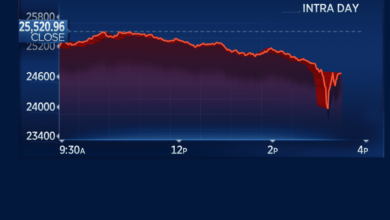
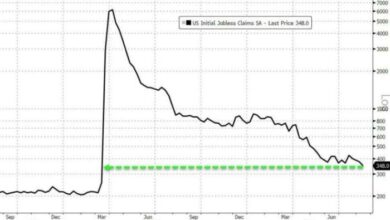
Live Market Pulse: Inflations Impact on US Stocks
Live market pulse sentiment inflation us stock market trends – The live market pulse, a constant ebb and flow of sentiment, is heavily influenced by inflation, especially in the US stock market. This delicate dance between investor optimism and economic realities paints a dynamic picture, where every data point and headline can shift the market’s direction.
We’ll explore how inflation’s impact on the US stock market unfolds, analyzing key indicators, investor strategies, and the crucial role of central banks.
From understanding the historical relationship between inflation and stock market performance to identifying sectors most sensitive to rising prices, this journey will unravel the complexities of navigating a market influenced by inflation. We’ll delve into the tools investors use to gauge sentiment, dissect common market patterns, and discuss strategies for managing risk in a volatile environment.
Understanding the Live Market Pulse
The “live market pulse” refers to the dynamic and constantly evolving sentiment surrounding the US stock market. It encompasses the collective mood and expectations of investors, traders, and market participants, which ultimately influences the direction and volatility of stock prices.
This pulse is not a static entity but rather a fluid force shaped by a multitude of factors, including economic data releases, corporate earnings announcements, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment.
The Influence of Sentiment on the Stock Market
Sentiment plays a crucial role in shaping stock market movements. When investor sentiment is optimistic, they tend to be more willing to buy stocks, leading to higher prices. Conversely, when sentiment is pessimistic, investors may sell their holdings, driving prices down.
This sentiment-driven behavior can sometimes create self-fulfilling prophecies, where a positive outlook leads to higher prices, further reinforcing optimism, and vice versa.
Real-Time Data Sources Contributing to the Live Market Pulse
Numerous real-time data sources contribute to the live market pulse, providing valuable insights into investor sentiment and market trends. These sources include:
- Social Media Sentiment Analysis:Platforms like Twitter and Reddit are analyzed to gauge public opinion on specific stocks, sectors, or the overall market. Tools and algorithms can extract sentiment from user posts and comments, offering real-time insights into market sentiment.
- News Sentiment Analysis:News articles and financial reports are scanned for positive or negative sentiment towards companies or the broader market. This analysis helps identify potential catalysts for stock price movements.
- Trading Volume and Activity:The volume of trades and the activity of buy and sell orders provide valuable insights into market momentum and sentiment. High trading volume often indicates strong interest and potential price movements.
- Options Market Activity:The options market, where investors buy and sell contracts that give them the right to buy or sell stocks at a certain price, provides insights into market expectations and volatility. High implied volatility in options contracts can signal heightened uncertainty and potential for large price swings.
- Real-Time Stock Quotes and Charts:Constant updates on stock prices, trading volume, and other market indicators offer a real-time view of market activity and sentiment. These data points can be analyzed to identify trends and potential trading opportunities.
Inflation’s Impact on the US Stock Market
Inflation, the persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services, has a complex and multifaceted relationship with the US stock market. While some sectors may thrive in an inflationary environment, others can struggle. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for investors navigating the market.
Historical Relationship Between Inflation and Stock Market Performance
The historical relationship between inflation and stock market performance is not always straightforward. There are periods when high inflation has coincided with stock market growth, and vice versa. For instance, during the 1970s, the US experienced high inflation, leading to a decline in stock market performance.
The live market pulse is a fascinating thing, constantly shifting with inflation, interest rates, and global events. Right now, the US stock market is grappling with the fallout from a slowing economy, and a recent example of this is Amazon’s stock fall despite strong revenue as cloud growth slows.
This kind of news reflects a broader trend of investors seeking more stable, less growth-dependent investments in a time of economic uncertainty.
However, in the 1980s, inflation declined, and the stock market experienced a significant bull run.
The impact of inflation on stock market performance can be influenced by factors such as interest rates, economic growth, and investor sentiment.
Sectors Sensitive to Inflation
Certain sectors of the economy are more sensitive to inflationary pressures than others. These sectors are often characterized by high input costs or a strong correlation with consumer spending.
The live market pulse is a constant ebb and flow, driven by factors like inflation and consumer sentiment. It’s crucial to stay informed about US stock market trends, but it’s also wise to manage your personal finances, especially credit debt.
Check out credit debt management tips strategies examples to gain control over your finances. A solid financial foundation can help you weather any market storm and make smart investment decisions.
Sectors Sensitive to Inflation
- Energy:As energy prices rise, energy companies often see increased profits, but consumers may reduce their spending on other goods and services. This can have a ripple effect on the broader economy.
- Materials:Companies in the materials sector, which produce raw materials like metals and chemicals, are directly impacted by inflation. As input costs rise, these companies may pass on the increased costs to consumers, potentially leading to higher prices and reduced demand.
- Consumer Discretionary:This sector includes companies that sell non-essential goods and services, such as automobiles, electronics, and restaurants. Consumer spending on these goods and services is often sensitive to inflation, as consumers may cut back on discretionary purchases when prices rise.
- Financials:Financial institutions are affected by inflation through interest rate changes. Rising interest rates can increase the cost of borrowing for banks, which can impact their profitability.
Investor Reactions to Inflation
Investors react to inflationary pressures in various ways. Some may attempt to hedge against inflation by investing in assets that are expected to appreciate in value, such as commodities or real estate. Others may seek out companies with strong pricing power, which can pass on rising costs to consumers.
Investors should carefully consider the impact of inflation on their investment portfolios and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Key Indicators and Sentiment Gauges
Understanding market sentiment is crucial for investors as it offers insights into the overall direction of the stock market. Investors use various economic indicators and sentiment gauges to assess the health of the economy and anticipate potential market trends.
Key Economic Indicators
These indicators provide valuable insights into the current state of the economy and can be used to forecast future market performance.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP):GDP is the total value of goods and services produced in a country. A strong GDP growth rate generally indicates a healthy economy and supports stock market growth.
- Inflation Rate:Inflation measures the rate at which prices for goods and services rise. High inflation can erode purchasing power and negatively impact corporate profits, potentially leading to stock market declines.
- Unemployment Rate:This indicator measures the percentage of the workforce that is unemployed. A low unemployment rate indicates a strong economy, boosting consumer spending and supporting stock market growth.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI):CPI measures the average change in prices paid by urban consumers for a basket of consumer goods and services. A rising CPI suggests inflation and can impact stock market performance.
- Interest Rates:Interest rates set by the Federal Reserve influence borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. Higher interest rates can slow economic growth and negatively impact stock market valuations.
- Retail Sales:Retail sales data reflects consumer spending patterns, offering insights into the health of the economy. Strong retail sales suggest robust consumer confidence and support stock market growth.
Consumer Confidence Surveys
Consumer confidence surveys provide valuable insights into consumer sentiment, which can be a leading indicator of economic activity and stock market performance. These surveys gauge consumer attitudes toward the economy, their willingness to spend, and their expectations for the future.
- The Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index:This index measures consumer confidence based on surveys regarding current economic conditions, future expectations, and the labor market. A high index reading indicates strong consumer confidence, which can boost economic growth and support stock market performance.
- The University of Michigan Consumer Sentiment Index:This index measures consumer sentiment based on surveys regarding current economic conditions, future expectations, and personal finances. A high index reading indicates strong consumer confidence, which can boost economic growth and support stock market performance.
Market Trends and Patterns
The stock market, a complex ecosystem driven by a multitude of factors, exhibits distinct patterns during periods of high inflation. Understanding these patterns is crucial for investors to navigate the market effectively and make informed decisions.
Inflation’s Impact on Stock Market Trends
Inflation, a persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services, significantly influences stock market trends. As inflation rises, the purchasing power of money declines, leading to higher interest rates and increased borrowing costs for businesses. This can negatively impact corporate profits and economic growth, potentially causing a decline in stock prices.
Inflation’s impact on the stock market can be summarized as follows:
Higher Interest Rates Inflation often leads to higher interest rates, making it more expensive for companies to borrow money. This can reduce investment and slow economic growth, potentially impacting stock prices.
Reduced Consumer Spending As prices rise, consumers may have less disposable income, leading to reduced spending. This can hurt businesses and impact their stock prices.
Increased Uncertainty High inflation can create uncertainty in the economy, making it difficult for businesses to plan and invest. This uncertainty can also make investors hesitant to invest in the stock market.
Geopolitical Events and Market Trends
Geopolitical events, such as wars, trade disputes, and political instability, can have a profound impact on market trends. These events often create uncertainty and volatility, affecting investor sentiment and market direction.
For example, the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022 caused significant volatility in the stock market, as investors reacted to the geopolitical uncertainty and potential economic consequences.
Technical Analysis and Market Trends
Technical analysis is a method of analyzing past market data, such as price charts and trading volume, to identify patterns and predict future price movements. This approach focuses on the supply and demand forces driving market trends and utilizes various indicators and tools to identify potential buy and sell signals.
Technical analysis can be useful for identifying market trends, but it’s important to note that it’s not foolproof. Market conditions can change rapidly, and technical indicators can sometimes provide misleading signals.
Investor Strategies and Portfolio Management
![]()
Navigating an inflationary environment requires a strategic approach to portfolio management. Investors need to adapt their strategies to preserve capital and potentially generate returns in the face of rising prices. Understanding how inflation impacts asset classes and adopting suitable strategies can help investors weather the storm and potentially thrive in this dynamic market.
Inflation-Resilient Investment Strategies
- Value Stocks:These stocks are typically undervalued by the market and offer potential for growth, particularly in an inflationary environment. Value stocks often operate in industries with pricing power, allowing them to pass on higher costs to consumers. Examples include companies in the energy, materials, and financials sectors.
- Real Estate:Real estate can serve as a hedge against inflation. As prices rise, the value of real estate assets tends to increase as well. Investing in rental properties can provide a steady stream of income, which can help offset the effects of inflation.
- Commodities:Commodities, such as gold and oil, can act as a store of value during periods of high inflation. Gold has historically been a safe haven asset, while oil prices tend to rise with inflation due to increased demand for energy.
- Inflation-Linked Bonds:These bonds offer a return that is tied to inflation, providing a hedge against rising prices. The principal and interest payments adjust with inflation, protecting investors from erosion of purchasing power.
- Dividend-Paying Stocks:Companies that pay dividends can provide a stream of income that can help offset the effects of inflation. Dividend stocks are typically mature companies with a history of profitability and a commitment to shareholder returns.
Diversification and Portfolio Risk Management
Diversification is a crucial element of portfolio management, particularly during periods of market volatility. Spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographies helps reduce overall risk.
- Asset Allocation:A well-diversified portfolio should allocate assets across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities. This helps to reduce the impact of any single asset class underperforming.
- Sector Diversification:Investing in a variety of sectors can help mitigate risk. For example, a portfolio might include investments in technology, healthcare, energy, and consumer staples. This diversification helps to balance out potential losses in one sector with gains in another.
- Geographic Diversification:Investing in companies or assets located in different countries can help reduce exposure to specific economic or political risks. This can help to mitigate the impact of events in one region on the overall portfolio.
Portfolio Adjustments to Mitigate Inflation Risks, Live market pulse sentiment inflation us stock market trends
Investors can take several steps to adjust their portfolios to mitigate inflation risks.
- Increase Exposure to Inflation-Resistant Assets:This could involve increasing allocations to value stocks, real estate, commodities, or inflation-linked bonds. These assets have historically performed well during periods of inflation.
- Reduce Exposure to Growth Stocks:Growth stocks are typically companies with high growth potential, but they can be vulnerable to inflation. As interest rates rise, the value of these stocks can decline. Investors may consider reducing their exposure to these stocks and reallocating to more value-oriented investments.
- Consider Short-Term Investments:Short-term investments, such as money market accounts or certificates of deposit, can provide a safe haven for cash during periods of inflation. While returns may be modest, these investments offer stability and liquidity.
- Rebalance Regularly:Inflation can impact asset prices and valuations, making it crucial to rebalance the portfolio regularly. Rebalancing involves adjusting asset allocations to maintain the desired risk profile and ensure that the portfolio remains aligned with investment goals.
Market Volatility and Risk Management: Live Market Pulse Sentiment Inflation Us Stock Market Trends

Market volatility is a natural characteristic of financial markets, but it can be amplified during periods of inflation. Understanding the factors that contribute to market volatility and implementing effective risk management strategies are crucial for investors navigating these turbulent times.
The live market pulse is a constant dance of sentiment, inflation, and stock market trends. It’s a rollercoaster ride that can leave even the most seasoned investor feeling dizzy. Sometimes, it’s nice to take a break from the financial frenzy and dream about hitting the jackpot, which is why I found understanding mega millions tips to increase your chances of winning so fascinating.
While the odds of winning are slim, it’s a fun exercise in probability and a reminder that even in the unpredictable world of finance, a little luck can go a long way. But back to reality, the live market pulse continues to churn, demanding our attention and forcing us to navigate the ever-shifting landscape of economic forces.
Factors Contributing to Market Volatility During Inflation
Inflation can create uncertainty in the market, leading to heightened volatility. Here are some key factors that contribute to this phenomenon:
- Rising Interest Rates:Central banks often raise interest rates to combat inflation, making borrowing more expensive for businesses and consumers. This can slow economic growth and lead to stock market declines.
- Uncertainty About Inflation Trajectory:When inflation is high and volatile, it becomes difficult for investors to predict future earnings and valuations, leading to increased market uncertainty and volatility.
- Erosion of Purchasing Power:Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, making investments less attractive and leading to a potential flight from equities.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:Inflation can be exacerbated by supply chain disruptions, which can lead to shortages and higher prices, further increasing market volatility.
- Geopolitical Events:Global events such as wars, trade tensions, and political instability can contribute to inflation and market volatility.
Strategies for Managing Risk in a Volatile Market
Effective risk management is essential for protecting portfolio value during periods of high volatility. Here are some strategies investors can consider:
- Diversification:Spreading investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographies can help reduce portfolio risk. Diversification can help mitigate losses in one part of the portfolio by offsetting gains in another.
- Rebalancing:Regularly rebalancing the portfolio to maintain the desired asset allocation can help control risk. Rebalancing involves selling assets that have outperformed and buying those that have underperformed, bringing the portfolio back to its target allocation.
- Defensive Investing:Shifting towards investments considered more defensive, such as high-quality bonds, consumer staples, and healthcare, can provide some protection during market downturns. These sectors are generally less affected by economic cycles.
- Short-Term Investments:For investors with a short-term horizon, considering liquid investments such as money market accounts or short-term bonds can provide a safe haven during periods of market volatility.
- Investment Horizon:Maintaining a long-term investment horizon can help weather market fluctuations. Short-term volatility is less relevant for investors focused on long-term goals.
The Role of Hedging in Protecting Portfolio Value
Hedging is a risk management strategy that involves taking a position in an asset that offsets potential losses in another asset. For example, an investor holding stocks might hedge their portfolio by buying put options, which give them the right to sell stocks at a specific price.
This strategy can help protect against potential downside risk in the stock market.
“Hedging is a risk management strategy that involves taking a position in an asset that offsets potential losses in another asset.”
Hedging can be a valuable tool for managing risk during periods of market volatility, but it’s important to understand the costs and complexities involved. It’s essential to consult with a financial advisor to determine if hedging is appropriate for your individual circumstances.
The Role of Central Banks
Central banks play a pivotal role in managing inflation and influencing the overall economy, including the stock market. The Federal Reserve (Fed), the central bank of the United States, employs various monetary policy tools to achieve its inflation and economic growth targets.
The Federal Reserve and Inflation Management
The Fed’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which translates to controlling inflation. The Fed aims to keep inflation at a target rate, typically around 2%. When inflation rises above the target, the Fed takes steps to cool down the economy and curb inflation.
Conversely, when inflation is too low, the Fed may stimulate economic activity to boost inflation.
Impact of Monetary Policy Decisions on the Stock Market
The Fed’s monetary policy decisions significantly impact the stock market.
Interest Rate Adjustments
- Interest Rate Hikes: When the Fed raises interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive for businesses and consumers. This can slow down economic growth, reduce corporate profits, and lead to lower stock prices.
- Interest Rate Cuts: Conversely, when the Fed lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging businesses to invest and consumers to spend. This can stimulate economic growth, boost corporate profits, and drive up stock prices.
Quantitative Easing
- Quantitative Easing (QE): During periods of economic crisis, the Fed may implement QE, a policy that involves buying government bonds and other securities to inject liquidity into the financial system. This can lower interest rates, boost lending, and support economic growth.
QE can also lead to higher stock prices as investors seek higher returns in a low-interest-rate environment.
Potential Consequences of Different Monetary Policy Approaches
The Fed’s monetary policy decisions can have various consequences for the stock market, depending on the approach taken.
Tightening Monetary Policy
- Tightening Monetary Policy: When the Fed tightens monetary policy, it can lead to a slowdown in economic growth, lower corporate profits, and a decline in stock prices. This can also increase the risk of a recession.
Loosening Monetary Policy
- Loosening Monetary Policy: Conversely, loosening monetary policy can stimulate economic growth, boost corporate profits, and drive up stock prices. However, it can also lead to higher inflation.
Future Outlook and Predictions
Predicting the future of the stock market is a complex endeavor, influenced by a multitude of factors. However, by analyzing current economic conditions and considering potential scenarios, we can gain insights into potential market trends.
Factors Influencing Future Market Trends
The future trajectory of the stock market is heavily influenced by various factors, including economic growth, inflation, interest rates, geopolitical events, and investor sentiment.
- Economic Growth:A robust economy with strong job creation and consumer spending typically supports stock market growth. However, economic slowdowns or recessions can lead to market declines.
- Inflation:High inflation erodes purchasing power and can lead to increased interest rates, potentially impacting corporate profits and stock valuations. Conversely, low inflation can support economic growth and market stability.
- Interest Rates:Rising interest rates can make borrowing more expensive for businesses and consumers, potentially slowing economic growth and impacting stock valuations. Conversely, low interest rates can stimulate borrowing and investment, supporting market growth.
- Geopolitical Events:Global events such as wars, trade disputes, and political instability can create uncertainty and volatility in the market. These events can impact investor confidence and lead to market fluctuations.
- Investor Sentiment:Market sentiment, driven by investor psychology and expectations, can significantly influence stock prices. Positive sentiment can lead to market rallies, while negative sentiment can trigger declines.
Potential Market Scenarios
Based on current economic conditions and historical trends, several potential scenarios for future market performance can be considered.
- Scenario 1: Continued Economic Growth:If the economy continues to grow at a healthy pace, with moderate inflation and stable interest rates, the stock market is likely to continue its upward trend. However, valuations may become stretched, leading to potential corrections.
- Scenario 2: Economic Slowdown:If the economy experiences a slowdown, with declining growth and rising inflation, the stock market could experience a correction or even a bear market. Investors may become more risk-averse, leading to lower stock prices.
- Scenario 3: Increased Volatility:Geopolitical events, unexpected economic shocks, or policy changes can lead to increased market volatility. Investors may experience periods of both gains and losses, making portfolio management more challenging.
Key Predictions
Based on current economic conditions and expert analysis, several key predictions can be made about the future of the stock market:
- Continued Growth:Many analysts predict continued economic growth in the coming years, albeit at a slower pace than in recent years. This could support continued stock market gains, but with potential for volatility.
- Inflationary Pressures:Inflation is expected to remain elevated in the short term, but could moderate over time as supply chain disruptions ease and demand cools. This could lead to higher interest rates, potentially impacting stock valuations.
- Interest Rate Hikes:Central banks are expected to continue raising interest rates to combat inflation. This could lead to slower economic growth and potentially impact stock market performance.
- Geopolitical Uncertainty:Geopolitical risks remain elevated, with ongoing conflicts and tensions creating uncertainty for investors. This could lead to market volatility and impact investor confidence.