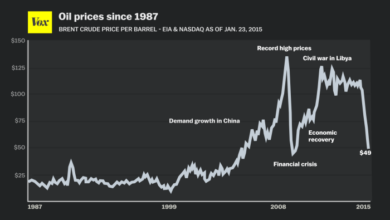
Oil Prices Drop: Challenges for OPEC as Supplies Rise
Oil prices drop challenges for opec as supplies keep growing sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. The global oil market is in a state of flux, with prices plummeting despite rising demand.
This downward trend is primarily driven by increased production from non-OPEC countries, who are now playing a more significant role in shaping the global oil landscape. As a result, OPEC, the organization of oil-exporting countries, faces a significant challenge in maintaining its influence and ensuring that prices remain at desired levels.
This situation has far-reaching implications for global economies, oil-producing nations, and geopolitical stability.
The decline in oil prices has been a major talking point in recent months, with experts and analysts scrambling to understand the driving forces behind this trend. While some argue that the drop is a temporary phenomenon, others believe that it signals a fundamental shift in the global oil market.
The increased production from non-OPEC countries, particularly the United States, has played a significant role in driving down prices. This rise in US production is a direct result of advancements in shale oil extraction technologies, which have made it more cost-effective to produce oil from previously untapped reserves.
The increased availability of oil from non-OPEC sources has effectively reduced OPEC’s influence over global oil prices, forcing the organization to re-evaluate its strategies.
Global Oil Market Dynamics
The global oil market is currently experiencing a period of volatility, with prices fluctuating significantly in recent months. This dynamic landscape is driven by a complex interplay of factors, including shifts in supply and demand, geopolitical tensions, and evolving energy policies.
Current State of Global Oil Supply and Demand
The global oil market is characterized by a delicate balance between supply and demand.
- Supply:The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) remains a significant player in global oil production, accounting for a substantial portion of global output. However, OPEC’s production capacity has been constrained by various factors, including internal disagreements among member countries and geopolitical instability in key producing regions.
Additionally, the rise of non-OPEC producers, such as the United States, has contributed to a more diversified global supply landscape.
- Demand:Global oil demand has been impacted by several factors, including economic growth, technological advancements, and government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions. The COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted global demand patterns, leading to a sharp decline in oil consumption. However, as the global economy recovers, oil demand is expected to rebound, although the pace of recovery remains uncertain.
Factors Driving the Recent Drop in Oil Prices
Several factors have contributed to the recent decline in oil prices.
The recent drop in oil prices is a significant challenge for OPEC as global supply continues to outpace demand. This situation is further complicated by factors like the ongoing war in Ukraine and the global economic slowdown. Meanwhile, in a completely different market, Chinese mutual fund houses injected 119 million amidst stock market turbulence , highlighting a strategy to stabilize markets in the face of uncertainty.
While these two situations seem unrelated, they both reflect the broader economic landscape, where volatility and unpredictable market movements are becoming increasingly common.
- Increased Production:Non-OPEC producers, particularly the United States, have significantly increased their oil production in recent years, adding to global supply and putting downward pressure on prices. The US shale oil revolution has transformed the country into a major oil producer, challenging OPEC’s traditional dominance.
- Global Economic Uncertainty:The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, coupled with geopolitical tensions and rising inflation, has created a sense of economic uncertainty, impacting global oil demand. As investors become more cautious, they may reduce their investments in oil, further contributing to price declines.
- OPEC+ Production Cuts:OPEC and its allies, known as OPEC+, have implemented production cuts in an attempt to stabilize the market and support oil prices. However, these cuts have not been enough to offset the impact of increased production from non-OPEC countries and the ongoing economic uncertainty.
Impact of Increased Production from Non-OPEC Countries
The rise of non-OPEC producers has had a significant impact on the global oil market.
- Shift in Market Power:The increased production from non-OPEC countries has reduced OPEC’s influence on global oil prices. OPEC’s ability to control supply and manipulate prices has been diminished, as non-OPEC producers have become more important players in the market.
- Price Volatility:The increased supply from non-OPEC producers has contributed to greater price volatility in the oil market. As production levels fluctuate, prices can swing dramatically, creating uncertainty for consumers and businesses.
- Strategic Implications:The rise of non-OPEC producers has significant strategic implications for global energy security. It reduces reliance on OPEC countries, potentially leading to a more balanced and diversified energy landscape.
OPEC’s Role and Challenges
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) plays a crucial role in global oil markets, influencing oil prices and supply dynamics. OPEC’s actions and decisions have significant implications for energy security, economic stability, and global trade.
OPEC’s Production Quotas and Their Impact on Oil Prices
OPEC member countries collectively agree on production quotas, aiming to control the amount of oil supplied to the global market. These quotas are determined through meetings and negotiations among member countries, considering factors such as global oil demand, economic conditions, and geopolitical considerations.
By adjusting production quotas, OPEC aims to maintain oil prices within a desired range, ensuring revenue stability for member countries and influencing global energy markets.
The oil market is facing a tough time as OPEC grapples with a glut of supply, pushing prices down. But there’s some good news on the horizon. The US stock market is starting the day on a positive note, driven by signs of cooling inflation, as you can see in this article us stock market news today wall street begins on a positive note with cooling inflation.
This could potentially lead to increased demand for energy, providing a much-needed boost to OPEC’s struggling market.
Challenges Faced by OPEC in Maintaining Oil Prices
Maintaining oil prices at desired levels presents significant challenges for OPEC.
- Non-OPEC Production:The rise of non-OPEC producers, such as the United States, has increased global oil supply, making it harder for OPEC to control prices. The US shale oil boom has significantly boosted global oil production, leading to increased competition and downward pressure on prices.
- Global Economic Fluctuations:Global economic recessions or slowdowns can significantly impact oil demand, leading to price declines. For example, the 2008 global financial crisis led to a sharp drop in oil prices as demand decreased.
- Technological Advancements:Technological advancements, such as hydraulic fracturing and horizontal drilling, have made it easier and more cost-effective to extract oil from unconventional sources, further increasing global supply and impacting OPEC’s ability to control prices.
- Geopolitical Instability:Geopolitical instability in key oil-producing regions can disrupt production and supply chains, leading to price volatility. Conflicts in the Middle East, for example, have historically impacted global oil markets.
OPEC’s Strategies for Responding to Current Market Conditions, Oil prices drop challenges for opec as supplies keep growing
OPEC has implemented various strategies to respond to the challenges it faces in maintaining oil prices.
It’s a tough time for OPEC as oil prices drop with increasing global supplies. The market is facing a perfect storm of factors, including slowing economic growth and the global energy transition. And if that wasn’t enough, even tech giants like Apple are feeling the heat, as you can see in this recent article on Apple’s stock decline amid concerns over China’s iPhone restrictions.
With such a turbulent global landscape, OPEC will need to navigate these challenges carefully to maintain stability in the energy market.
- Production Cuts:OPEC has frequently resorted to production cuts to reduce global supply and support prices. These cuts are coordinated among member countries and involve reducing individual production quotas.
- Production Agreements:OPEC has also entered into production agreements with non-OPEC producers, such as Russia, to coordinate production levels and stabilize oil prices. These agreements aim to reduce market volatility and ensure a more balanced supply-demand equation.
- Investment in Renewable Energy:Some OPEC members have begun investing in renewable energy sources, acknowledging the need to diversify their economies and reduce reliance on oil revenue. This diversification strategy aims to mitigate the long-term risks associated with declining oil demand and price volatility.
Economic and Geopolitical Implications: Oil Prices Drop Challenges For Opec As Supplies Keep Growing
The decline in oil prices has significant ramifications for global economies and international relations. While lower prices offer benefits to consumers and certain industries, they also present challenges for oil-producing nations and can trigger geopolitical tensions.
Impact on Global Economies
Lower oil prices generally have a positive impact on global economies. This is because oil is a key input in many industries, and lower prices translate to lower production costs, which can lead to:
- Increased consumer spending:Lower fuel prices leave consumers with more disposable income, stimulating demand for goods and services.
- Boost to manufacturing and transportation:Reduced energy costs can make manufacturing and transportation more efficient, leading to lower prices for goods and services.
- Economic growth:The combined effect of increased consumer spending and lower production costs can contribute to overall economic growth.
However, it’s important to note that the benefits of lower oil prices are not evenly distributed. Countries heavily reliant on oil exports, for example, can experience significant economic hardship.
Future Outlook and Potential Scenarios

Predicting the future trajectory of oil prices is a complex endeavor, influenced by a multitude of factors. While the recent drop in prices presents challenges for OPEC, the future holds both potential upswings and continued uncertainty.
Short-Term Price Fluctuations
The short-term outlook for oil prices is likely to remain volatile, influenced by several factors.
- Global Economic Growth:A slowdown in global economic growth, particularly in major economies like China and the United States, could dampen demand for oil, putting downward pressure on prices.
- OPEC+ Production Cuts:OPEC and its allies (OPEC+) have already announced production cuts to stabilize prices.
The effectiveness of these cuts will depend on adherence by member countries and the response of other producers.
- Geopolitical Events:Unforeseen geopolitical events, such as conflicts or sanctions, could significantly impact oil supply and prices. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine has already disrupted energy markets.
- Inventory Levels:Global oil inventories are currently elevated, providing a buffer against potential supply disruptions. However, if inventories continue to rise, it could signal weak demand and further pressure on prices.
Long-Term Trends and Scenarios
Over the long term, several factors will shape the future of the oil market.
- Energy Transition:The global shift towards renewable energy sources, driven by climate change concerns and technological advancements, poses a significant challenge to the long-term demand for oil. However, the transition is expected to be gradual, with oil remaining a crucial energy source for many years to come.
- Emerging Markets Demand:Rapid economic growth in emerging markets, particularly in Asia, is expected to drive demand for oil in the coming years. This growth could offset the decline in demand from developed countries.
- Technological Advancements:Technological advancements, such as improved efficiency in oil extraction and refining, could increase supply and potentially lower prices.
However, the development and deployment of these technologies may take time.
- Sustainable Oil Production:Increased focus on sustainable oil production practices, including reducing environmental impact and carbon emissions, will be crucial for the long-term viability of the oil industry.
Factors Influencing Future Oil Prices
The future of oil prices will be determined by a complex interplay of several factors.
- Supply and Demand Dynamics:The balance between global oil supply and demand will remain a key driver of prices. Factors such as OPEC production quotas, non-OPEC supply growth, and global economic growth will influence this balance.
- Geopolitical Stability:Political instability in major oil-producing regions can disrupt supply chains and lead to price volatility.
- Investment in Renewable Energy:Investments in renewable energy technologies will influence the long-term demand for oil. As renewable energy becomes more cost-competitive, it could displace oil consumption in certain sectors.
- Technological Advancements:Breakthroughs in energy storage, electric vehicles, and other technologies could further accelerate the energy transition and impact oil demand.
- Government Policies:Government policies, such as carbon taxes, subsidies for renewable energy, and regulations on oil production, can significantly influence oil prices.