Oil Market Faces Uncertainty Amid Fed Rate Hike and Tightening Supply
Oil market faces uncertainty amid fed rate hike and tightening supply. The global oil market is currently navigating a complex landscape, with rising interest rates from the Federal Reserve adding to existing pressures from tightening supply. The Fed’s recent rate hikes, aimed at curbing inflation, are expected to slow economic growth, potentially impacting oil demand.
Meanwhile, production cuts from OPEC+ and geopolitical events have further tightened the supply of crude oil, pushing prices higher.
This confluence of factors has created a volatile environment for the oil market, with prices experiencing significant fluctuations. Understanding the interplay between these forces is crucial for investors, businesses, and policymakers alike. In this analysis, we will delve into the intricate relationship between the Fed rate hike, supply constraints, and the global economic outlook, examining their potential impact on oil demand and prices.
The Fed Rate Hike and its Impact on the Oil Market: Oil Market Faces Uncertainty Amid Fed Rate Hike And Tightening Supply
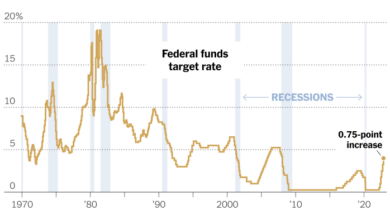
The Federal Reserve’s recent decision to raise interest rates has sent ripples through the global economy, and the oil market is no exception. This move, aimed at curbing inflation, could have significant implications for oil prices and the overall energy landscape.
The oil market is navigating a turbulent landscape, with the Fed’s interest rate hikes and supply constraints casting a shadow of uncertainty. Meanwhile, the news cycle is filled with stories of consumer product recalls, like the recent Peloton recall of 2.2 million bikes due to safety concerns.
These events, while seemingly disparate, underscore the importance of vigilance and adaptability in today’s economic climate, as both consumers and investors grapple with evolving risks and uncertainties.
Impact on Economic Outlook
The Fed’s rate hike signals a tightening of monetary policy, which can influence the overall economic outlook. Higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive for businesses and consumers, potentially leading to reduced investment and spending. This slowdown in economic activity can, in turn, affect demand for oil, as businesses and individuals may consume less energy.
Impact on Oil Demand
Higher interest rates can directly impact oil demand by influencing consumer behavior. When borrowing costs rise, individuals may choose to delay major purchases, such as new vehicles, which could decrease demand for gasoline. Additionally, businesses might postpone expansion plans or reduce production, leading to a decrease in industrial energy consumption.
The oil market is facing a perfect storm of uncertainty, with the Fed’s rate hikes threatening to dampen demand while OPEC+ production cuts tighten supply. This volatility is further amplified by global economic anxieties, like the one facing Argentina, which is currently in critical talks with the IMF to avert a looming debt crisis.
Argentina faces critical IMF talks to resolve looming debt crisis. The outcome of these negotiations could have ripple effects on the global economy, potentially further influencing the already unpredictable oil market.
Historical Comparisons
Historical data provides insights into the relationship between interest rate changes and oil prices. During periods of significant interest rate hikes, oil prices have often experienced a downward trend. For example, the Federal Reserve’s aggressive rate hikes in the early 1980s contributed to a sharp decline in oil prices.
However, it’s important to note that other factors, such as global economic conditions and geopolitical events, also play a role in determining oil prices.
Tightening Oil Supply and its Implications
The oil market is currently facing a period of tightening supply, driven by a confluence of factors, including production cuts by OPEC+ and geopolitical events. This tightening supply is expected to have a significant impact on oil prices and availability, potentially leading to higher energy costs and economic uncertainty.
The oil market is in a state of flux, with the Fed’s rate hikes and tightening supply creating a volatile landscape. It’s a reminder that navigating uncertainty is a key skill, whether it’s in the financial markets or in our personal lives.
Just like balancing your budget, maintaining good health requires a strategic approach, and that’s where resources like balancing your finances and health top tips for achieving both can be incredibly valuable. With a little planning and effort, we can find stability and success, even in unpredictable times.
OPEC+ Production Cuts
The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies, collectively known as OPEC+, have been implementing production cuts since 2020, aiming to stabilize oil prices and ensure market balance. These cuts have resulted in a significant reduction in global oil supply, contributing to the current tightening conditions.
The most recent round of cuts, announced in October 2023, involved a reduction of 2 million barrels per day, further tightening the market.
Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events, particularly the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, have also contributed to the tightening of oil supply. The war has disrupted oil production and exports from Russia, a major oil producer, and led to uncertainty in global energy markets. Western sanctions imposed on Russia have also restricted its ability to export oil, further exacerbating supply constraints.
Impact on Oil Prices and Availability
The tightening oil supply is expected to have a significant impact on oil prices and availability. As supply dwindles, demand remains relatively robust, leading to an upward pressure on prices. This could result in higher energy costs for consumers and businesses, potentially impacting inflation and economic growth.
Additionally, the reduced availability of oil could create challenges for certain industries and sectors that rely heavily on oil-based products.
Key Regions and Countries Affected, Oil market faces uncertainty amid fed rate hike and tightening supply
The supply crunch is expected to have a particularly significant impact on regions and countries heavily reliant on oil imports, such as Europe and Asia. Europe, in particular, has been seeking to reduce its dependence on Russian oil imports, which has increased demand for alternative sources.
The tightening supply could make it more challenging for Europe to secure adequate oil supplies at affordable prices. Asia, with its growing energy demand, is also vulnerable to the supply constraints, potentially facing higher energy costs and economic uncertainties.
Market Volatility and Price Fluctuations
The oil market is currently experiencing a high degree of volatility, driven by a complex interplay of factors including the Fed’s interest rate hikes, tightening supply, and geopolitical uncertainties. This volatility translates into significant price fluctuations, making it challenging for investors, businesses, and consumers to predict and manage their energy costs.
Relationship Between Fed Rate Hikes, Supply Constraints, and Price Fluctuations
The Fed’s interest rate hikes are a significant factor contributing to oil market volatility. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, making it more expensive for oil producers to finance exploration and production activities. This can lead to reduced investment and potentially lower oil supply in the long run.
Additionally, rising interest rates can strengthen the US dollar, making oil, which is priced in dollars, more expensive for buyers using other currencies. This can lead to lower demand and further price fluctuations.The relationship between tightening oil supply and price fluctuations is straightforward.
As supply decreases, prices tend to rise due to the basic principles of supply and demand. This is particularly true in the current environment where global demand for oil remains strong.
Recent Price Swings and Contributing Factors
Recent months have witnessed significant price swings in the oil market. For instance, in early 2023, oil prices surged due to supply disruptions caused by the Russia-Ukraine conflict and OPEC+ production cuts. However, prices retreated later in the year as concerns about global economic slowdown and potential demand destruction emerged.
The interplay of these factors creates a complex and dynamic environment where price fluctuations are the norm.
Global Economic Outlook and Oil Demand

The global economic outlook plays a pivotal role in shaping oil demand, as economic growth directly influences energy consumption. The projected growth rates of major economies, along with prevailing economic uncertainties and geopolitical tensions, can significantly impact oil demand.
Global Economic Growth and Oil Consumption
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) projects global economic growth to moderate to 2.9% in 2023 and 3.1% in 2024. This projected slowdown in growth is attributed to several factors, including high inflation, rising interest rates, and ongoing geopolitical tensions.
- China:The world’s second-largest economy is expected to experience a rebound in 2023, with the IMF forecasting growth of 5.2%. This growth is driven by the easing of COVID-19 restrictions and government stimulus measures. China’s economic recovery is crucial for global oil demand, as it is the world’s largest oil importer.
- United States:The US economy is projected to grow at a slower pace in 2023, with the IMF forecasting growth of 1.4%. The Federal Reserve’s aggressive interest rate hikes aim to curb inflation, but they also pose risks to economic growth.
- Eurozone:The Eurozone is expected to experience a mild recession in 2023, with the IMF forecasting a contraction of 0.6%. The war in Ukraine, energy crisis, and rising inflation are weighing heavily on the Eurozone economy.
The projected growth rates of major economies have significant implications for oil demand. Strong economic growth in China and other emerging markets will likely drive increased oil consumption. However, slower growth in the US and Europe could dampen oil demand.
Economic Uncertainties and Geopolitical Tensions
The global economy faces numerous uncertainties, including high inflation, rising interest rates, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions. These uncertainties can negatively impact oil demand by creating economic instability and discouraging investment.
- Inflation:High inflation erodes consumer purchasing power, reducing demand for discretionary goods and services, including transportation. This can lead to a decline in oil consumption.
- Interest Rates:Rising interest rates make borrowing more expensive, which can slow economic growth and reduce investment. This can also impact oil demand by making it more costly for businesses to expand operations or invest in new projects.
- Geopolitical Tensions:Geopolitical tensions, such as the war in Ukraine, can disrupt energy markets and lead to price volatility. This can create uncertainty for consumers and businesses, impacting oil demand.
The potential impact of economic uncertainties and geopolitical tensions on oil demand is complex and uncertain. These factors can create volatility in oil prices and influence investment decisions in the energy sector.
Strategies for Navigating Market Uncertainty
The current oil market is characterized by significant volatility and uncertainty, driven by factors such as the Fed’s interest rate hikes, tightening supply, and global economic headwinds. This environment presents challenges for both oil producers and consumers, demanding strategic approaches to manage risks and navigate market fluctuations.
Hedging Strategies and Risk Management
Hedging strategies are essential for oil producers and consumers to mitigate price volatility and protect their profits. These strategies involve using financial instruments to offset potential losses arising from price fluctuations.
- Futures Contracts:Oil producers can sell futures contracts to lock in a future selling price for their oil, ensuring a minimum revenue even if prices fall. Consumers can purchase futures contracts to secure a fixed purchase price, shielding them from price increases.
- Options:Options provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell oil at a specific price on or before a certain date. Producers can buy put options to protect against price declines, while consumers can buy call options to protect against price increases.
- Swaps:Swaps allow producers and consumers to exchange future cash flows based on oil prices. This can help them manage price risk by locking in a fixed price for a portion of their production or consumption.
Alternative Energy Sources and their Role in Mitigating Volatility
The rise of alternative energy sources, such as solar, wind, and biofuels, has the potential to reduce dependence on oil and mitigate market volatility.
- Renewable Energy Transition:As the adoption of renewable energy sources accelerates, demand for oil is expected to decline, potentially reducing price fluctuations and creating a more stable market.
- Energy Efficiency:Investments in energy efficiency technologies can reduce overall energy consumption, further lowering demand for oil and contributing to price stability.
- Diversification of Energy Sources:A diversified energy mix, including renewable and traditional sources, can help to buffer against price shocks in the oil market.
Market Volatility and Price Fluctuations
Market volatility and price fluctuations are inherent to the oil market. Understanding the factors driving these fluctuations is crucial for effective risk management.
- Geopolitical Events:Conflicts, sanctions, and political instability in oil-producing regions can disrupt supply and lead to price spikes.
- Economic Growth:Global economic growth and demand for energy are closely linked. Strong economic growth typically drives up oil demand, leading to higher prices.
- Supply and Demand Imbalances:Shortages or surpluses in oil supply can significantly impact prices.