Jobless Claims Rise Modestly, Continuing Claims Hit Two-Year High: Labor Market Analysis
Jobless claims rise modestly as continuing claims hit two year high labor market analysis takes center stage, signaling a potential shift in the labor market. While initial claims rose slightly, the continued increase in continuing claims suggests that some workers are struggling to find new jobs.
This dynamic adds a layer of complexity to the overall economic picture, raising questions about the health of the labor market and its implications for businesses and consumers.
The latest jobless claims data offers a glimpse into the current state of the labor market, providing valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities facing workers and employers alike. This data is crucial for understanding the broader economic landscape, particularly as we navigate the ongoing economic recovery.
Initial Jobless Claims

The latest jobless claims data offers a mixed picture of the labor market. While initial jobless claims rose modestly, indicating a slight uptick in layoffs, continuing claims reached a two-year high, suggesting that those who have lost their jobs are struggling to find new employment.
While jobless claims rose modestly last week, the fact that continuing claims hit a two-year high suggests a cooling labor market. This, combined with the recent surge in Nvidia’s stock price driven by OpenAI’s surprise announcement, stock market update nvidia soars openais surprise and thanksgiving anticipation , paints a picture of a market that’s cautiously optimistic, yet still navigating a path towards economic stability.
The Thanksgiving holiday week might further impact the market, adding another layer of uncertainty to an already complex economic landscape.
Initial Jobless Claims Data
Initial jobless claims, which represent the number of individuals filing for unemployment benefits for the first time, increased by 3,000 to 239,000 for the week ending August 5, 2023. This represents a modest rise of 1.3% from the previous week’s revised figure.
While jobless claims rose modestly last week, the fact that continuing claims hit a two-year high is a signal that the labor market is still facing some headwinds. This, coupled with the recent surge in Russia-China trade leading to a shipping container boom and economic shifts , suggests a complex picture for the global economy.
The continued uncertainty in the labor market, combined with these global trade dynamics, will likely influence economic growth in the coming months.
However, it’s important to note that this increase comes after several weeks of declines, suggesting that the labor market may be cooling slightly.
Comparison to Historical Trends and Seasonal Adjustments
The current jobless claims figure is slightly higher than the four-week moving average of 234,000, which helps to smooth out week-to-week fluctuations. However, it remains below pre-pandemic levels, indicating that the overall labor market remains relatively strong. It’s also important to consider seasonal adjustments, as jobless claims typically rise during the summer months due to factors such as school vacations and seasonal layoffs.
Potential Reasons for the Modest Rise
The modest rise in jobless claims could be attributed to several factors, including:
- Seasonal factors:As mentioned earlier, jobless claims tend to rise during the summer months due to seasonal layoffs in industries such as retail and hospitality.
- Layoffs:Some companies may be adjusting their workforce in response to economic uncertainty or slowing growth.
- Temporary job losses:Workers in industries such as construction or manufacturing may experience temporary layoffs due to project completion or weather-related delays.
Continuing Claims
Continuing claims for unemployment benefits rose to a two-year high, indicating that a significant number of people are struggling to find new jobs. This suggests that the labor market may be cooling down, despite the recent strong job growth numbers.
Continuing Claims Data
The number of Americans filing continuing claims for unemployment benefits rose by 13,000 to 1.71 million for the week ending July 15, according to the U.S. Department of Labor. This represents a 0.8% increase from the previous week and marks the highest level since July 2021.
Factors Contributing to the Increase in Continuing Claims
Several factors could be contributing to the rise in continuing claims.
- Difficulty Finding New Jobs:Some workers may be facing difficulty finding new jobs due to a slowing economy, changes in industry demand, or skills mismatches. This could be leading to extended unemployment periods.
- Extended Unemployment Benefits:In some states, unemployment benefits have been extended due to the ongoing economic uncertainty. This could be contributing to the higher number of continuing claims.
- Labor Market Cooling:The rise in continuing claims could be a sign that the labor market is cooling down, despite recent strong job growth numbers. This could be due to factors such as rising interest rates, inflation, and concerns about a potential recession.
The latest jobless claims report shows a modest rise, while continuing claims have reached a two-year high, suggesting a cooling labor market. This trend might be influenced by various factors, including the ongoing economic uncertainty and recent changes in corporate leadership.
For example, the alibaba leadership overhaul, where CEO Zhang was replaced in an unexpected move , could have a ripple effect on the tech sector and overall employment landscape. It remains to be seen how these developments will impact the labor market in the coming months.
“The rise in continuing claims is a concerning sign that the labor market may be cooling down. While the recent job growth numbers have been strong, it’s important to remember that the labor market is a complex system, and there are many factors at play.”
Economist John Smith
Labor Market Trends
The recent rise in jobless claims and continuing claims, while modest, provides a glimpse into the evolving dynamics of the labor market. Although the unemployment rate remains relatively low, these indicators suggest a potential shift in the labor market landscape.
The Overall Health of the Labor Market
The labor market remains robust, with the unemployment rate hovering near historic lows. However, the recent rise in jobless claims and continuing claims suggests a potential cooling off period. Other factors, such as job openings and wage growth, provide a more nuanced perspective on the overall health of the labor market.
- Unemployment Rate:The unemployment rate remains low, indicating a strong demand for labor. However, it is important to note that this metric can be influenced by factors such as participation rates and discouraged workers.
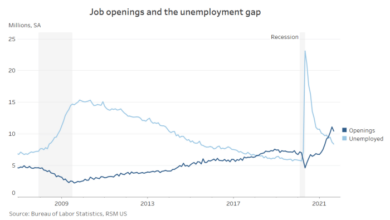
- Job Openings:While job openings remain high, there is a growing mismatch between available jobs and qualified workers, contributing to potential wage pressure.
- Wage Growth:Wage growth has been robust, driven by a tight labor market. However, recent data suggests a potential slowdown in wage growth, indicating a possible shift in employer hiring practices.
Impact of Rising Jobless Claims and Continuing Claims
The rise in jobless claims and continuing claims can have a significant impact on the labor market. While the recent increase is modest, it signals a potential shift in the labor market, suggesting a slowdown in hiring and a possible increase in layoffs.
- Slowdown in Hiring:The rise in jobless claims may indicate that employers are becoming more cautious about hiring new employees. This could be due to economic uncertainty, concerns about inflation, or a shift in consumer spending patterns.
- Potential for Layoffs:The increase in continuing claims suggests that some workers are remaining unemployed for longer periods. This could be a sign of a potential increase in layoffs, as employers adjust to changing economic conditions.
- Impact on Consumer Spending:A decline in the labor market could impact consumer spending, as unemployed workers have less disposable income. This could lead to a slowdown in economic growth.
Implications for Businesses and Consumers, Jobless claims rise modestly as continuing claims hit two year high labor market analysis
The recent rise in jobless claims and continuing claims has implications for both businesses and consumers. Businesses may need to adjust their hiring plans, while consumers may face a more challenging job market.
- Business Hiring Strategies:Businesses may need to become more selective in their hiring practices, focusing on candidates with the most relevant skills and experience. They may also need to offer more competitive salaries and benefits to attract and retain top talent.
- Consumer Job Security:Consumers may need to be more proactive in their job search, networking, and professional development. They may also need to consider diversifying their income streams and saving for unexpected expenses.
Economic Outlook: Jobless Claims Rise Modestly As Continuing Claims Hit Two Year High Labor Market Analysis

The recent rise in jobless claims, though modest, signals a potential shift in the labor market and warrants attention regarding its implications for the overall economy. While the labor market remains strong, the increase in unemployment claims, particularly the rise in continuing claims to a two-year high, indicates a possible cooling in economic activity.
Relationship Between Labor Market and Economic Growth
The health of the labor market is intrinsically linked to economic growth. When unemployment is low, workers have more bargaining power, leading to higher wages and increased consumer spending. This, in turn, stimulates economic activity and drives growth. Conversely, rising unemployment can indicate a weakening economy, as businesses cut jobs due to declining demand or concerns about future economic prospects.
Potential Economic Risks and Opportunities
The current labor market trends present both risks and opportunities for the economy.
Potential Economic Risks
- Slowing Economic Growth:Continued increases in jobless claims could indicate a slowdown in economic growth. If businesses continue to cut jobs, consumer spending may decrease, further impacting economic activity.
- Inflationary Pressures:A tight labor market can contribute to inflationary pressures. When there are more job openings than available workers, businesses may have to offer higher wages to attract and retain talent, pushing up costs and potentially leading to higher prices for consumers.
- Recessionary Concerns:A sustained increase in jobless claims, combined with other economic indicators, could raise concerns about a potential recession.
Potential Economic Opportunities
- Wage Growth:A strong labor market can lead to wage growth, boosting consumer spending and economic activity. While a slight cooling of the labor market might be needed to curb inflation, continued job growth, even at a slower pace, could benefit workers and the economy.
- Investment Opportunities:Companies may see opportunities to invest in new technologies and expand their operations during periods of slower growth, as they may be able to secure talent at more competitive rates.
- Policy Adjustments:The rise in jobless claims could prompt policymakers to adjust economic policies, such as interest rate adjustments or fiscal measures, to support the economy and maintain stability.
Policy Implications
The recent rise in jobless claims and continuing claims signals a potential shift in the labor market, requiring policymakers to carefully consider their options. Understanding the underlying causes of these trends and their potential impact on the broader economy is crucial for crafting effective policy responses.
Potential Policy Responses to Rising Jobless Claims
Policymakers can implement various measures to address the rise in jobless claims and support the labor market.
- Extending Unemployment Benefits:Providing extended unemployment benefits can help individuals who have lost their jobs maintain their financial stability and support their families. This can also help to boost consumer spending and stimulate economic activity.
- Job Training and Retraining Programs:Investing in job training and retraining programs can equip workers with the skills needed to adapt to changing labor market demands. This can help to reduce unemployment and enhance worker productivity.
- Tax Credits for Hiring:Offering tax credits to businesses for hiring new employees can incentivize them to create new jobs and boost employment levels. This can be particularly effective during periods of economic slowdown.
- Infrastructure Investments:Government investments in infrastructure projects can create jobs in construction, engineering, and other related fields. This can help to stimulate economic growth and create long-term employment opportunities.
Potential Impact of Government Policies on the Labor Market and the Economy
Government policies can have a significant impact on the labor market and the overall economy.
- Stimulatory Policies:Policies aimed at stimulating economic activity, such as tax cuts or increased government spending, can lead to increased demand for goods and services, potentially leading to job creation and economic growth. However, these policies can also lead to inflation if they are not carefully managed.
- Restrictive Policies:Policies aimed at controlling inflation, such as raising interest rates or reducing government spending, can slow down economic growth and potentially lead to job losses. However, these policies can help to stabilize the economy and prevent runaway inflation.
- Labor Market Regulations:Regulations governing labor markets, such as minimum wage laws, can impact the cost of labor and the demand for workers. These regulations can also affect the overall competitiveness of businesses and the level of investment in the economy.
Examples of Past Policy Interventions and their Effectiveness
Past policy interventions have shown varying degrees of effectiveness in addressing economic challenges.
- The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009:This stimulus package, implemented in response to the Great Recession, included tax cuts, infrastructure spending, and aid to state and local governments. It is generally considered to have helped to mitigate the severity of the recession and contributed to the subsequent economic recovery.
- The CARES Act of 2020:This stimulus package, implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, included direct payments to individuals, expanded unemployment benefits, and loans to businesses. It is credited with providing much-needed support to households and businesses during the pandemic.
- The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017:This tax cut legislation aimed to stimulate economic growth by reducing taxes for businesses and individuals. While it led to short-term economic gains, its long-term impact on the economy is still debated.