Jobless Claims Rise, But Layoffs Remain Low: Labor Market Resilience Amidst Interest Rates
Jobless claims inch up but layoffs remain historically low labor market resilience amidst rising interest rates – Jobless claims inch up but layoffs remain historically low, showcasing the resilience of the labor market even amidst rising interest rates. This intriguing paradox raises questions about the current state of the economy and its impact on employment. While initial jobless claims have seen a recent uptick, the overall number of layoffs remains remarkably low, suggesting a strong underlying demand for workers and a robust business environment.
The Federal Reserve’s efforts to combat inflation through interest rate hikes have undoubtedly impacted borrowing costs and investment decisions, but the labor market seems to be holding its own. This begs the question: how long can this resilience persist, and what are the potential implications for the future of the workforce?
Several factors contribute to this unexpected resilience. The strong consumer demand, fueled by pent-up savings and a desire for goods and services after pandemic restrictions eased, has sustained businesses and bolstered employment. Furthermore, ongoing labor shortages across various industries have forced companies to retain their workforce, even in the face of rising costs.
These shortages stem from a confluence of factors, including aging demographics, a mismatch between available skills and employer needs, and a reluctance among some workers to return to pre-pandemic employment levels.
Layoffs Remain Historically Low: Jobless Claims Inch Up But Layoffs Remain Historically Low Labor Market Resilience Amidst Rising Interest Rates
Despite rising interest rates and concerns about a potential recession, the labor market continues to show resilience, with layoffs remaining historically low. This suggests that businesses are still confident in their future prospects and are hesitant to let go of valuable employees.
It’s fascinating to see how the labor market continues to show resilience despite rising interest rates. While jobless claims have ticked up slightly, layoffs remain historically low, suggesting a strong underlying economy. This resilience is reflected in the real estate market, which is still seeing strong demand in many areas.
To get a better understanding of the regional variations, check out this comprehensive state-by-state analysis of residential and commercial properties exploring real estate in united states state by state analysis residential commercial properties. Understanding these trends can be key for investors and homebuyers alike, as it helps to navigate the complex interplay of economic forces and real estate market dynamics.
Reasons for Low Layoff Rates
Several factors contribute to the current low layoff rates, including:
- Strong Consumer Demand:The post-pandemic recovery has seen a surge in consumer spending, driving demand for goods and services. This strong demand has supported businesses and kept them from resorting to layoffs.
- Robust Business Investment:Businesses have been investing heavily in expansion and new technologies, further contributing to job creation and limiting the need for layoffs. This investment is fueled by strong corporate profits and access to capital.
- Ongoing Labor Shortages:The labor market remains tight, with many employers struggling to find qualified workers. This shortage gives workers more bargaining power and makes employers less likely to lay off employees, as replacing them could be challenging.
Impact of Low Layoff Rates on the Labor Market
The low layoff rates have a significant impact on the overall labor market, including:
- Wage Growth:With low unemployment and a tight labor market, workers have more leverage to negotiate higher wages. This has led to increased wage growth, particularly for low-wage workers.
- Job Security:The low layoff rates provide workers with a sense of job security, leading to increased confidence and stability in the workforce.
- Worker Confidence:Low layoff rates contribute to a positive outlook for workers, boosting their confidence and willingness to spend, further stimulating the economy.
Labor Market Resilience

Despite rising interest rates, the labor market has shown remarkable resilience. This suggests that the economy is not as vulnerable as some might have predicted.
The recent uptick in jobless claims, while concerning, doesn’t paint the whole picture. Layoffs remain historically low, demonstrating the labor market’s resilience even amidst rising interest rates. This stability might be attracting interest from global players, as evidenced by Lufthansa’s CEO stating that discussions about a potential takeover of Portugal’s TAP are premature.
It’s clear that airlines are keeping a close eye on the global economic landscape, looking for opportunities in a market that remains relatively strong despite the recent challenges.
Factors Contributing to Labor Market Resilience
The resilience of the labor market can be attributed to several factors:
- Strong Consumer Demand:Consumers continue to spend, fueled by pent-up demand from the pandemic and a robust savings rate. This sustained demand keeps businesses busy and supports employment growth.
- Tight Labor Market:The labor market remains tight, with a low unemployment rate and a high number of job openings. This gives workers bargaining power and encourages businesses to retain their employees.
- Strong Business Investment:Businesses are still investing in new equipment, technology, and expansion, contributing to job creation and economic growth.
- Government Support:Government programs, such as unemployment benefits and infrastructure spending, have helped to cushion the impact of rising interest rates and support employment.
Impact of Rising Interest Rates on Businesses and Employment
Rising interest rates can have a mixed impact on businesses and employment.
It’s fascinating to see how the labor market continues to defy expectations. Jobless claims are inching up, but layoffs remain historically low, suggesting a surprising resilience amidst rising interest rates. This stability is even more remarkable when you consider the global economic shifts unfolding, like the surge in Russia-China trade that’s leading to a shipping container boom.
It seems the US economy is weathering these storms better than anticipated, at least for now.
- Investment Decisions:Higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive, potentially discouraging businesses from investing in expansion or new projects. This could lead to slower job growth in the long term.
- Hiring Plans:Businesses may become more cautious about hiring new employees as they face higher borrowing costs and uncertainty about future economic conditions.
- Consumer Spending:Rising interest rates can lead to higher borrowing costs for consumers, potentially reducing their disposable income and dampening consumer spending. This could negatively impact businesses that rely heavily on consumer spending.
Comparison to Previous Periods of Economic Uncertainty, Jobless claims inch up but layoffs remain historically low labor market resilience amidst rising interest rates
While the current labor market resilience is notable, it’s important to compare it to previous periods of economic uncertainty.
- The Great Recession (2008-2009):The labor market experienced a significant downturn during the Great Recession, with high unemployment and widespread layoffs. This was largely due to a collapse in the housing market and a subsequent financial crisis.
- The COVID-19 Pandemic (2020-2021):The pandemic led to a sharp decline in economic activity and a surge in unemployment. However, the labor market recovered relatively quickly due to government stimulus measures and pent-up demand.
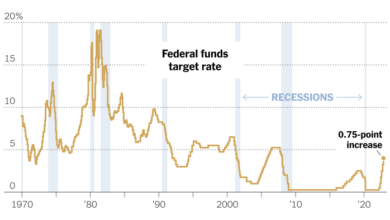
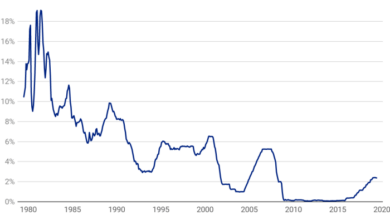
Rising Interest Rates
The Federal Reserve has been aggressively raising interest rates in recent months, marking a significant shift in monetary policy. This move comes as inflation remains stubbornly high, prompting the central bank to take action to cool the economy and bring inflation back down to its 2% target.The Federal Reserve’s primary goal in raising interest rates is to curb inflation.
By increasing the cost of borrowing, the Fed aims to reduce consumer spending and business investment, ultimately slowing down economic growth and putting downward pressure on prices.
Impact of Rising Interest Rates on the Labor Market
Rising interest rates can have a significant impact on the labor market, both directly and indirectly. Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs for businesses, making it more expensive to invest in new projects, hire new employees, or expand operations. This can lead to slower hiring growth and potentially even layoffs in certain sectors.
Higher interest rates can also affect consumer spending. As borrowing becomes more expensive, consumers may reduce their spending on discretionary items, impacting industries like retail and hospitality. This can lead to slower job growth in these sectors.The impact of rising interest rates on the labor market is complex and can vary depending on a number of factors, including the overall health of the economy, the specific industries affected, and the magnitude of the interest rate increases.
Implications for the Future
The recent trends in jobless claims, layoffs, and interest rates paint a complex picture for the future of the labor market. While the current situation appears relatively robust, several factors could influence the trajectory of the labor market in the coming months and years.
Potential Scenarios for the Labor Market
The current resilience of the labor market amidst rising interest rates could continue, but several factors could influence the future landscape.
- Continued Economic Growth:If the economy continues to grow at a moderate pace, the labor market is likely to remain strong. Businesses would continue hiring to meet demand, leading to low unemployment and potentially even wage growth.
- Recession:A recession could significantly impact the labor market. Businesses might respond to reduced demand by laying off workers, leading to increased unemployment and potentially slower wage growth. The severity of the recession and its duration would influence the extent of these impacts.
- Inflation:Persistent high inflation could force businesses to raise prices, leading to reduced consumer spending and potentially impacting job creation.
- Policy Decisions:The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions will play a crucial role in shaping the labor market. Further interest rate hikes could slow economic growth and potentially lead to job losses.