
Global Economic Events: Impact on Forex Markets Explained
The impact of global economic events on forex markets explained is a topic that fascinates both seasoned investors and curious newcomers alike. Understanding how these events influence currency fluctuations is crucial for anyone navigating the dynamic world of forex trading.
From interest rate adjustments by central banks to geopolitical shifts, the interconnectedness between global economics and forex markets is undeniable.
This intricate relationship plays out in a complex dance of supply and demand, where economic indicators, political events, and market sentiment all contribute to the ever-changing value of currencies. By dissecting these factors, we can gain valuable insights into the underlying forces driving forex markets and make informed decisions about our investments.
Understanding the Interplay: The Impact Of Global Economic Events On Forex Markets Explained
The foreign exchange (forex) market is the largest and most liquid financial market globally, facilitating the exchange of currencies between countries. This market is constantly in motion, driven by a multitude of factors, with global economic events playing a pivotal role in shaping its dynamics.
The intricate relationship between global economic events and forex markets is not merely a correlation but a deep-rooted interdependence. Understanding this interplay is crucial for investors and traders alike, as it provides valuable insights into currency fluctuations and potential investment opportunities.
The Significance of Analyzing the Interplay
Analyzing the relationship between global economic events and forex markets offers several benefits for investors and traders:
- Informed Decision-Making:By understanding the impact of economic events on currencies, investors and traders can make more informed decisions about buying or selling currencies, thereby maximizing their returns and minimizing their risks.
- Predicting Currency Movements:Analyzing economic indicators can help anticipate future currency movements, enabling traders to capitalize on profitable opportunities. For instance, a strong economic growth forecast for a country could lead to an appreciation of its currency, presenting a buy opportunity for traders.
- Risk Management:Recognizing the potential impact of economic events on forex markets is crucial for risk management. By understanding these influences, investors and traders can adjust their portfolios and strategies accordingly to mitigate potential losses.
Economic Indicators and Their Impact
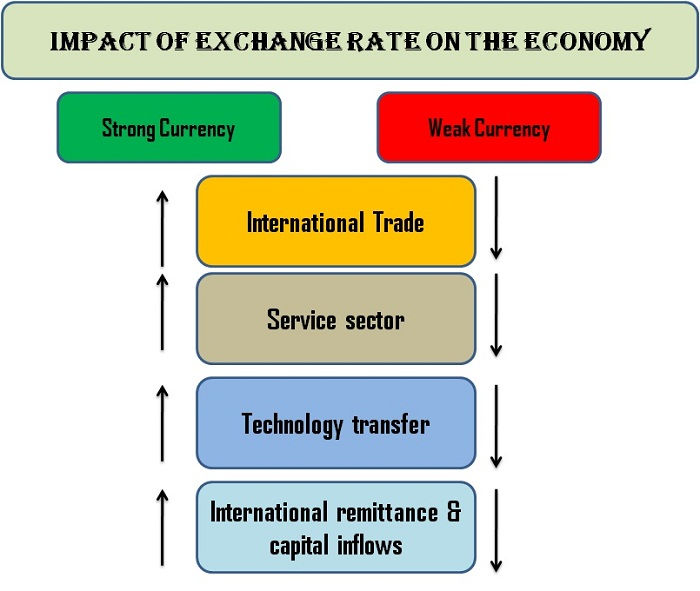
Economic indicators play a crucial role in shaping forex market movements. These indicators provide insights into the health and direction of a country’s economy, influencing investor sentiment and currency valuations. Understanding the relationship between economic indicators and forex markets is essential for traders and investors seeking to navigate the dynamic landscape of currency trading.
Impact of Key Economic Indicators
Economic indicators can be categorized into various groups, each providing valuable information about different aspects of a country’s economic performance. These indicators offer a comprehensive view of the economy’s health, growth potential, and inflationary pressures.
The impact of global economic events on forex markets is often unpredictable, as recent events have shown. One example is the recent bank turmoil, which has had a significant impact on market sentiment. The news that bank turmoil results in 72 billion loss of deposits for first republic has raised concerns about the stability of the financial system, leading to increased volatility in currency markets.
As investors seek safe haven assets, we can expect to see further fluctuations in forex exchange rates in the coming weeks.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): GDP is the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders over a specific period. A strong GDP growth rate indicates a healthy economy, potentially leading to a stronger currency. Conversely, a decline in GDP growth can weaken a currency as it signals economic weakness.
For example, a strong GDP growth rate in the United States could strengthen the US dollar against other currencies.
- Inflation: Inflation refers to the rate at which prices for goods and services rise over time. High inflation erodes purchasing power and can weaken a currency. Central banks often raise interest rates to combat inflation, which can attract foreign investment and strengthen the currency.
For instance, if inflation in the Eurozone rises, the European Central Bank might increase interest rates, making the euro more attractive to investors.
- Interest Rates: Interest rates set by central banks influence borrowing costs and investment decisions. Higher interest rates can attract foreign capital, boosting demand for a currency and strengthening it. Conversely, lower interest rates can make a currency less attractive, leading to depreciation.
For example, the Bank of England raising interest rates could make the British pound more attractive to investors, strengthening the GBP/USD currency pair.
- Unemployment Rate: The unemployment rate reflects the percentage of the labor force that is unemployed but actively seeking work. A low unemployment rate suggests a strong economy and can support a currency’s value. Conversely, a high unemployment rate can signal economic weakness and lead to currency depreciation.
For example, a decline in the unemployment rate in the United States could boost investor confidence in the US economy and strengthen the USD/EUR currency pair.
- Trade Balance: The trade balance measures the difference between a country’s exports and imports. A trade surplus (exports exceeding imports) can indicate a strong economy and a potential currency appreciation. Conversely, a trade deficit (imports exceeding exports) can signal economic weakness and lead to currency depreciation.
For instance, a widening trade deficit in Japan could weaken the Japanese yen against the US dollar.
- Consumer Confidence: Consumer confidence reflects consumer sentiment about the economy’s current and future state. High consumer confidence can lead to increased spending, boosting economic growth and supporting a currency’s value. Conversely, low consumer confidence can dampen spending and weaken a currency.
For example, rising consumer confidence in Germany could strengthen the euro against the US dollar.
Impact of Economic Indicators on Currency Pairs
The impact of economic indicators on currency pairs can be complex and multifaceted, depending on various factors such as the specific indicators, the economic context, and market sentiment. However, understanding the general impact of these indicators can provide valuable insights into potential currency movements.
| Economic Indicator | Impact on USD/EUR | Impact on GBP/USD |
|---|---|---|
| Strong US GDP Growth | USD strengthens against EUR | USD strengthens against GBP |
| High US Inflation | USD weakens against EUR | USD weakens against GBP |
| US Interest Rate Hike | USD strengthens against EUR | USD strengthens against GBP |
| Low US Unemployment Rate | USD strengthens against EUR | USD strengthens against GBP |
| US Trade Surplus | USD strengthens against EUR | USD strengthens against GBP |
| High US Consumer Confidence | USD strengthens against EUR | USD strengthens against GBP |
Global Economic Events and Forex Volatility
The forex market is constantly in flux, driven by a myriad of factors, including global economic events. These events can significantly impact currency valuations, leading to increased volatility and potential opportunities for traders. Understanding the relationship between global economic events and forex volatility is crucial for navigating this dynamic market.
Impact of Global Economic Events on Forex Volatility
Global economic events, particularly those with significant implications for a country’s economy, often trigger volatility in the forex market. These events can be political, financial, or natural disasters, each with its own unique impact on currency fluctuations.
Global economic events, like interest rate changes or trade wars, can send shockwaves through the forex markets, creating opportunities for savvy traders. However, understanding the impact of these events requires a strong grasp of economic fundamentals and a well-defined trading strategy.
It’s also crucial to manage your financial risks, which is why I recommend checking out credit debt management tips strategies examples to gain a solid foundation in responsible financial practices. By combining a keen understanding of global economics with effective risk management, you can navigate the forex markets with confidence and potentially reap significant rewards.
- Political Events:Political instability, changes in government policies, and geopolitical tensions can significantly influence currency valuations. For instance, a change in government leadership, particularly if it suggests a shift in economic policies, can lead to uncertainty and volatility in the market.
Geopolitical tensions, such as trade wars or military conflicts, can also create market uncertainty and impact currency exchange rates.
- Financial Events:Financial events, such as changes in interest rates, inflation, and economic growth, have a direct impact on currency valuations. Central banks often adjust interest rates to manage inflation and stimulate economic growth. When a central bank raises interest rates, it can attract foreign investment, leading to an appreciation of the domestic currency.
Conversely, a decrease in interest rates can weaken the currency. Similarly, a surge in inflation can erode purchasing power and lead to currency depreciation.
- Natural Disasters:Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, floods, or hurricanes, can disrupt economic activity and impact currency valuations. These events can damage infrastructure, disrupt supply chains, and lead to increased costs for businesses. The impact on the currency can be significant, depending on the severity of the disaster and the country’s economic resilience.
Mechanisms of Currency Fluctuations
The mechanisms through which global economic events influence currency fluctuations are complex and interconnected. Here are some key factors:
- Investor Sentiment:Investor sentiment plays a crucial role in currency valuations. When investors are optimistic about a country’s economic prospects, they tend to invest in its currency, leading to appreciation. Conversely, negative sentiment can lead to currency depreciation.
- Interest Rate Differentials:Interest rate differentials, the difference between interest rates in two countries, influence currency valuations. When a country’s interest rates are higher than those of other countries, it can attract foreign investment, leading to an appreciation of its currency.
- Economic Growth:Economic growth is a key driver of currency valuations. When a country’s economy is growing, it can attract foreign investment, leading to an appreciation of its currency. Conversely, a slowdown in economic growth can lead to currency depreciation.
- Government Policies:Government policies, such as fiscal and monetary policies, can significantly impact currency valuations. Fiscal policies, such as government spending and taxation, can influence economic growth and inflation, which in turn affect currency valuations. Monetary policies, such as interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing, can directly impact currency exchange rates.
Comparison of Impact of Different Types of Events
The impact of different types of global economic events on forex markets can vary significantly. For example, political events can trigger sudden and sharp movements in currency valuations, as they often involve uncertainty and fear. Financial events, such as interest rate changes, can have a more gradual and predictable impact on currency exchange rates.
Natural disasters, depending on their severity and impact on the economy, can lead to both short-term and long-term fluctuations in currency valuations.
“The forex market is a complex and dynamic system, and understanding the interplay between global economic events and currency valuations is essential for making informed trading decisions.”
Monetary Policy and Currency Values
Central banks play a crucial role in influencing currency values through their monetary policy adjustments. By manipulating interest rates, controlling the money supply, and implementing other measures, central banks aim to achieve their macroeconomic objectives, which often have a direct impact on the exchange rate.
Interest Rate Changes and Currency Movements
Changes in interest rates are one of the most direct and powerful tools central banks use to influence currency values. When a central bank raises interest rates, it becomes more attractive for foreign investors to invest in that country’s assets, as they can earn higher returns.
This increased demand for the country’s currency leads to its appreciation. Conversely, when interest rates are lowered, the currency tends to depreciate as investors seek higher returns elsewhere.
The relationship between interest rates and currency movements is often summarized as the “carry trade.”
For example, if the US Federal Reserve raises interest rates while the European Central Bank keeps rates low, the US dollar is likely to appreciate against the euro. This is because investors would prefer to invest in US dollar-denominated assets, which offer higher returns, leading to increased demand for the dollar and a strengthening of its value.
Quantitative Easing and Other Non-Traditional Monetary Policies
In recent years, central banks have resorted to unconventional monetary policies, such as quantitative easing (QE), to stimulate economic growth and combat deflation. QE involves injecting liquidity into the financial system by purchasing government bonds or other assets. This increases the money supply and lowers interest rates, which can have a significant impact on currency values.QE can lead to currency depreciation, as the increased money supply can reduce the purchasing power of the currency.
Understanding how global economic events impact forex markets is crucial for any trader. It’s not just about central bank announcements and trade wars; it’s about the ripple effects that reach every corner of the financial world. For example, the recent appearance of Vitalik Buterin on Bloomberg Studio 10, discussing the future of Ethereum, bloombergs studio 10 ethereum co founder vitalik buterin , highlights how even cryptocurrency trends can influence forex markets.
This is because cryptocurrencies are becoming increasingly intertwined with traditional finance, creating new opportunities and risks for investors.
However, the impact of QE on exchange rates is complex and depends on various factors, including the scale of the program, the economic context, and market expectations. For instance, during the global financial crisis, the US Federal Reserve implemented a massive QE program, which contributed to the depreciation of the US dollar.
However, in subsequent years, the dollar has appreciated despite continued QE, indicating that other factors, such as economic growth and global demand, can outweigh the impact of QE.
Trade and Investment Flows
The intricate dance of global trade and investment flows exerts a significant influence on forex markets. Currency exchange rates act as the invisible hand that facilitates international transactions, impacting the flow of goods, services, and capital across borders. Understanding the interplay between these flows and currency values is crucial for investors and traders seeking to navigate the dynamic forex landscape.
Impact of Global Trade Flows
International trade, the exchange of goods and services between countries, relies heavily on currency exchange rates. When a country exports goods or services, it receives payment in the currency of the importing country. This necessitates converting the foreign currency into the domestic currency, creating demand for the domestic currency and potentially appreciating its value.
Conversely, imports lead to demand for foreign currencies to pay for imported goods, potentially depreciating the domestic currency.
For instance, if the United States imports a large quantity of goods from China, it will need to buy Chinese yuan to pay for these imports. This increased demand for yuan will likely lead to a rise in the yuan’s value against the US dollar.
Impact of Foreign Direct Investment and Portfolio Investment Flows
Foreign direct investment (FDI) involves investing in a foreign country to gain control of an existing business or to create a new one. This investment flow typically leads to an increase in demand for the target country’s currency, as investors need to convert their own currency into the local currency to finance their investments.
Portfolio investment flows, on the other hand, involve investing in foreign securities such as stocks and bonds. These flows can also influence currency values, as investors buy and sell securities in different currencies.
A surge in FDI into a country can boost the value of its currency, reflecting the positive outlook investors have on the country’s economic prospects. Similarly, large-scale portfolio investments into a country can lead to appreciation of its currency, as investors buy up local assets, increasing demand for the local currency.
Examples of Trade and Investment Flows Impacting Currency Pairs
| Currency Pair | Trade Flow Impact | Investment Flow Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| USD/JPY | Increased US exports to Japan would increase demand for USD, leading to USD appreciation against JPY. | Increased FDI from Japan to the US would increase demand for USD, leading to USD appreciation against JPY. | Strong US economic growth leading to increased exports of US goods to Japan, combined with Japanese investors seeking opportunities in the US stock market, could strengthen the USD against the JPY. |
| EUR/USD | Increased German exports to the US would increase demand for EUR, leading to EUR appreciation against USD. | Increased FDI from the US to Germany would increase demand for EUR, leading to EUR appreciation against USD. | High demand for German manufactured goods in the US market, alongside US companies investing in German infrastructure projects, could push the EUR higher against the USD. |
| GBP/USD | Increased UK exports to the US would increase demand for GBP, leading to GBP appreciation against USD. | Increased FDI from the US to the UK would increase demand for GBP, leading to GBP appreciation against USD. | Strong performance of the UK’s financial sector attracting US investment, coupled with rising demand for UK-made products in the US, could contribute to GBP strength against the USD. |
| AUD/USD | Increased Australian exports of commodities to China would increase demand for AUD, leading to AUD appreciation against USD. | Increased FDI from China to Australia would increase demand for AUD, leading to AUD appreciation against USD. | High demand for Australian iron ore and coal in China, combined with Chinese investors seeking opportunities in the Australian mining sector, could strengthen the AUD against the USD. |
Risk Sentiment and Currency Fluctuations

Investor confidence, also known as risk sentiment, plays a significant role in influencing forex markets. When investors are optimistic about the global economy, they are more likely to take on risks, leading to increased demand for higher-yielding currencies. Conversely, when investors are pessimistic, they tend to move towards safe-haven currencies, seeking stability and security.
The Relationship Between Risk Aversion and Safe-Haven Currencies
Risk aversion refers to investors’ tendency to avoid risky assets and seek out safe-haven assets during periods of uncertainty or economic turmoil. Safe-haven currencies, such as the Japanese yen (JPY), Swiss franc (CHF), and US dollar (USD), are typically perceived as relatively stable and less volatile during times of global economic stress.
This is because these currencies are often associated with strong economies, stable political environments, and low inflation.
- Demand for Safe-Haven Currencies:During periods of risk aversion, investors tend to sell risky assets, such as stocks and emerging market currencies, and buy safe-haven currencies. This increased demand for safe-haven currencies leads to their appreciation against other currencies.
- Example:During the 2008 financial crisis, the US dollar strengthened significantly as investors sought refuge from the global economic turmoil. The Japanese yen and Swiss franc also experienced significant appreciation as investors moved towards perceived safe-haven assets.
Examples of How Changes in Risk Sentiment Can Impact Currency Values
Changes in global risk sentiment can significantly impact currency values. For example, if there is positive news about economic growth in a particular country, investors may become more optimistic about that country’s prospects and increase their demand for its currency.
This increased demand will lead to the currency’s appreciation. Conversely, if there is negative news about a country’s economic outlook, investors may become more risk-averse and sell that country’s currency, leading to its depreciation.
- Example:The Australian dollar (AUD) is often considered a risk-on currency due to its close ties to commodity prices. When global risk sentiment is high, investors are more likely to invest in commodity-related assets, leading to increased demand for the AUD.
However, during periods of risk aversion, the AUD tends to depreciate as investors seek safe-haven assets.
- Example:The South African rand (ZAR) is another example of a currency that is sensitive to changes in global risk sentiment. The ZAR is considered a high-yielding currency, but it is also vulnerable to global economic shocks. When global risk sentiment is high, the ZAR tends to appreciate.
However, during periods of risk aversion, the ZAR can depreciate significantly.
Technical Analysis and Forex Trading Strategies
Technical analysis is a method used by forex traders to identify trading opportunities based on historical price patterns and trends. It involves analyzing price charts and using technical indicators to predict future price movements. While fundamental analysis focuses on economic factors, technical analysis focuses on the supply and demand dynamics within the market itself.
Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on historical price data, such as closing prices, trading volumes, and highs/lows. These indicators provide traders with insights into price trends, momentum, and volatility. They can help identify potential buy or sell signals, support and resistance levels, and overbought or oversold conditions.
- Moving Averages (MA):Moving averages smooth out price fluctuations and identify trends. A simple moving average (SMA) calculates the average price over a specific period, while an exponential moving average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices. Traders use crossovers between different moving averages to identify potential buy or sell signals.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI):The RSI measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions. An RSI value above 70 suggests a potential overbought condition, while a value below 30 indicates an oversold condition.
- Stochastic Oscillator:The Stochastic Oscillator compares a closing price to its price range over a given period. It can identify overbought or oversold conditions and potential trend reversals.
- Bollinger Bands:Bollinger Bands are used to measure price volatility and identify potential breakout opportunities. They consist of a moving average and two standard deviation bands above and below it.
Chart Patterns, The impact of global economic events on forex markets explained
Chart patterns are recognizable formations on price charts that indicate potential future price movements. These patterns can be bullish, bearish, or neutral, providing traders with insights into the market’s sentiment and potential trading opportunities.
- Head and Shoulders:This pattern is a bearish reversal pattern that suggests a potential downtrend. It consists of three peaks, with the middle peak (the head) being the highest.
- Double Top/Bottom:These patterns are reversal patterns that suggest a potential change in trend. A double top is bearish, while a double bottom is bullish.
- Triangles:Triangles are consolidation patterns that indicate a period of indecision in the market. They can be symmetrical, ascending, or descending.
- Flags and Pennants:These patterns are continuation patterns that suggest a continuation of the existing trend. They are characterized by a brief period of consolidation followed by a breakout in the direction of the trend.
Technical Analysis Strategies
Technical analysis can be used in conjunction with other trading strategies to improve trading decisions. Some common technical analysis strategies include:
- Trend Trading:This strategy involves identifying and trading in the direction of the prevailing trend. Traders use technical indicators to confirm the trend and identify potential entry and exit points.
- Breakout Trading:This strategy involves identifying and trading breakouts from established price ranges or support and resistance levels. Traders use technical indicators and chart patterns to identify potential breakout opportunities.
- Scalping:This strategy involves taking small profits on short-term price fluctuations. Scalpers use technical indicators and chart patterns to identify potential entry and exit points within a short timeframe.






