US Federal Reserves Covert Stress Testing and Bidenomics Revealed
Us federal reserves covert stress testing and bidenomics revealed – US Federal Reserve’s covert stress testing and Bidenomics revealed: These are the two seemingly disparate forces shaping the American economy today. On one hand, the Federal Reserve, the nation’s central bank, conducts covert stress tests to gauge the resilience of financial institutions.
On the other hand, the Biden administration is implementing a series of economic policies known as “Bidenomics,” aiming to address economic inequality, climate change, and infrastructure. These two forces, though seemingly independent, are intricately intertwined, and their interactions have significant implications for the future of the US economy.
This article delves into the intricacies of these forces, examining their individual roles and the potential impact of their interactions. We will explore the Federal Reserve’s covert stress testing methods, the core principles of Bidenomics, and the potential consequences of their interplay.
Ultimately, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this dynamic relationship and its implications for the future of the US economy.
The Federal Reserve’s Role in the Economy: Us Federal Reserves Covert Stress Testing And Bidenomics Revealed
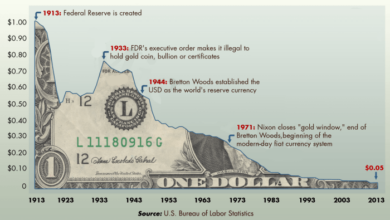
The Federal Reserve, often referred to as the Fed, is the central bank of the United States. Established in 1913, the Fed plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and health of the US economy. Its actions directly impact interest rates, inflation, and the overall financial system, influencing the lives of every American citizen.
Primary Responsibilities of the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve’s primary responsibilities are to:
- Maintain price stability:The Fed aims to keep inflation at a low and stable level, typically around 2%. This is achieved by controlling the money supply and influencing interest rates. Stable prices encourage economic growth and investment.
- Promote maximum employment:The Fed strives to create an environment that fosters job creation and economic growth. This involves managing interest rates and credit conditions to stimulate economic activity and reduce unemployment.
- Supervise and regulate financial institutions:The Fed ensures the safety and soundness of banks and other financial institutions by setting capital requirements, conducting stress tests, and monitoring their operations. This helps to prevent financial crises and protect consumers.
- Provide financial services to the government:The Fed acts as the banker for the US government, managing its accounts and providing financial services. It also issues currency and manages the national debt.
Tools of Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve utilizes various tools to influence monetary policy and achieve its objectives. These tools include:
- Federal Funds Rate:This is the target interest rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. The Fed sets the target rate through open market operations, buying or selling US Treasury securities to inject or withdraw liquidity from the banking system.
- Discount Rate:This is the interest rate at which commercial banks can borrow directly from the Federal Reserve. It serves as a safety net for banks and helps to ensure the stability of the financial system.
- Reserve Requirements:These are the minimum percentage of deposits that banks are required to hold in reserve. By adjusting reserve requirements, the Fed can influence the amount of money available for lending in the economy.
- Quantitative Easing:This involves the Fed purchasing large amounts of government bonds and other assets to inject liquidity into the financial system. This can help to lower long-term interest rates and stimulate borrowing and investment.
Historical Context of the Federal Reserve’s Actions
Throughout its history, the Federal Reserve has played a critical role in responding to economic challenges and shaping the course of the US economy. Some key moments include:
- The Great Depression:The Fed’s failure to adequately respond to the economic crisis of the 1930s contributed to the severity of the Depression. This led to the establishment of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) to protect bank deposits and restore confidence in the banking system.
- The Great Recession:In response to the financial crisis of 2008, the Fed implemented a series of aggressive measures, including lowering interest rates to near zero and engaging in quantitative easing. These actions helped to stabilize the financial system and prevent a deeper recession.
- The COVID-19 Pandemic:The Fed responded to the economic fallout of the pandemic by further lowering interest rates, implementing new lending programs, and purchasing large amounts of government bonds. These measures aimed to support businesses and individuals, and prevent a severe economic downturn.
The recent revelations about the US Federal Reserve’s covert stress testing and their impact on Bidenomics have sent shockwaves through the financial world. While the Fed attempts to navigate a complex economic landscape, some investors are seeking havens in luxury goods, a sector known for its resilience during economic downturns.
For insights into this strategy, check out investing in luxury goods stocks billionaire ken fishers recommendations and top analyst favored companies , which explores the recommendations of billionaire investor Ken Fisher and top analysts in the field. Ultimately, the success of these strategies hinges on the Fed’s ability to effectively manage the economy and mitigate the potential for a recession.
Covert Stress Testing and its Implications
Covert stress testing is a relatively new and less-discussed aspect of financial regulation. It’s a powerful tool used by central banks, like the Federal Reserve, to assess the resilience of financial institutions and the overall financial system in the face of unexpected economic shocks.
This process, while shrouded in secrecy, plays a crucial role in maintaining stability and preventing potential crises.
Differences between Covert and Traditional Stress Testing
Covert stress testing, unlike its traditional counterpart, operates in the shadows. While traditional stress testing involves publicly announced scenarios and publicly disclosed results, covert stress testing operates discreetly. This allows central banks to gain a deeper understanding of financial institutions’ vulnerabilities without triggering any defensive or strategic responses.
The recent revelations about the US Federal Reserve’s covert stress testing and the impact on Bidenomics are certainly making waves. It’s fascinating to see how these hidden maneuvers might be playing out in the real world. Meanwhile, breaking news of significant price declines in gasoline, natural gas, and other energy sources is raising eyebrows, potentially suggesting a shift in market dynamics that could have far-reaching consequences for the economy.
The connection between these two events, however, remains unclear, leaving us to speculate about the potential interplay between monetary policy and energy markets.
- Scenarios:Traditional stress testing often focuses on pre-defined scenarios, like a sudden rise in interest rates or a sharp decline in asset prices. Covert stress testing, however, can explore a broader range of scenarios, including those that are less predictable or politically sensitive.
- Data Collection:Traditional stress testing relies on data provided by financial institutions. Covert stress testing, on the other hand, can access a wider range of data sources, including internal bank records and market intelligence, to gain a more comprehensive picture of their operations.
- Results:The results of traditional stress testing are often publicly disclosed, allowing market participants to assess the health of financial institutions. Covert stress testing results, however, are kept confidential, providing central banks with a more nuanced understanding of vulnerabilities and allowing them to intervene discreetly if necessary.
Implications of Covert Stress Testing
Covert stress testing can have significant implications for financial institutions and the overall economy. While the secrecy surrounding the process can raise concerns about transparency and accountability, it also offers several potential benefits.
- Early Detection of Vulnerabilities:By examining financial institutions’ operations in a discreet manner, central banks can identify potential vulnerabilities that might not be apparent through traditional stress testing. This early detection allows for proactive intervention, reducing the risk of systemic crises.
- Improved Financial Stability:By understanding the true resilience of financial institutions, central banks can develop more effective regulatory policies and supervision practices. This can help to prevent financial instability and promote a more stable economic environment.
- Strategic Advantage for Central Banks:Covert stress testing provides central banks with a strategic advantage, allowing them to assess the health of the financial system and take appropriate action without tipping their hand to market participants. This can help to maintain confidence in the financial system and avoid unnecessary market volatility.
Bidenomics

Bidenomics refers to the economic policies implemented by the Biden administration since its inauguration in 2021. These policies aim to address key economic challenges, including income inequality, climate change, and infrastructure needs. They are characterized by a focus on government intervention, investment in infrastructure and clean energy, and social programs aimed at boosting the middle class.
Key Economic Policies
The Biden administration has implemented a range of economic policies, including:
- The American Rescue Plan Act of 2021: This stimulus package provided direct payments to individuals, expanded unemployment benefits, and funded vaccine distribution and other pandemic-related efforts. It aimed to mitigate the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and stimulate recovery.
- The Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act: This legislation invests heavily in infrastructure projects, including roads, bridges, broadband internet, and clean energy. The goal is to modernize the nation’s infrastructure, create jobs, and enhance competitiveness.
- The Build Back Better Act: This ambitious plan aimed to address climate change, expand healthcare access, and provide tax credits for childcare and eldercare. While the full bill did not pass, some of its provisions were included in other legislation.
- The American Jobs Plan: This plan focused on investments in infrastructure, clean energy, and manufacturing, with the goal of creating jobs and promoting economic growth.
- The American Families Plan: This plan proposed investments in education, childcare, and healthcare, aimed at supporting families and boosting the middle class.
Impact on the Federal Reserve
Bidenomics’ focus on government intervention and spending has significant implications for the Federal Reserve. The increased government spending can lead to higher inflation, which the Federal Reserve may need to address by raising interest rates. This could impact the availability of credit and slow economic growth.The Federal Reserve’s covert stress testing, which assesses the resilience of financial institutions to economic shocks, may need to be adjusted to account for the potential impact of Bidenomics.
The increased government debt and potential for inflation could pose new risks to the financial system.
The recent revelations about the Federal Reserve’s covert stress testing and the impact of Bidenomics on the economy have sparked a wave of concern. This, coupled with the US imposing sanctions on Chinese and Mexican companies linked to counterfeit pill-making equipment, as reported by The Venom Blog , raises questions about the fragility of our supply chains and the potential for instability in the global pharmaceutical market.
These events underscore the need for transparency and robust oversight in both economic and healthcare sectors to ensure the safety and security of our nation.
Comparison with Previous Policies
Bidenomics contrasts with the economic policies of the previous administration, which emphasized tax cuts and deregulation. The Trump administration’s policies aimed to stimulate economic growth through business investment and job creation.Bidenomics, on the other hand, prioritizes social programs, infrastructure investment, and addressing income inequality.
The focus on government intervention and social spending represents a shift in economic philosophy.The impact of these different policies on the US economy is still being debated. Some argue that Bidenomics will lead to higher inflation and slower economic growth, while others believe it will stimulate investment and create jobs.The Federal Reserve’s actions will be crucial in navigating the potential economic consequences of Bidenomics.
The covert stress testing process will play a critical role in assessing the risks and vulnerabilities of the financial system under these new economic policies.
The Relationship between the Federal Reserve, Covert Stress Testing, and Bidenomics
The Federal Reserve, through its monetary policy tools and oversight of financial institutions, plays a critical role in shaping the economic landscape. Covert stress testing, a relatively recent development, adds another layer of complexity to this dynamic. Bidenomics, the economic policy agenda of the Biden administration, further influences the interplay between the Fed and the financial system.
Understanding the interconnectedness of these three elements is crucial for navigating the complexities of the contemporary economic environment.
Interconnectedness of the Federal Reserve, Covert Stress Testing, and Bidenomics
The relationship between the Federal Reserve, covert stress testing, and Bidenomics is multifaceted and dynamic. The following table illustrates the potential influence of each element on the others, highlighting their respective functions and potential consequences.
| Element | Function | Impact on Other Elements | Potential Consequences | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Federal Reserve | Monetary policy (interest rates, reserve requirements), financial regulation, oversight of financial institutions | – Influences the effectiveness of covert stress testing by setting the regulatory environment and providing economic data.
|
– Potential for policy misalignment with Bidenomics, leading to conflicting economic signals.
|
|
| Covert Stress Testing | Evaluates the resilience of financial institutions to economic shocks and stresses. | – Informs the Federal Reserve’s regulatory decisions and oversight of financial institutions.
|
– Potential for unintended consequences if the results of covert stress testing are not communicated effectively or lead to overly conservative regulatory measures.
|
|
| Bidenomics | Economic policy agenda focused on infrastructure investment, clean energy, and social programs. | – Influences the Federal Reserve’s policy objectives and the design of covert stress testing scenarios.
|
– Potential for economic growth or stagnation depending on the effectiveness of Bidenomics. | – Potential for increased financial stability or instability depending on the impact of Bidenomics on the financial system.
|
Potential Risks and Opportunities
The interaction between the Federal Reserve, covert stress testing, and Bidenomics presents both risks and opportunities.
Risks:
* Policy Misalignment:The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy objectives may not align with the goals of Bidenomics, leading to conflicting economic signals and potential instability.
Unintended Consequences Covert stress testing, if not implemented carefully, could lead to unintended consequences, such as overly conservative regulatory measures or a lack of transparency.
Financial Instability Bidenomics’ policies, if not carefully managed, could potentially destabilize the financial system, especially if they lead to increased inflation or a decline in economic growth.
Opportunities:
* Enhanced Financial Stability:By working together, the Federal Reserve, covert stress testing, and Bidenomics can contribute to a more stable and resilient financial system.
Increased Transparency and Accountability Covert stress testing can promote greater transparency and accountability in the financial system, helping to build public trust.
Economic Growth and Prosperity Through coordinated efforts, the Federal Reserve, covert stress testing, and Bidenomics can contribute to economic growth and prosperity, benefiting all Americans.
Future Considerations and Potential Scenarios
The Federal Reserve’s covert stress testing, while designed to assess systemic risk and vulnerabilities, could reveal significant weaknesses within the financial system. This scenario raises concerns about the potential impact on the economy and the Biden administration’s response.
The Potential Impact of Significant Vulnerabilities
If the covert stress testing reveals significant vulnerabilities within the financial system, the Biden administration would face a complex and challenging situation. The potential impact on the economy could be substantial, ranging from market instability to a full-blown financial crisis.
- Market Volatility:The revelation of systemic vulnerabilities could trigger a wave of market volatility, leading to sharp declines in asset prices, increased borrowing costs, and reduced investment activity.
- Credit Crunch:Banks, fearing potential losses, might become more reluctant to lend, creating a credit crunch that could stifle economic growth and exacerbate the downturn.
- Financial Crisis:In a worst-case scenario, the identified vulnerabilities could trigger a financial crisis, leading to bank failures, widespread unemployment, and a severe economic recession.
Potential Responses of the Biden Administration, Us federal reserves covert stress testing and bidenomics revealed
The Biden administration would need to respond swiftly and decisively to mitigate the potential consequences of significant vulnerabilities identified through covert stress testing. The administration’s response would likely involve a combination of policy adjustments and interventions.
- Increased Regulation:The administration could introduce stricter regulations for financial institutions to address the identified vulnerabilities and reduce systemic risk. This could involve increased capital requirements, tighter oversight of lending practices, and stricter rules for derivatives trading.
- Fiscal Stimulus:The administration could implement fiscal stimulus measures to support the economy, such as tax cuts, increased government spending, and infrastructure investments. This would aim to boost consumer confidence, stimulate economic activity, and prevent a recession.
- Monetary Policy Adjustments:The Federal Reserve could adjust its monetary policy to provide additional liquidity to the financial system and support economic growth. This could involve lowering interest rates, expanding the money supply, or providing emergency loans to banks.
Consequences of Different Responses
The consequences of different responses by the Biden administration would depend on the severity of the identified vulnerabilities, the effectiveness of the chosen policies, and the overall economic climate.
- Aggressive Intervention:A proactive and aggressive response, involving substantial regulatory changes, significant fiscal stimulus, and accommodative monetary policy, could help stabilize the financial system and prevent a major economic downturn. However, it could also lead to higher inflation, increased government debt, and potential distortions in the market.
- Moderate Intervention:A more moderate response, focusing on targeted interventions and less drastic policy adjustments, could help mitigate the impact of vulnerabilities without causing significant economic disruptions. However, it might not be sufficient to address all the underlying risks and could lead to a prolonged period of economic stagnation.
- Limited Intervention:A limited response, relying primarily on market forces and minimal government intervention, could be seen as a more conservative approach. However, it could lead to a more severe economic downturn and potentially trigger a financial crisis if the identified vulnerabilities are not addressed effectively.