
AI Elections in the US: Threats & Opportunities for Democracy
The first ai election in us threats and opportunities for democracy – The first AI election in the US: threats and opportunities for democracy – a phrase that conjures images of a future where algorithms decide our leaders, where data reigns supreme, and where the very fabric of democracy hangs in the balance.
It’s a future that’s not so far off, as AI increasingly infiltrates every aspect of our lives, including the electoral process.
This technology holds immense potential to revolutionize elections, from increasing voter participation to combating fraud. But, as with any powerful tool, AI comes with inherent risks. The potential for manipulation, disinformation, and bias looms large, raising serious questions about the future of democratic governance.
The Rise of AI in Elections
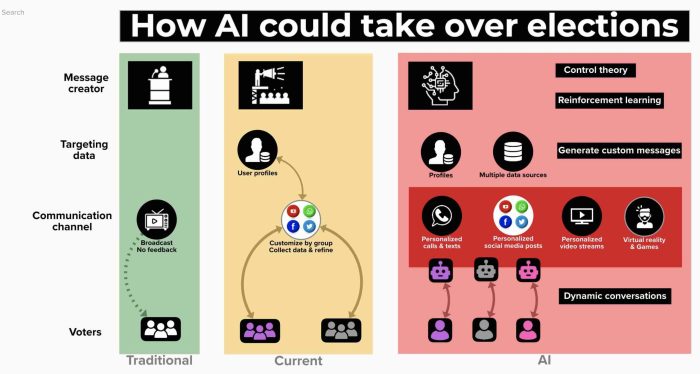
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in US elections is rapidly increasing, transforming the way campaigns are run and voters are engaged. From targeted advertising to sophisticated data analysis, AI is becoming an integral part of the electoral landscape.AI-powered tools are being used in various aspects of elections, including voter targeting, campaign strategy optimization, and misinformation detection.
Voter Targeting
AI algorithms are used to analyze vast amounts of data about voters, including demographics, voting history, and social media activity. This information is then used to create highly targeted campaign messages and advertisements that are more likely to resonate with specific voter segments.
For example, campaigns can use AI to identify potential swing voters and tailor their messages to appeal to their concerns.
Campaign Strategy Optimization
AI can help campaigns optimize their spending, messaging, and outreach strategies. By analyzing data on voter sentiment and campaign performance, AI algorithms can provide insights into which tactics are most effective and how to allocate resources for maximum impact. AI can also help campaigns identify potential problems and adjust their strategies accordingly.
The prospect of an AI-powered election in the US raises significant concerns about the future of democracy. Will algorithms be able to accurately reflect the will of the people, or will they be susceptible to manipulation and bias? While we grapple with these complex questions, it’s worth considering the impact of technology on our everyday lives, like the choice between gas and electric vehicles.
For those seeking a greener and potentially more cost-effective option, gas vs electric vehicles which is a better deal know the experts suggestions provides valuable insights. Ultimately, navigating the future of both our political systems and personal transportation choices will require careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks associated with emerging technologies.
Misinformation Detection
The spread of misinformation and fake news poses a significant threat to democratic elections. AI can help combat this by identifying and flagging false or misleading content. AI-powered tools can analyze the content of news articles, social media posts, and other online materials to detect patterns that indicate potential misinformation.
Examples of AI-Powered Tools
Several AI-powered tools have been used in recent US elections, including:
- Cambridge Analytica:This company used AI to analyze Facebook data and create targeted political advertisements. The company’s work was controversial, raising concerns about data privacy and the potential for manipulation.
- VoterScore:This tool uses AI to predict voter turnout and behavior. It analyzes data on voter registration, voting history, and demographic information to create detailed profiles of individual voters.
- Google Political Ads Transparency:Google has implemented AI-powered tools to track and disclose political advertising on its platform. This transparency helps to prevent the spread of misinformation and ensure that campaigns are accountable for their spending.
Potential Benefits and Challenges of AI in Elections
The integration of AI into the electoral process has the potential to both enhance and threaten democratic values.
- Benefits:
- Increased voter engagement:AI can help campaigns reach voters with more relevant and personalized messages, potentially increasing voter turnout and engagement.
- Improved campaign efficiency:AI can help campaigns optimize their resources and strategies, making them more efficient and effective.
- Enhanced transparency:AI can help track and disclose campaign spending and activity, promoting transparency and accountability.
- Challenges:
- Data privacy concerns:The use of AI in elections raises concerns about data privacy and the potential for misuse of personal information.
- Algorithmic bias:AI algorithms can be biased, potentially leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
- Misinformation and manipulation:AI can be used to create and spread misinformation, potentially undermining public trust in elections.
Threats to Democracy

The integration of AI into elections presents both opportunities and challenges. While AI can enhance efficiency and voter engagement, it also poses significant risks to democratic processes. The potential for manipulation, disinformation, and algorithmic bias raises concerns about the integrity and fairness of elections.
Voter Manipulation
AI can be used to manipulate voters in various ways, potentially undermining the democratic principle of free and fair elections. This manipulation can take several forms, including:
- Targeted Propaganda:AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data on individual voters, including their demographics, online behavior, and political leanings. This information can be used to create highly targeted propaganda messages that exploit vulnerabilities and manipulate opinions. For example, AI-powered chatbots can engage in personalized conversations with voters, spreading misinformation or subtly influencing their views.
- Microtargeting:AI can be used to microtarget voters with specific messages designed to sway their decisions. This can involve tailoring campaign messaging to individual voters based on their preferences, anxieties, and fears. For instance, AI algorithms could identify voters who are susceptible to fear-mongering tactics and target them with messages that emphasize threats to their safety or well-being.
- Social Media Manipulation:AI can be used to manipulate social media platforms, amplifying certain narratives and suppressing others. This can involve creating fake accounts, spreading misinformation, and using bots to generate artificial engagement. The goal is to create an echo chamber effect, where voters are exposed only to information that confirms their existing biases, potentially leading to polarization and mistrust in democratic institutions.
Targeted Disinformation Campaigns
AI can facilitate the creation and dissemination of targeted disinformation campaigns, which can erode public trust in elections and undermine democratic processes. This can involve:
- Deepfakes:AI can be used to create realistic deepfakes, which are manipulated videos or audio recordings that make it appear as if someone is saying or doing something they never did. Deepfakes can be used to spread false information about candidates or elections, potentially swaying voters and undermining the credibility of democratic processes.
- Automated Propaganda:AI-powered bots and social media accounts can be used to spread disinformation at scale, amplifying false narratives and undermining public trust in legitimate sources of information. This can involve creating fake news articles, spreading rumors, and manipulating online conversations to create an illusion of widespread support for a particular candidate or agenda.
- Personalized Disinformation:AI can be used to personalize disinformation campaigns, tailoring messages to specific demographics and exploiting individual vulnerabilities. This can involve targeting voters with messages that appeal to their fears, prejudices, or anxieties, potentially influencing their voting decisions and eroding public trust in democratic institutions.
Algorithmic Bias
AI algorithms can perpetuate and amplify existing societal biases, potentially leading to unfair and discriminatory outcomes in elections. This can involve:
- Voter Suppression:AI algorithms can be used to identify and target voters based on demographic factors, such as race, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status. This can lead to voter suppression tactics, such as removing voters from registration lists or making it more difficult for them to cast their ballots.
The prospect of an AI-driven election in the US raises a complex web of ethical and practical considerations. While the potential for increased efficiency and transparency is undeniable, we must also confront the risks of manipulation and algorithmic bias.
The recent financial turmoil, exemplified by the bank turmoil resulting in a 72 billion loss of deposits for First Republic , highlights the fragility of our economic systems. This instability underscores the need for robust safeguards as we navigate the uncharted waters of AI-powered elections, ensuring that technology serves democracy, not undermines it.
- Gerrymandering:AI algorithms can be used to manipulate electoral districts, creating districts that favor one party or candidate over another. This can result in unfair elections, where the outcome is predetermined by the way districts are drawn, rather than by the will of the voters.
- Campaign Targeting:AI algorithms can be used to target campaign resources and messaging based on demographic factors, potentially reinforcing existing inequalities and excluding certain groups from the political process. This can lead to a situation where certain groups are underrepresented in the political system, undermining the principle of equal representation.
The prospect of the first AI-powered election in the US raises crucial questions about the future of democracy. While AI could potentially enhance efficiency and transparency, it also presents risks like manipulation and bias. A recent federal reserve report on SVB collapse highlights mismanagement and supervisory failures , highlighting the potential for unchecked power and lack of accountability.
Similarly, AI systems need rigorous oversight to prevent them from becoming tools for misinformation or undue influence, ensuring a fair and democratic process.
Opportunities for Democracy: The First Ai Election In Us Threats And Opportunities For Democracy
While the potential threats of AI in elections are significant, it’s crucial to acknowledge the opportunities it presents for enhancing democracy and ensuring a more inclusive and secure electoral process. AI can be a powerful tool for improving voter participation, increasing accessibility, combating voter suppression, and safeguarding the integrity of elections.
Enhancing Voter Participation and Accessibility, The first ai election in us threats and opportunities for democracy
AI can be instrumental in making elections more accessible and engaging for all citizens.
- Personalized Voter Information:AI can analyze voter data to provide personalized information about candidates, voting procedures, and polling locations, tailored to individual preferences and needs. This can help overcome barriers to participation, especially for first-time voters or those with limited access to information.
- Multilingual Support:AI-powered translation tools can provide real-time language support for voters who speak different languages, ensuring that everyone can understand election materials and participate effectively.
- Accessible Voting Platforms:AI can be used to develop accessible voting platforms for individuals with disabilities, such as screen readers, text-to-speech software, and alternative input methods. This can significantly increase voter participation among those who might otherwise face barriers.
- Voter Outreach and Education:AI can be leveraged for targeted voter outreach campaigns, identifying potential voters and providing them with relevant information about the election. AI-powered chatbots can also answer voter questions and provide guidance on registration and voting procedures.
Public Perception and Trust in AI-Driven Elections
The prospect of AI-driven elections raises significant concerns about public perception and trust. While AI offers potential benefits, its implementation in such a sensitive domain requires careful consideration of public anxieties regarding privacy, data security, and potential bias. Building public trust in AI-powered election systems is paramount to ensure the integrity and legitimacy of the electoral process.
Public Concerns About AI in Elections
Public concerns about AI in elections stem from a variety of factors, including:
- Privacy Concerns:The use of AI in elections involves the collection and analysis of vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy violations. For example, the use of facial recognition technology at polling stations could potentially lead to the unauthorized tracking and identification of voters.
- Data Security Risks:AI systems are susceptible to cyberattacks and data breaches, which could compromise the integrity of election results. Hackers could potentially manipulate data or disrupt the voting process, undermining public confidence in the election outcome.
- Algorithmic Bias:AI algorithms are trained on data sets that may reflect existing societal biases, potentially leading to discriminatory outcomes in elections. For instance, an AI system used for voter registration could inadvertently disenfranchise certain groups based on their demographic characteristics.
The Future of AI in US Elections
The potential of AI to revolutionize US elections is undeniable, but so are the risks. Navigating this future requires a delicate balance between embracing innovation and safeguarding democratic values. The path forward demands a collective effort from policymakers, technology companies, and civil society to ensure AI enhances, not undermines, our democratic processes.
A Framework for Responsible AI in Elections
A comprehensive framework for responsible AI development and deployment in elections is crucial. This framework should encompass ethical considerations, data privacy, transparency, and accountability.
- Ethical Guidelines: Clear guidelines should be established to ensure AI systems are fair, unbiased, and do not perpetuate existing inequalities. This includes addressing potential biases in algorithms and data sets, ensuring transparency in decision-making processes, and promoting accountability for any unintended consequences.
- Data Privacy and Security: Robust measures are needed to protect voter data from unauthorized access, misuse, or manipulation. This includes implementing strong encryption protocols, limiting data collection and retention, and ensuring informed consent for data use.
- Transparency and Explainability: AI systems used in elections should be transparent and explainable. This means making the decision-making processes clear, allowing for independent audits and verification, and providing voters with understandable information about how AI is being used.
- Accountability and Oversight: Mechanisms for accountability and oversight are essential to ensure that AI systems are used responsibly and ethically. This could involve independent oversight bodies, clear lines of responsibility, and mechanisms for redress in case of misuse or harm.
The Role of Policymakers, Technology Companies, and Civil Society
A multi-stakeholder approach is essential to shape the future of AI in elections. Policymakers, technology companies, and civil society all have critical roles to play.
- Policymakers: Policymakers must create a legal and regulatory framework that promotes responsible AI development and deployment in elections. This includes setting standards for data privacy, transparency, and accountability, and establishing mechanisms for oversight and enforcement.
- Technology Companies: Technology companies have a responsibility to develop AI systems that are ethical, transparent, and accountable. This includes investing in research and development of bias-detection tools, promoting data privacy, and collaborating with policymakers and civil society to ensure responsible use of their technologies.
- Civil Society: Civil society organizations play a vital role in monitoring the use of AI in elections, advocating for ethical guidelines, and educating the public about the potential risks and benefits of AI. They can also help build trust in AI systems by promoting transparency and accountability.
Potential Scenarios for the Future of AI in US Elections
The future of AI in US elections presents both challenges and opportunities. It is crucial to consider potential scenarios and prepare for them accordingly.
- Scenario 1: AI-Enhanced Democracy: In this scenario, AI is used to enhance democratic processes, making elections more accessible, efficient, and secure. For example, AI could be used to personalize voter information, improve voter registration, and detect and prevent voter fraud.
- Scenario 2: AI-Driven Disinformation: AI could be used to create and spread disinformation at an unprecedented scale, potentially undermining public trust in elections and democratic institutions. For example, AI could be used to generate fake news articles, manipulate social media algorithms, and create deepfakes.
- Scenario 3: AI-Powered Voter Suppression: AI could be used to identify and suppress specific groups of voters, potentially undermining the fairness and legitimacy of elections. For example, AI could be used to create targeted voter suppression campaigns, manipulate district boundaries, or discriminate against certain demographics.

