Dollar Ascends, Yen Retreats: Forex Markets React to Rate Expectations
Dollar ascends yen retreats forex markets react to rate expectations – Dollar Ascends, Yen Retreats: Forex Markets React to Rate Expectations. This headline, echoing the current sentiment in the global currency market, encapsulates a fascinating interplay between interest rates, economic policies, and market sentiment. The US dollar’s recent surge against the Japanese yen, a trend observed across various forex markets, is a direct consequence of diverging monetary policies adopted by the Federal Reserve and the Bank of Japan.
This dynamic, driven by contrasting rate expectations, has sent ripples through the global economy, impacting everything from trade flows to inflation.
Understanding the forces behind these currency movements is crucial for investors, traders, and anyone seeking to navigate the complex world of international finance. This article delves into the intricate relationship between interest rates and currency value, exploring how market expectations about future rate changes shape the current exchange rate landscape.
We’ll examine the impact of recent statements from central banks, analyze technical indicators, and discuss trading strategies for the USD/JPY pair. Furthermore, we’ll explore the broader economic implications of these movements, considering their potential impact on the US and Japanese economies.
Understanding the Relationship between Interest Rates and Currency Value
The value of a currency is influenced by a multitude of factors, with interest rates playing a significant role. The relationship between interest rates and currency value is generally inverse, meaning that as interest rates rise, the currency tends to appreciate, and vice versa.
This relationship is driven by the concept of carrying cost and the attractiveness of a currency for investment.
Interest Rates and Currency Value: An Inverse Relationship
Higher interest rates make a currency more attractive to foreign investors. When a country’s central bank raises interest rates, it becomes more profitable for investors to hold assets denominated in that currency. This is because they can earn a higher return on their investment.
The increased demand for the currency due to foreign investment leads to its appreciation. Conversely, when interest rates fall, the currency becomes less attractive to foreign investors, leading to a decrease in demand and depreciation of the currency.
Higher US Interest Rates and the USD/JPY Exchange Rate
The current scenario in the forex market, with the dollar ascending and the yen retreating, is largely driven by the interest rate differential between the US and Japan. The US Federal Reserve has been aggressively raising interest rates to combat inflation, while the Bank of Japan has maintained its ultra-loose monetary policy.
This significant interest rate differential has made the US dollar more attractive to investors seeking higher returns, leading to a surge in demand for the dollar and weakening the yen.
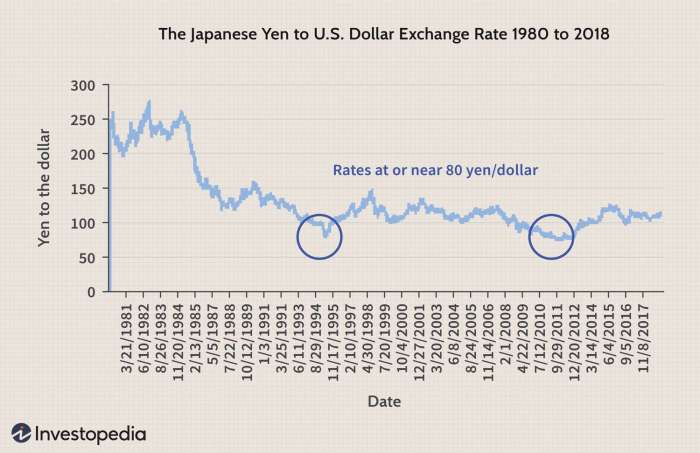
Historical Examples of Interest Rate Differentials Impacting the USD/JPY Exchange Rate
Throughout history, changes in interest rate differentials have consistently impacted the USD/JPY exchange rate. For example, during the 1980s, the US dollar experienced a significant appreciation against the yen due to the higher interest rates offered in the US compared to Japan.
Conversely, in the early 2000s, the yen strengthened against the dollar as Japan’s interest rates remained higher than those in the US. These examples highlight the strong correlation between interest rate differentials and the USD/JPY exchange rate.
The Role of Rate Expectations in Forex Market Reactions
The forex market is highly sensitive to interest rate expectations. When investors anticipate that a central bank will raise interest rates, it often leads to a strengthening of the corresponding currency. Conversely, expectations of lower interest rates can weaken a currency.
This is because higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency and pushing its value up.
Impact of Rate Expectations on USD/JPY, Dollar ascends yen retreats forex markets react to rate expectations
The relationship between interest rate expectations and currency movements is clearly evident in the USD/JPY pair. The Federal Reserve (Fed) and the Bank of Japan (BOJ) have contrasting monetary policies, with the Fed raising interest rates to combat inflation and the BOJ maintaining a dovish stance with near-zero interest rates.
This divergence in monetary policies has significantly impacted the USD/JPY exchange rate.Recent statements from the Fed have indicated a continued commitment to raising interest rates, reinforcing expectations of a stronger US dollar. On the other hand, the BOJ’s commitment to maintaining ultra-low interest rates has kept the Japanese yen under pressure.
This has resulted in a sustained appreciation of the USD against the JPY.
The dollar’s climb against the yen reflects the market’s anticipation of further interest rate hikes, a move that could potentially impact global trade flows. Meanwhile, on a different front, India has allocated a hefty $48 billion for food and fertilizer subsidies in the upcoming year, a move aimed at mitigating inflation and ensuring food security.
The impact of these developments on the global economy remains to be seen, but it’s clear that the forex markets are closely watching the unfolding economic landscape.
Interpreting Statements and Trading Strategies
Market analysts and traders carefully scrutinize statements from central banks to gauge their future policy intentions. These statements often provide clues about the direction of interest rates and, consequently, currency movements. For example, a hawkish statement from a central bank, indicating a potential for higher interest rates, might lead traders to buy the corresponding currency, anticipating its appreciation.
Conversely, a dovish statement, suggesting a continuation of low interest rates, could prompt traders to sell the currency, anticipating its depreciation.
“Traders are constantly looking for any hints or signals that might suggest a change in central bank policy. Even subtle changes in language or tone can have a significant impact on market expectations and trading strategies.”
Traders often employ technical analysis tools and economic indicators to confirm their interpretations of central bank statements and develop trading strategies. They also consider factors such as economic growth, inflation, and political stability to assess the overall outlook for a currency.
Impact on the US and Japanese Economies
The fluctuations in the exchange rate between the US dollar and the Japanese yen can have significant implications for both economies. A strong dollar can benefit US exporters, making their goods more competitive in global markets. Conversely, a weak yen can boost Japanese exports, as their products become more affordable for foreign buyers.
However, these currency movements also come with potential drawbacks, impacting trade flows, inflation, and economic growth in both countries.
Impact of a Strong Dollar on the US Economy
A strong dollar can have both positive and negative consequences for the US economy. On the one hand, it can boost US exports, making them more competitive in international markets. This can lead to increased sales, higher production, and job creation in export-oriented sectors.
On the other hand, a strong dollar can make imports more expensive for US consumers, potentially leading to higher inflation and reduced consumer spending.
- Increased Exports:A strong dollar makes US goods cheaper for foreign buyers, leading to increased demand for US products. This can benefit industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, and technology, which rely heavily on exports. For example, the US automotive industry has seen a rise in exports to countries like China and Japan, where the dollar has strengthened.
- Reduced Imports:Conversely, a strong dollar makes imported goods more expensive for US consumers. This can lead to a decrease in imports, potentially benefiting domestic producers and creating jobs in industries that compete with imported goods. For example, the US apparel industry has seen a decline in imports from countries like China and Vietnam, as the dollar has strengthened against their currencies.
- Inflationary Pressure:While a strong dollar can help control inflation by making imported goods cheaper, it can also lead to inflationary pressures if businesses pass on the higher costs of imported raw materials and components to consumers. For example, the US oil and gas industry has seen an increase in the price of imported crude oil, leading to higher gasoline prices for consumers.
<h3
The dollar’s climb against the yen reflects the market’s anticipation of further interest rate hikes, while the yen’s retreat suggests investors are seeking higher returns elsewhere. But amidst the financial fluctuations, there’s a glimmer of good news for sneakerheads: adidas launches new wave of exclusive yeezy shoes for clearance , offering a chance to snag coveted kicks at a discount.
This unexpected release might even divert some attention away from the forex markets, at least for a while, as sneaker enthusiasts scramble to secure their favorite pairs.
>Impact of a Weak Yen on the Japanese Economy
A weak yen can have a mixed impact on the Japanese economy. It can boost Japanese exports, making them more competitive in global markets, and lead to increased investment in Japanese companies. However, it can also increase the cost of imported goods, leading to higher inflation and reduced consumer spending.
- Increased Exports:A weak yen makes Japanese goods cheaper for foreign buyers, leading to increased demand for Japanese products. This can benefit industries such as electronics, automobiles, and machinery, which rely heavily on exports. For example, Japanese car manufacturers have seen a rise in exports to the US and Europe, where the yen has weakened.
- Increased Investment:A weak yen can also attract foreign investment in Japanese companies, as their assets become cheaper in dollar terms. This can lead to increased investment in Japanese businesses, potentially boosting economic growth and creating jobs. For example, foreign investors have been increasingly investing in Japanese real estate and stock markets, as the yen has weakened.
- Inflationary Pressure:However, a weak yen can also lead to higher inflation, as imported goods become more expensive for Japanese consumers. This can reduce consumer spending and dampen economic growth. For example, the price of imported oil and gas has increased for Japanese consumers, as the yen has weakened against the dollar.
Impact of Exchange Rate on Trade Flows
The exchange rate plays a crucial role in determining the competitiveness of a country’s exports and imports. A strong dollar makes US exports more expensive for foreign buyers, while a weak yen makes Japanese exports more affordable for foreign buyers.
This can impact trade flows, potentially leading to trade imbalances between countries.
Example:If the dollar strengthens against the yen, US exports to Japan become more expensive, while Japanese exports to the US become cheaper. This can lead to a decrease in US exports to Japan and an increase in Japanese exports to the US, potentially widening the trade deficit between the two countries.
Impact of Exchange Rate on Inflation
Exchange rate fluctuations can also impact inflation in both countries. A strong dollar can lead to lower inflation in the US by making imported goods cheaper, while a weak yen can lead to higher inflation in Japan by making imported goods more expensive.
Example:If the dollar strengthens against the yen, imported goods from Japan become cheaper for US consumers, potentially leading to lower inflation in the US. Conversely, imported goods from the US become more expensive for Japanese consumers, potentially leading to higher inflation in Japan.
Impact of Exchange Rate on Economic Growth
The exchange rate can also influence economic growth in both countries. A strong dollar can boost US exports, leading to increased production and job creation, while a weak yen can boost Japanese exports, leading to similar effects. However, the impact on economic growth can be complex and depends on various factors, including the strength of domestic demand and the level of investment.
Example:A strong dollar can boost US economic growth by increasing exports and investment. However, if domestic demand is weak, the impact on economic growth may be limited. Similarly, a weak yen can boost Japanese economic growth by increasing exports. However, if inflation rises significantly, it can dampen consumer spending and reduce economic growth.
Technical Analysis of the USD/JPY Pair: Dollar Ascends Yen Retreats Forex Markets React To Rate Expectations
The USD/JPY pair, reflecting the value of the US dollar against the Japanese yen, has been a focal point for traders due to the recent fluctuations driven by interest rate differentials and economic developments. Analyzing recent price action and identifying key support and resistance levels can provide valuable insights into potential future trends in the exchange rate.
Recent Price Action and Key Levels
The USD/JPY pair has been trending upwards in recent months, driven by the Federal Reserve’s aggressive interest rate hikes, which have widened the interest rate differential between the US and Japan. The pair has broken through several resistance levels, indicating strong bullish momentum.
- Support Levels:Traders often look for support levels where the price is likely to find buyers and bounce back. For the USD/JPY pair, key support levels have been observed at 130.00 and 135.00.
- Resistance Levels:Resistance levels are price points where selling pressure is expected to emerge, potentially halting the upward trend. Recent resistance levels have been seen at 140.00 and 145.00.
Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on historical price data that can provide signals about potential future trends. Some commonly used indicators for the USD/JPY pair include:
- Moving Averages:Moving averages are widely used to identify trends and potential reversals. A popular moving average is the 200-day moving average, which can act as a long-term trend indicator. When the price is above the 200-day moving average, it suggests an uptrend, while a break below it could signal a bearish trend.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI):The RSI is a momentum indicator that measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. An RSI reading above 70 is often considered overbought, suggesting a potential reversal, while a reading below 30 indicates oversold conditions.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence):The MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages. A bullish crossover occurs when the MACD line crosses above the signal line, potentially indicating a buy signal. Conversely, a bearish crossover occurs when the MACD line crosses below the signal line, potentially indicating a sell signal.
Example
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario where the USD/JPY pair is trading at 142.00. The 200-day moving average is at 138.00, and the RSI is at 65. The MACD line is above the signal line, suggesting bullish momentum. In this situation, a technical analyst might conclude that the pair is in an uptrend and could potentially continue to rise, with the next resistance level at 145.00.
However, it is crucial to remember that technical indicators are not perfect predictors, and they should be used in conjunction with other forms of analysis, such as fundamental analysis.
Trading Strategies for the USD/JPY Pair
The USD/JPY pair is a popular choice for forex traders due to its high volatility and strong trends. Several trading strategies can be employed to capitalize on these movements. Here’s an exploration of common strategies, their associated risks and rewards, and practical implementation examples.
Trend Following
Trend-following strategies aim to identify and trade with the prevailing direction of the USD/JPY pair. These strategies rely on technical indicators like moving averages, MACD, or RSI to pinpoint trends.
The dollar’s ascent against the yen is a clear indicator of how forex markets are reacting to anticipated interest rate hikes. This dynamic isn’t isolated to the US; it’s a global phenomenon. The recent surge in US yields, as discussed in this insightful article on global financial dynamics and their impact on Indian bond yields , is prompting investors to seek out higher returns, leading to a strengthening dollar and a weaker yen.
Advantages
- Potential for significant profits during strong trends.
- Relatively straightforward to implement.
Disadvantages
- Susceptible to whipsaws and false breakouts, leading to losses.
- Difficult to predict trend reversals.
Implementation Example
A trader could employ a 200-day moving average as a trend indicator. Buy orders would be placed when the price crosses above the 200-day moving average, indicating an upward trend. Conversely, sell orders would be placed when the price crosses below the 200-day moving average, indicating a downward trend.
Range Trading
Range trading strategies exploit the price fluctuations within a defined support and resistance level. These strategies aim to profit from price reversals within a range.
Advantages
- Reduced risk compared to trend-following strategies due to defined entry and exit points.
- Suitable for traders with a short-term trading horizon.
Disadvantages
- Limited profit potential compared to trend-following strategies.
- Requires accurate identification of support and resistance levels.
Implementation Example
A trader could identify a price range between 130.00 and 135.00. Buy orders would be placed near the 130.00 support level, aiming to profit from a price bounce back towards the 135.00 resistance level. Sell orders would be placed near the 135.00 resistance level, aiming to profit from a price drop back towards the 130.00 support level.
Scalping
Scalping strategies involve entering and exiting trades quickly to capture small price fluctuations. Scalpers utilize technical indicators like moving averages, Bollinger Bands, and stochastic oscillators to identify short-term trading opportunities.
Advantages
- Potential for frequent profits due to rapid trading.
- Suitable for traders with high risk tolerance and quick decision-making abilities.
Disadvantages
- High transaction costs due to frequent trading.
- Requires constant monitoring of market activity and swift execution.
Implementation Example
A scalper might use a 5-minute chart and enter a buy order when the price breaks above a 20-period moving average. The exit order would be placed a few pips above the entry order, aiming to capture a small profit.
News Trading
News trading strategies involve exploiting price movements triggered by economic releases and geopolitical events. Traders analyze economic calendars and news headlines to identify potential market-moving events.
Advantages
- Potential for significant price swings following major news releases.
- Allows traders to capitalize on market reactions to economic data.
Disadvantages
- High volatility and unpredictable price movements following news releases.
- Requires a deep understanding of economic indicators and geopolitical events.
Implementation Example
A trader could anticipate a rise in the USD/JPY pair following a positive US economic report. A buy order would be placed shortly before the report’s release, aiming to profit from a potential upward surge in the pair.
Carry Trade
Carry trade strategies involve borrowing a low-interest-rate currency (like the Japanese yen) and investing it in a high-interest-rate currency (like the US dollar). The difference in interest rates generates a profit, known as the “carry.”
Advantages
- Potential for consistent returns over time, especially in a low-interest-rate environment.
- Suitable for traders with a long-term investment horizon.
Disadvantages
- High risk due to potential for currency depreciation of the borrowed currency.
- Requires a significant capital investment.
Implementation Example
A trader could borrow Japanese yen at a low-interest rate and invest it in US dollar-denominated assets at a higher interest rate. The difference in interest rates would generate a profit, assuming the USD/JPY exchange rate remains stable or appreciates.
Global Economic Factors Influencing the Forex Market
The USD/JPY exchange rate is not solely driven by interest rate differentials. Global economic events, economic indicators, and geopolitical developments play a significant role in shaping currency movements. Understanding these factors is crucial for traders seeking to navigate the forex market effectively.
Impact of Global Economic Events on the USD/JPY Exchange Rate
Global economic events can have a profound impact on the USD/JPY exchange rate. For example, a global recession could weaken demand for Japanese exports, leading to a decline in the yen. Conversely, strong global economic growth could boost demand for Japanese goods, strengthening the yen.
Key Economic Indicators Traded Closely
Traders closely monitor various economic indicators to gauge the health of the US and Japanese economies, which directly influence the USD/JPY exchange rate. Some of the key indicators include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): Measures the total value of goods and services produced in a country. A strong GDP growth rate in the US could strengthen the dollar, while weak GDP growth in Japan could weaken the yen.
- Inflation: Measures the rate at which prices for goods and services increase. High inflation in the US could lead to higher interest rates, potentially strengthening the dollar. Conversely, low inflation in Japan could lead to lower interest rates, potentially weakening the yen.
- Unemployment Rate: Measures the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. A low unemployment rate in the US could signal a strong economy, potentially strengthening the dollar. Conversely, a high unemployment rate in Japan could signal a weak economy, potentially weakening the yen.
- Consumer Confidence: Measures consumer sentiment about the economy. High consumer confidence in the US could boost spending and economic growth, potentially strengthening the dollar. Conversely, low consumer confidence in Japan could lead to reduced spending and economic weakness, potentially weakening the yen.
Geopolitical Events Influencing Currency Movements
Geopolitical events can significantly influence currency movements. For example, a trade war between the US and Japan could lead to a decline in the yen. Conversely, a resolution to a geopolitical conflict could boost investor confidence and strengthen the yen.
Geopolitical events can create uncertainty and volatility in the forex market, making it crucial for traders to stay informed and adapt their strategies accordingly.
Risk Management in Forex Trading
The forex market is a volatile and unpredictable environment, making risk management an essential aspect of successful trading. By implementing effective risk management strategies, traders can mitigate potential losses and protect their capital, ensuring a more sustainable and profitable trading journey.
Importance of Risk Management in Forex Trading
Risk management in forex trading is paramount for several reasons. It helps traders:
- Protect their capital:By setting limits on potential losses, risk management prevents traders from losing their entire investment on a single trade.
- Maintain trading discipline:It encourages traders to stick to their trading plan and avoid impulsive decisions driven by emotions or greed.
- Increase trading longevity:By preventing significant losses, risk management allows traders to stay in the market for the long term and benefit from long-term trends.
- Improve trading performance:It enables traders to make more informed decisions, manage their positions effectively, and maximize their profits.
Common Risk Management Techniques
Several risk management techniques are commonly employed by forex traders:
- Stop-loss orders:Stop-loss orders automatically close a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses. For example, a trader buying USD/JPY at 135.00 might set a stop-loss order at 134.50, ensuring that their loss is limited to 50 pips if the price moves against their position.
- Position sizing:This involves determining the appropriate size of a trade based on the trader’s risk tolerance and account balance. It ensures that losses on any single trade do not exceed a predetermined percentage of the account balance. For instance, a trader with a $10,000 account might decide to risk only 1% of their capital per trade, limiting their potential loss to $100.
- Risk-reward ratio:This ratio compares the potential profit of a trade to the potential loss. A favorable risk-reward ratio ensures that the potential profit outweighs the potential loss. For example, a trader might aim for a risk-reward ratio of 1:2, meaning they are willing to risk $1 to potentially make $2.
- Diversification:Spreading trades across different currency pairs or asset classes can reduce overall risk. For instance, a trader might not only trade USD/JPY but also EUR/USD and GBP/USD to diversify their portfolio and minimize the impact of any single currency pair’s volatility.
- Trading plan:A well-defined trading plan Artikels the trader’s entry and exit strategies, risk management rules, and overall trading approach. It helps maintain discipline and consistency, reducing the likelihood of impulsive decisions.
Risk Management Strategies for Trading the USD/JPY Pair
Implementing risk management strategies is crucial when trading the USD/JPY pair, given its high volatility and frequent price swings. Here are some specific examples:
- Using stop-loss orders:Given the USD/JPY’s volatility, setting tight stop-loss orders is essential to limit potential losses. For instance, a trader buying USD/JPY at 135.00 might set a stop-loss order at 134.80, limiting their potential loss to 20 pips.
- Adjusting position size:The USD/JPY’s volatility requires careful position sizing to ensure that losses on any single trade do not exceed a predetermined percentage of the account balance. For example, a trader might choose to risk only 0.5% of their account balance on a USD/JPY trade, limiting their potential loss to $50 on a $10,000 account.
- Considering the economic calendar:The USD/JPY is highly sensitive to economic data releases from both the US and Japan. Monitoring the economic calendar and adjusting trading strategies accordingly can help manage risk. For instance, traders might avoid trading during periods of high economic volatility or adjust their stop-loss orders based on the expected impact of economic data releases.