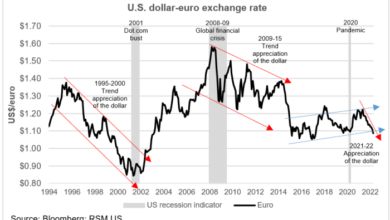
Dollar Stumbles, Yuan Slips on Rate Cut Ahead of Inflation Data
Dollar stumbles ahead of inflation data yuan slips on rate cut – Dollar Stumbles, Yuan Slips on Rate Cut Ahead of Inflation Data – these are the headlines that have investors on edge. The dollar, already weakened by a series of economic indicators, is facing a potential further decline as the US prepares to release crucial inflation data.
Meanwhile, the yuan has slipped following a rate cut by the Chinese central bank, raising questions about the health of the Chinese economy. These events highlight the interconnected nature of global currency markets and the impact they have on economies around the world.
The upcoming inflation data is particularly important for the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions. If inflation proves to be stickier than expected, it could lead to further interest rate hikes, which would strengthen the dollar but potentially slow economic growth.
The yuan’s depreciation, on the other hand, reflects concerns about China’s economic slowdown and its potential impact on global trade. As these two major economies grapple with their own challenges, the global currency landscape is likely to remain volatile in the coming months.
Dollar Stumble
The dollar has been weakening in recent weeks, leading up to the release of the latest inflation data. This decline can be attributed to several factors, including expectations for a potential pause in the Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes and a growing sense of optimism about the global economic outlook.
The upcoming inflation data is crucial because it could provide further insights into the Fed’s future monetary policy decisions, which will have a significant impact on the dollar’s trajectory.
The dollar is taking a tumble ahead of key inflation data, while the yuan is slipping after a surprise rate cut. This weakness in the dollar is likely playing a role in the recent surge in gold prices, which is often seen as a safe haven asset.
Meanwhile, the Chinese government’s new initiatives to support the real estate sector are expected to boost demand for base metals, as seen in this article. It’s a fascinating interplay of global economic forces, with the dollar’s weakness potentially fueling a rally in precious metals and boosting demand for industrial commodities in China.
Potential Impact of Inflation Data on the Dollar
The release of inflation data is a major event for the financial markets, as it can influence the Fed’s monetary policy decisions. If the data shows that inflation is cooling down more quickly than expected, it could lead to a further weakening of the dollar.
This is because a lower inflation rate might encourage the Fed to pause or even reverse its interest rate hikes, which would make the dollar less attractive to investors seeking higher returns. Conversely, if the data indicates that inflation remains stubbornly high, it could strengthen the dollar as the Fed might feel compelled to continue its aggressive rate hikes.
The dollar stumbled ahead of inflation data, while the yuan slipped on a rate cut, reflecting the global economic uncertainty. This comes as the cryptocurrency sector faces increasing regulatory pressure, as seen in the SEC’s lawsuit against Coinbase. This legal action highlights the growing scrutiny of the crypto space, adding to the market volatility and challenging the outlook for both the dollar and the yuan.
Recent Economic Indicators Contributing to the Dollar’s Decline
Several recent economic indicators have contributed to the dollar’s decline. The most notable is the slowdown in US economic growth, as evidenced by the recent decline in GDP growth and the weak performance of manufacturing and consumer spending. This slowdown has led to concerns about a potential recession, which could further weaken the dollar.
Additionally, the Fed’s recent hawkish statements, which suggested that interest rates would remain high for a longer period, have also weighed on the dollar. This is because investors have become less optimistic about the US economic outlook, which has reduced the demand for the dollar.
Comparison to Previous Instances of Dollar Weakness
The current weakness in the dollar is not unprecedented. In the past, the dollar has weakened during periods of economic uncertainty, such as the global financial crisis of 2008 and the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the current situation is somewhat different, as the Fed is facing a more complex economic environment, with inflation remaining high while economic growth is slowing.
This makes it difficult for the Fed to predict the future course of monetary policy, which has increased uncertainty about the dollar’s future direction.
Inflation Data
The upcoming release of inflation data is a crucial event for the US economy, as it will provide insights into the current state of price pressures and the trajectory of the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy. This data is expected to influence investor sentiment and market volatility, potentially leading to significant shifts in asset prices.
The dollar is struggling as we wait for inflation data, and the yuan is slipping after a rate cut. It’s a volatile market, and it’s hard to know what’s going to happen next. But while we’re on the topic of unexpected moves, check out daniel baldwin joins ishook 202879 , a surprising development in the world of finance.
Back to the dollar and the yuan, I guess we’ll just have to wait and see what the next few days bring.
Inflation Data’s Significance
The inflation data release is highly anticipated by economists, investors, and policymakers as it provides a snapshot of the overall price level in the economy. This data is a key indicator of the health of the economy and helps to gauge the effectiveness of the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy.
Inflation Data’s Impact on Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve closely monitors inflation data to determine the appropriate course of action for monetary policy. If inflation is running higher than the Fed’s target of 2%, the central bank may raise interest rates to cool down the economy and curb inflation.
Conversely, if inflation is below the target, the Fed may lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth. The inflation data release can therefore have a significant impact on the Fed’s decision-making process.
Impact on Investor Sentiment and Market Volatility
Inflation data can significantly influence investor sentiment and market volatility. If inflation comes in higher than expected, investors may become concerned about the potential for the Fed to tighten monetary policy more aggressively, leading to a sell-off in stocks and other assets.
Conversely, if inflation comes in lower than expected, investors may become more optimistic about the economic outlook, leading to a rally in markets.
Historical Inflation Trends
| Year | Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 2023 | 4.9 |
| 2022 | 8.0 |
| 2021 | 4.7 |
| 2020 | 1.2 |
| 2019 | 1.8 |
This table highlights the recent trend of rising inflation in the US economy. The inflation rate has been steadily increasing since 2020, reaching a peak of 8.0% in 2022. While inflation has moderated in recent months, it remains above the Fed’s target of 2%.
Yuan Slip: Dollar Stumbles Ahead Of Inflation Data Yuan Slips On Rate Cut

The Chinese yuan depreciated against the US dollar following the People’s Bank of China’s (PBOC) decision to cut interest rates. This move, aimed at stimulating economic growth, has raised concerns about the yuan’s future trajectory and its potential impact on the Chinese economy.
Factors Contributing to the Yuan’s Depreciation
The yuan’s depreciation can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Rate Cut:The PBOC’s decision to cut interest rates, signaling a looser monetary policy, made the yuan less attractive to investors seeking higher returns.
- Weakening Economic Outlook:China’s economic growth has slowed in recent months, raising concerns about the country’s ability to meet its growth targets. This uncertainty has prompted investors to reduce their exposure to the yuan.
- Stronger Dollar:The US dollar has been strengthening against other major currencies, making the yuan relatively weaker.
- Trade Tensions:Ongoing trade tensions between the US and China have created uncertainty and volatility in the currency markets, contributing to the yuan’s depreciation.
Rationale Behind the Rate Cut
The PBOC’s decision to cut interest rates was aimed at stimulating economic growth and offsetting the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. The rate cut is expected to:
- Lower Borrowing Costs:Reducing interest rates makes it cheaper for businesses and consumers to borrow money, potentially leading to increased investment and spending.
- Boost Economic Activity:Lower borrowing costs can stimulate economic activity by encouraging businesses to expand operations and consumers to make larger purchases.
- Support Growth Targets:The rate cut is intended to help China achieve its economic growth targets, which have been impacted by the pandemic.
Potential Impact of the Rate Cut on the Chinese Economy
The rate cut is expected to have a mixed impact on the Chinese economy. While it could stimulate economic growth in the short term, it also carries potential risks:
- Inflation:Lower interest rates could lead to increased inflation, as businesses and consumers are more likely to borrow and spend money.
- Asset Bubbles:Lower interest rates could encourage excessive borrowing and investment in assets, potentially leading to asset bubbles.
- Currency Volatility:The rate cut could further weaken the yuan, making it more volatile and unpredictable.
Comparison with Previous Instances of Currency Fluctuations
The recent depreciation of the yuan is not unprecedented. In the past, the yuan has experienced periods of both appreciation and depreciation, often driven by factors such as global economic conditions, trade tensions, and government policies. For example, the yuan depreciated significantly during the 2008 financial crisis, but it later recovered and appreciated as China’s economy grew.
Timeline of Key Events Leading to the Yuan’s Slip
- January 2023:The PBOC cut interest rates for the first time since 2020, signaling a loosening of monetary policy.
- February 2023:The yuan depreciated against the US dollar, as investors reacted to the rate cut and concerns about China’s economic outlook.
- March 2023:The yuan continued to depreciate, as the US dollar strengthened and trade tensions between the US and China remained elevated.
- April 2023:The PBOC intervened in the currency market to stabilize the yuan, but the currency remained under pressure.
Global Currency Dynamics
The recent stumble of the dollar and the yuan’s slip on a rate cut are not isolated events. These movements reflect the interconnectedness of global currency markets and the intricate interplay of economic forces. Understanding the broader context of global currency dynamics is crucial for navigating the complexities of international trade, investment, and economic policy.
The Interplay of Major Economies
The global currency landscape is a complex web of interconnected relationships. The value of a currency is influenced by a multitude of factors, including economic growth, interest rates, inflation, government policies, and investor sentiment. These factors are not independent but rather intertwined, creating a delicate balance that can shift rapidly.For instance, the dollar’s weakness can be attributed to several factors, including the Federal Reserve’s recent pause in interest rate hikes, concerns about the US economy’s trajectory, and the relative attractiveness of other currencies.
Meanwhile, the yuan’s slip is linked to China’s efforts to stimulate its economy and the widening interest rate differential between the US and China. These movements are not isolated events but rather reflect a broader trend of global currency realignment.
Impact on Other Currencies, Dollar stumbles ahead of inflation data yuan slips on rate cut
The dollar’s weakness and the yuan’s slip can have significant implications for other currencies. When the dollar weakens, it makes US goods and services cheaper for foreign buyers, potentially boosting US exports. However, it also makes imports more expensive, potentially contributing to inflation.The yuan’s depreciation can make Chinese exports more competitive, but it can also lead to capital outflows and exacerbate inflationary pressures.
These movements can also impact other emerging market currencies, particularly those that are closely linked to the yuan.
Visual Representation of Currency Relationships
A visual representation of currency relationships can help to illustrate the interconnectedness of global markets. Imagine a network diagram where each currency is represented by a node. The connections between the nodes represent the strength of the relationships between currencies.For example, the dollar would be a central node with strong connections to the euro, yen, and other major currencies.
The yuan would have a strong connection to the dollar, but also connections to other Asian currencies. This diagram would show how movements in one currency can ripple through the network, affecting other currencies.
Impact on Global Trade and Investment Flows
Currency movements can have a significant impact on global trade and investment flows. When the dollar weakens, it becomes more expensive for US companies to import goods and services, potentially reducing their competitiveness in the global market.Conversely, a weaker dollar can make US assets, such as stocks and bonds, more attractive to foreign investors, potentially increasing capital inflows into the US.
The yuan’s depreciation can make Chinese exports more competitive, potentially boosting Chinese trade surplus.However, it can also lead to capital outflows and reduced foreign investment in China. These movements can also affect the attractiveness of other emerging markets, depending on their economic fundamentals and their relationship with the dollar and the yuan.