Oil Prices Stabilize Near $81 Amid Demand Uncertainty
Oil prices stabilize near 81 amid demand uncertainty – Oil Prices Stabilize Near $81 Amid Demand Uncertainty, a headline that reflects a complex interplay of global economic factors, supply chain dynamics, and the ever-present energy transition. The recent stabilization of oil prices near $81 per barrel, while seemingly a positive sign, is a delicate balancing act, influenced by a mix of optimistic and cautious indicators.
This article delves into the key factors driving this stability, exploring the underlying uncertainties that could disrupt the current trajectory.
The world’s dependence on oil remains substantial, and the price of this crucial commodity impacts everything from transportation costs to inflation. While the current price point might offer some relief, the road ahead remains uncertain. Factors like economic growth, geopolitical tensions, and the accelerating energy transition continue to shape the future of oil demand, making it a dynamic and unpredictable market.
Current Oil Price Situation
Oil prices have recently stabilized near the $81 per barrel mark, a significant development amidst the ongoing global economic uncertainty. This price point represents a delicate balance between supply and demand forces, with several factors influencing the current market dynamics.
Recent Trends in Oil Prices
Recent trends in oil prices have been characterized by volatility, with fluctuations driven by a complex interplay of factors. While prices have stabilized near $81 per barrel, they have exhibited notable fluctuations in recent months. For example, in early 2023, prices surged to over $85 per barrel, driven by concerns over potential supply disruptions due to geopolitical tensions and the ongoing war in Ukraine.
However, these gains were later pared back as demand concerns emerged, particularly in China, the world’s largest oil importer.
Oil prices are holding steady near $81 per barrel, but the market is grappling with uncertainty around future demand. It’s a balancing act between the global economic outlook and the impact of recent production cuts. Meanwhile, live news coverage wall street faces mixed earnings reports and anticipates fed rate decision , adding another layer of complexity to the equation.
The Fed’s decision on interest rates will likely have a significant impact on the broader market, and ultimately, on the energy sector’s trajectory.
Factors Contributing to Price Stabilization
Several factors have contributed to the stabilization of oil prices near $81 per barrel. These include:
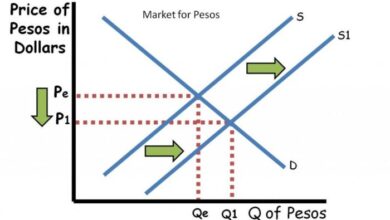
- Supply Concerns:The ongoing war in Ukraine has raised concerns about potential supply disruptions, particularly from Russia, a major oil exporter. These concerns have supported oil prices.
- Demand Outlook:The global economic outlook remains uncertain, with concerns over inflation, rising interest rates, and potential recessions. These factors could weigh on oil demand, potentially capping price gains.
- OPEC+ Production Cuts:The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies, known as OPEC+, have implemented production cuts to support oil prices. These cuts have helped to tighten global oil supplies, supporting prices.
- Strategic Petroleum Reserve Releases:In response to high oil prices, several countries, including the United States, have released oil from their strategic petroleum reserves. These releases have helped to alleviate supply concerns, but their impact on prices has been limited.
Demand Uncertainty
Demand uncertainty is a major factor influencing oil prices. It refers to the unpredictable nature of global oil consumption, which can be influenced by various economic, geopolitical, and technological factors.
Key Factors Driving Demand Uncertainty
Demand uncertainty arises from various sources, including:
- Economic Growth:Global economic growth is a significant driver of oil demand. Recessions or slowdowns in major economies can lead to decreased oil consumption as industrial activity and transportation demand decline. Conversely, robust economic growth can boost oil demand.
- Geopolitical Events:Geopolitical tensions and conflicts can disrupt oil supply chains and create uncertainty about future oil availability.
This can lead to price spikes as buyers scramble to secure supplies. For example, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine has disrupted oil exports from Russia, a major oil producer, leading to increased demand for oil from other sources.
- Energy Transition:The shift towards renewable energy sources and electric vehicles is a long-term trend that could eventually reduce oil demand.
However, the pace of this transition remains uncertain, and the potential impact on oil demand in the short to medium term is unclear.
- Government Policies:Governments can influence oil demand through policies such as fuel taxes, subsidies, and regulations on vehicle emissions.
These policies can impact consumer behavior and affect oil consumption patterns.
- Consumer Behavior:Consumer preferences and choices also play a role in oil demand. Factors such as rising fuel prices, concerns about climate change, and the availability of alternative transportation options can influence driving habits and fuel consumption.
Impact of Demand Uncertainty on Oil Prices
Demand uncertainty can have a significant impact on oil prices, leading to volatility and price swings.
- Price Volatility:When demand is uncertain, oil prices can fluctuate significantly in response to even small changes in supply or demand expectations. This volatility can make it difficult for producers and consumers to plan for the future.
- Price Spikes:Periods of high demand uncertainty can lead to price spikes as buyers rush to secure supplies, fearing shortages.
For example, the 2008 global financial crisis led to a sharp decline in oil demand, resulting in a significant drop in oil prices. However, as the economy recovered, oil demand increased, leading to a surge in prices.
- Price Depressions:Conversely, periods of low demand uncertainty can lead to price depressions as buyers are less willing to pay high prices for oil, fearing a future surplus.
For example, the COVID-19 pandemic led to a sharp decline in oil demand as travel restrictions and lockdowns were imposed globally, resulting in a significant drop in oil prices.
Comparison with Previous Periods of Uncertainty
The current demand outlook is characterized by a complex interplay of factors, including the ongoing economic recovery from the pandemic, geopolitical tensions, and the energy transition. This creates a level of uncertainty that is comparable to previous periods of economic and geopolitical turmoil.
- 2008 Global Financial Crisis:The 2008 global financial crisis led to a sharp decline in oil demand as economic activity slowed down globally. This resulted in a significant drop in oil prices, which fell from over $140 per barrel in July 2008 to below $40 per barrel in December 2008.
However, as the global economy recovered, oil demand increased, leading to a surge in prices.
- COVID-19 Pandemic:The COVID-19 pandemic led to an unprecedented decline in oil demand as travel restrictions and lockdowns were imposed globally. This resulted in a significant drop in oil prices, which fell to below $20 per barrel in April 2020.
While oil prices have stabilized near $81 per barrel, uncertainty surrounding global demand continues to cast a shadow. The recent decision by Saudi Arabia to extend its oil production cut, as reported in this article , has sparked a price surge and fueled market speculation.
This move by Saudi Arabia is likely to further complicate the global oil market, potentially impacting prices in the coming months.
As the global economy began to recover, oil demand gradually increased, leading to a rise in prices.
Global Economic Factors

The global economy plays a significant role in shaping oil demand and, consequently, oil prices. Factors like inflation, interest rates, and economic growth can have a direct impact on how much oil is consumed worldwide.
Oil prices are hovering around $81 per barrel, a sign of stability amidst lingering concerns about global demand. The market is grappling with mixed signals, particularly after the stock market’s mixed performance in August , following a record-breaking rally in July.
With economic uncertainties looming, investors are carefully watching how these factors will ultimately shape the future trajectory of oil prices.
Impact of Inflation and Interest Rates
Inflation and interest rates can influence oil prices by affecting consumer spending and investment decisions.
- High inflation can erode purchasing power, leading consumers to reduce discretionary spending, including fuel consumption. This can result in lower oil demand and potentially lower prices.
- Rising interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, impacting businesses and consumers. This can lead to reduced investment in energy-intensive industries and lower economic activity, ultimately affecting oil demand.
Impact of Economic Growth
Economic growth is closely linked to oil demand.
- Strong economic growth typically leads to increased industrial activity, transportation, and energy consumption, driving up oil demand and prices. For example, during periods of robust economic expansion, countries often see increased demand for oil as industries ramp up production and consumers engage in more travel and leisure activities.
- Conversely, economic slowdowns or recessions can significantly impact oil demand. Reduced industrial activity, lower consumer spending, and decreased travel can lead to a decline in oil consumption, potentially putting downward pressure on prices.
Impact of Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events can significantly impact oil markets, leading to price volatility and supply disruptions.
- Political instability in oil-producing regions, such as the Middle East, can disrupt production and supply chains, leading to higher prices. For instance, conflicts or sanctions in oil-rich countries can restrict oil exports, causing a shortage and driving up prices.
- Geopolitical tensions and sanctions can also impact global trade flows, leading to uncertainty in the oil market and price fluctuations. For example, trade disputes between major oil-consuming and producing nations can create disruptions in supply chains and influence market sentiment.
Supply Dynamics
The current oil price stability near $81 per barrel is influenced by a complex interplay of supply and demand factors. While demand uncertainty lingers, the global oil market is also grappling with a shifting supply landscape.
OPEC+ Role in Influencing Oil Supply
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies, collectively known as OPEC+, play a crucial role in shaping global oil supply. OPEC+ members have implemented production cuts to stabilize the market and maintain prices. Their decisions have a significant impact on the oil market, and their actions are closely watched by market participants.
Impact of Sanctions and Geopolitical Tensions on Oil Production
Sanctions imposed on Russia, a major oil producer, have disrupted global supply chains and contributed to price volatility. These sanctions have limited Russia’s ability to export oil, impacting global supply and pushing prices higher. Geopolitical tensions in regions like the Middle East also pose risks to oil production and supply, further adding to market uncertainty.
Energy Transition
The energy transition, a shift towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, is a significant factor influencing oil demand. This transition involves the adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, to replace fossil fuels like oil and gas.
The impact of this shift on oil demand is multifaceted, with both challenges and opportunities for oil producers.
Impact of Energy Transition on Oil Demand
The energy transition is expected to have a significant impact on oil demand. As renewable energy sources become more cost-effective and widely adopted, the demand for oil is projected to decrease. This decline is driven by several factors:
- Increased adoption of electric vehicles (EVs):EVs are powered by electricity, reducing the need for gasoline. As EV adoption accelerates, the demand for gasoline, a major oil product, is expected to decrease significantly.
- Growth of renewable energy sources:Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are increasingly replacing fossil fuels for electricity generation. This shift reduces the demand for oil used in power plants.
- Government policies promoting clean energy:Many governments are implementing policies to encourage the adoption of renewable energy and reduce carbon emissions. These policies, such as carbon taxes and subsidies for renewable energy projects, further contribute to the decline in oil demand.
Potential for Renewable Energy Sources to Displace Oil
Renewable energy sources have the potential to significantly displace oil in various sectors.
- Electricity generation:Solar and wind power are becoming increasingly competitive with fossil fuels for electricity generation. In some regions, they are already the cheapest source of new power generation.
- Transportation:EVs are rapidly gaining popularity, reducing the need for gasoline. As battery technology improves and EV prices decline, their market share is expected to grow significantly.
- Heating and cooling:Renewable energy sources, such as geothermal and solar thermal, can provide heating and cooling solutions, reducing reliance on oil-based heating systems.
Challenges and Opportunities for Oil Producers
The energy transition presents both challenges and opportunities for oil producers.
- Decreasing demand:The shift towards renewable energy sources poses a significant challenge to oil producers, as it leads to a decrease in demand for their products.
- Investment in renewable energy:Oil producers can mitigate the risks of declining oil demand by investing in renewable energy sources. This diversification allows them to participate in the growing renewable energy market and reduce their dependence on oil.
- Developing new technologies:Oil producers can also focus on developing new technologies, such as carbon capture and storage, to reduce the environmental impact of oil production and enhance its sustainability. This could help them maintain market share in a changing energy landscape.
Market Outlook: Oil Prices Stabilize Near 81 Amid Demand Uncertainty

The current oil price stability near $81 per barrel reflects a delicate balance between supply and demand factors. While the near-term outlook suggests continued volatility, the long-term trajectory hinges on several key factors that could influence oil prices significantly.
Short-Term Outlook
The short-term outlook for oil prices is characterized by uncertainty, primarily driven by fluctuating demand patterns. The global economic slowdown, particularly in China, could impact oil consumption. However, increased travel and industrial activity in other regions could offset some of this decline.
Moreover, OPEC+ production cuts and geopolitical tensions could further contribute to price volatility.
Long-Term Outlook
The long-term outlook for oil prices is more complex and depends on a combination of factors, including:
- Energy Transition:The global shift towards renewable energy sources, coupled with advancements in energy efficiency, is expected to reduce demand for oil in the long run. However, the pace of this transition remains uncertain, and oil will likely remain a significant energy source for several decades.
- Supply Dynamics:OPEC+ production capacity, investment in new oil fields, and technological advancements in extraction methods will influence the availability of oil. Tightening supply conditions could lead to higher prices, while increased production could exert downward pressure.
- Geopolitical Factors:Political instability, sanctions, and conflicts in oil-producing regions can disrupt supply chains and drive prices higher. The geopolitical landscape is constantly evolving, making it difficult to predict the long-term impact on oil prices.
Impact of Technological Advancements, Oil prices stabilize near 81 amid demand uncertainty
Technological advancements can significantly impact oil prices. Innovations in oil extraction, such as horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing, have increased supply and lowered production costs. Similarly, advancements in renewable energy technologies and energy storage solutions could accelerate the energy transition and reduce demand for oil.