high, the Fed typically raises interest rates to make borrowing more expensive and slow economic activity, thus curbing inflation.
Conversely, when inflation is low, the Fed may lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth.
Historical Context of Interest Rate Adjustments in Response to Inflation
Historically, the Fed has adjusted interest rates in response to inflation. For example, during the 1970s and early 1980s, the United States experienced high inflation, prompting the Fed to raise interest rates significantly. These rate hikes helped to bring inflation under control but also led to a recession.
It’s a wild ride out there in the markets! Federal Reserve Chair Powell’s recent comments about potential interest rate changes due to inflation have everyone on edge. Meanwhile, the Dow futures are dipping as Disney reports losses, and we’re waiting for the latest inflation data to drop.
Keep an eye on the situation, and be sure to check out this blog for live updates on all the latest market moves. It’s a volatile time, so buckle up and stay informed!
In recent decades, the Fed has employed a more gradual approach to interest rate adjustments, aiming to control inflation without causing significant economic disruptions.
Possible Interest Rate Changes

Powell’s recent statements about potential interest rate adjustments have sparked significant discussion about the future direction of monetary policy. The Federal Reserve, tasked with maintaining price stability and maximizing employment, carefully weighs various economic indicators to determine the appropriate course of action.
Potential Scenarios for Interest Rate Adjustments
Powell’s remarks suggest that the Federal Reserve is considering a range of options for interest rate adjustments, with the ultimate decision hinging on the evolving economic landscape. * Maintaining Current Interest Rates:This scenario implies that the Fed believes the current level of interest rates is appropriate, given the current state of the economy.
This approach could be favored if inflation shows signs of cooling down without significantly impacting economic growth.
Raising Interest Rates This scenario reflects the Fed’s intention to curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive, thus slowing down economic activity. The magnitude of the rate hike would depend on the severity of inflation and the Fed’s assessment of the economy’s resilience.
Lowering Interest Rates
While Powell grapples with the delicate balance of inflation and interest rates, Elon Musk has taken a different kind of leap, unveiling dramatic changes to Twitter’s logo and branding, even ditching the iconic blue bird. It’s a stark reminder that while the Fed navigates economic storms, the world of tech continues to evolve at breakneck speed, often with unexpected and eye-catching twists.
The question remains, will Powell’s decisions on interest rates have a similar impact on the digital landscape as Musk’s bold moves?
Impact of Different Interest Rate Changes on the Economy
The impact of interest rate changes on the economy can be complex and multifaceted. * Raising Interest Rates:Higher interest rates can slow down economic growth by making borrowing more expensive for businesses and consumers. This can lead to decreased investment, lower consumer spending, and potentially a reduction in job creation.
Federal Reserve Chair Powell’s recent statements about potential interest rate adjustments have sent ripples through the financial world. The Fed’s ongoing battle against inflation is a complex and delicate balancing act, as evidenced by the recent considerations of rate cuts, which are explored in depth on this insightful blog post.
It remains to be seen how Powell’s comments will ultimately translate into policy decisions, but one thing is certain: the Fed’s actions will have a significant impact on the economy and the lives of ordinary Americans.
However, it can also help to control inflation by reducing demand for goods and services.
Lowering Interest Rates Lower interest rates can stimulate economic growth by making borrowing cheaper. This can lead to increased investment, higher consumer spending, and potentially an increase in job creation. However, it can also lead to higher inflation if it fuels excessive borrowing and spending.
Maintaining Current Interest Rates Maintaining current interest rates allows the Fed to observe the impact of existing policies on the economy. This can be a prudent approach if the economy is showing signs of stability, but it also carries the risk of allowing inflation to persist or even worsen.
Consequences of Maintaining or Raising Interest Rates
The decision to maintain or raise interest rates carries significant implications for the economy.* Maintaining Interest Rates:Maintaining current interest rates could allow inflation to persist or even worsen, potentially leading to higher prices for goods and services, eroding consumer purchasing power, and impacting the overall economic outlook.
Raising Interest Rates Raising interest rates could lead to slower economic growth, potentially resulting in job losses and decreased investment. However, it could also help to control inflation and prevent the economy from overheating.
“The Federal Reserve is committed to using its tools to bring inflation back down to 2 percent,” Powell stated. “We are prepared to raise interest rates further if needed.”
Economic Impact

The Federal Reserve’s decision to adjust interest rates has far-reaching consequences for the economy. Changes in borrowing costs impact consumer behavior, investment decisions, and the overall health of various sectors.
Consumer Spending and Investment
Interest rate changes significantly influence consumer spending and investment. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, making it more expensive for consumers to finance purchases like cars, homes, and appliances. This can lead to a decrease in consumer spending, as individuals may choose to save more or delay major purchases.
Conversely, lower interest rates encourage borrowing and spending, as the cost of financing becomes more attractive.
Higher interest rates can also discourage investment by businesses, as the cost of capital becomes more expensive.
Housing Market
The housing market is particularly sensitive to interest rate fluctuations. Higher interest rates make mortgages more expensive, leading to a decrease in demand for housing. This can result in lower home prices, reduced sales activity, and a slowdown in construction.
Conversely, lower interest rates can stimulate the housing market by making mortgages more affordable, leading to increased demand and potentially higher home prices.
Labor Market
Interest rate changes can have indirect effects on the labor market. A strong economy with low interest rates can lead to increased business investment and job creation. Conversely, higher interest rates can slow economic growth and potentially lead to job losses, as businesses may reduce hiring or even lay off workers.
Businesses and Economic Growth
Interest rate changes impact businesses in several ways. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for businesses, making it more expensive to finance operations, expansions, and investments. This can lead to slower economic growth, as businesses may reduce investment and hiring.
Lower interest rates, on the other hand, can encourage business investment and growth, as the cost of borrowing becomes more attractive.
The impact of interest rate changes on businesses and economic growth can vary depending on the specific economic conditions and the sensitivity of different sectors to interest rate fluctuations.
Market Reactions

Powell’s statements on potential interest rate changes will likely trigger significant reactions in financial markets. Investors will closely analyze his remarks and the Federal Reserve’s outlook on inflation to gauge the future trajectory of monetary policy. These reactions will likely manifest in shifts in asset prices, including stocks, bonds, and the US dollar.
Impact on Stock Prices
The potential for higher interest rates can have a mixed impact on stock prices. On the one hand, rising rates can increase borrowing costs for companies, potentially slowing down economic growth and corporate earnings. This could lead to a decline in stock prices, especially for companies heavily reliant on debt financing.
On the other hand, higher interest rates can signal a strong economy, potentially boosting investor confidence and driving up stock prices.
The relationship between interest rates and stock prices is complex and depends on various factors, including the overall economic outlook, inflation expectations, and the specific sectors of the market.
Impact on Bond Yields
Bond yields are expected to rise in response to the Federal Reserve’s tightening monetary policy. When interest rates increase, the yields on existing bonds become less attractive compared to newly issued bonds with higher yields. This can lead to a sell-off in existing bonds, driving down their prices and pushing up yields.
For example, during the Federal Reserve’s aggressive rate hikes in 2022, the yield on the 10-year Treasury note surged from around 1.5% to over 4%. This increase in yields reflected investor expectations of higher inflation and tighter monetary policy.
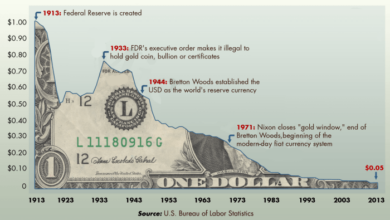
Impact on the Value of the Dollar
A tightening monetary policy can strengthen the US dollar. Higher interest rates make US assets more attractive to foreign investors, increasing demand for the dollar and pushing up its value. A stronger dollar can make US exports more expensive and imports cheaper, potentially impacting trade balances.
For instance, during the early 2000s, the Federal Reserve’s rate hikes led to a significant appreciation of the US dollar, which contributed to a widening trade deficit.
Policy Considerations: Federal Reserve Chief Powell Talks About Possible Changes In Interest Rates Due To Inflation
The Federal Reserve faces a complex balancing act in managing inflation and economic growth. Raising interest rates can help curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive, but it can also slow down economic activity. Lowering interest rates can stimulate economic growth but may lead to higher inflation.
This trade-off is often referred to as the “inflation-growth trade-off.”
Risks Associated with Different Interest Rate Strategies
The Federal Reserve must carefully consider the potential risks associated with different interest rate strategies. Raising interest rates too aggressively could stifle economic growth and potentially lead to a recession. Conversely, raising interest rates too slowly could allow inflation to spiral out of control, leading to economic instability.
Different Perspectives on the Appropriate Course of Action
There are various perspectives on the appropriate course of action for the Federal Reserve. Some economists argue that the Fed should focus on controlling inflation, even if it means sacrificing some economic growth. They believe that high inflation is more damaging to the economy in the long run.
Others argue that the Fed should prioritize economic growth, even if it means accepting a higher level of inflation. They believe that a strong economy is essential to maintain employment and living standards.
- Hawks: Advocates of this approach argue that the Fed should act decisively to combat inflation, even if it means raising interest rates significantly. They believe that early and aggressive action is necessary to prevent inflation from becoming entrenched.
- Doves: Advocates of this approach argue that the Fed should proceed cautiously and avoid raising interest rates too quickly. They believe that the economy is still recovering from the pandemic and that aggressive rate hikes could derail the recovery.
The Federal Reserve must weigh these different perspectives and make a decision that balances the risks of inflation and economic growth. The appropriate course of action will depend on a variety of factors, including the current state of the economy, the outlook for inflation, and the level of uncertainty in the economy.