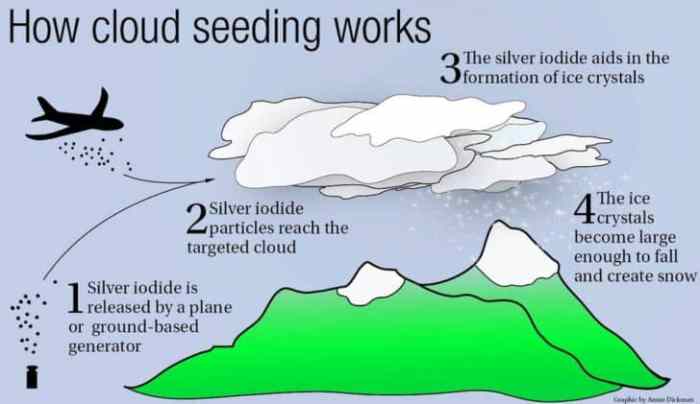
Cloud Seeding: Enhancing Rainfall for Water Security
Cloud seeding enhancing rainfall water resource management drought water scarcity is a fascinating and increasingly important topic in our water-stressed world. Imagine harnessing the power of nature to boost rainfall and combat drought. This is the promise of cloud seeding, a technology that has been around for decades, and is now gaining renewed attention as climate change intensifies water scarcity.
At its core, cloud seeding involves introducing substances like silver iodide or dry ice into clouds, aiming to create more favorable conditions for precipitation. While the effectiveness of cloud seeding is still debated, it holds significant potential for augmenting water resources, particularly in arid and semi-arid regions.
This technology has the potential to play a vital role in bolstering water security, supporting agriculture, and mitigating the impacts of drought.
Introduction to Cloud Seeding: Cloud Seeding Enhancing Rainfall Water Resource Management Drought Water Scarcity
Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique that aims to increase precipitation by dispersing substances into the atmosphere that can serve as condensation nuclei, encouraging the formation of cloud droplets and, ultimately, rain. The concept of cloud seeding has been around for decades, with its roots dating back to the early 20th century.The science behind cloud seeding relies on the fundamental principles of atmospheric physics.
Clouds form when water vapor in the atmosphere condenses around tiny particles called condensation nuclei. These nuclei can be natural, such as dust, sea salt, or pollen, or they can be introduced artificially. Cloud seeding aims to enhance the concentration of these nuclei, leading to the formation of more cloud droplets and, consequently, more precipitation.
Different Methods of Cloud Seeding, Cloud seeding enhancing rainfall water resource management drought water scarcity
The effectiveness of cloud seeding methods has been a subject of ongoing research and debate. While some studies have shown promising results, others have yielded less conclusive findings. The effectiveness of cloud seeding can be influenced by various factors, including the type of cloud, the atmospheric conditions, and the specific method used.Cloud seeding is typically performed by dispersing seeding agents into the atmosphere.
The most common methods include:
- Silver Iodide Seeding:Silver iodide is a highly effective ice nucleator, meaning it can trigger the formation of ice crystals in supercooled water droplets. This method is often used for seeding cold clouds, which contain temperatures below freezing but remain in a liquid state due to the lack of ice nuclei.
Silver iodide can be dispersed from aircraft, ground-based generators, or even rockets.
- Dry Ice Seeding:Dry ice, which is solid carbon dioxide, is another effective ice nucleator. When dry ice is dispersed into a cloud, it rapidly sublimates (transitions from solid to gas), creating a localized cooling effect. This cooling effect can trigger the formation of ice crystals, leading to precipitation.
Dry ice is typically dispersed from aircraft.
- Hygroscopic Seeding:Hygroscopic seeding involves dispersing substances that readily absorb moisture, such as salt or calcium chloride, into the atmosphere. These substances attract water vapor, increasing the size of cloud droplets and potentially enhancing precipitation. Hygroscopic seeding is often used for seeding warm clouds, which contain temperatures above freezing.
“The effectiveness of cloud seeding can be influenced by various factors, including the type of cloud, the atmospheric conditions, and the specific method used.”
Cloud Seeding for Rainfall Enhancement
Cloud seeding is a weather modification technique that aims to increase precipitation by dispersing substances into the atmosphere that can serve as condensation nuclei, promoting the formation of cloud droplets and ultimately leading to rainfall. This technique has been explored for decades as a potential tool to enhance water resources, particularly in regions experiencing drought or water scarcity.
Cloud seeding, a technique to enhance rainfall, holds immense potential for addressing water scarcity and drought, especially in regions heavily reliant on agriculture. However, the economic impacts of such initiatives can be complex, as seen in the recent market fluctuations.
For instance, the dow futures dip as disney reports losses inflation data ahead live updates highlights the delicate balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability, underscoring the need for robust strategies to ensure the long-term viability of cloud seeding programs while navigating economic uncertainties.
Potential of Cloud Seeding to Increase Rainfall
The potential of cloud seeding to increase rainfall varies depending on several factors, including the type of clouds present, the availability of moisture, and the atmospheric conditions.
- Cloud seeding is most effective in clouds that are already saturated with moisture and have the potential to produce precipitation. This is because the seeding agents act as catalysts, accelerating the process of cloud droplet formation and growth.
- The presence of sufficient moisture in the atmosphere is crucial for successful cloud seeding operations.
Without adequate moisture, the seeding agents will not be able to effectively promote cloud droplet formation.
- Atmospheric conditions, such as temperature, wind speed, and atmospheric stability, can also influence the effectiveness of cloud seeding. For instance, strong winds can disperse the seeding agents before they have a chance to interact with the clouds, reducing their effectiveness.
Factors Influencing the Success of Cloud Seeding Operations
The success of cloud seeding operations is influenced by several factors:
- The type of seeding agent used: Various seeding agents, such as silver iodide, dry ice, and salt, have been used in cloud seeding. The effectiveness of each agent can vary depending on the specific cloud conditions.
- The delivery method: Seeding agents can be dispersed using aircraft, ground-based generators, or rockets.
The choice of delivery method depends on factors such as the size and location of the target cloud.
- The timing of the seeding operation: Cloud seeding is most effective when conducted during periods of favorable atmospheric conditions, such as when clouds are actively forming and there is sufficient moisture present.
- The target cloud: The type of cloud targeted for seeding is crucial. Some cloud types, such as cumulus congestus clouds, are more responsive to seeding than others.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
There have been numerous case studies and real-world examples of cloud seeding projects, with varying degrees of success.
- In the United Arab Emirates, cloud seeding operations have been conducted for decades, with reports of significant increases in rainfall in some regions. The UAE’s National Center of Meteorology has documented increases in rainfall of up to 30% in areas where cloud seeding has been implemented.
- In China, cloud seeding has been used to enhance rainfall in various regions, particularly in the semi-arid northwest, where water resources are scarce. Studies have shown that cloud seeding operations in China have led to significant increases in precipitation, contributing to water resource management and drought mitigation.
Cloud seeding, a technique to enhance rainfall, holds potential to address water scarcity and drought. While the science behind it is still evolving, the potential benefits are undeniable, especially in regions facing water stress. The financial implications of such initiatives, however, are significant, mirroring the massive investment in the Indian Premier League (IPL), which has become a lucrative business, as detailed in this fascinating article, the money game of indian cricket how ipl scores big in finances.
Just as the IPL attracts huge sponsorships and viewership, successful cloud seeding programs would require substantial investment, but could yield long-term benefits in terms of water resource management and agricultural productivity.
- The United States has also conducted cloud seeding experiments in various regions, with varying results. For example, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) has conducted cloud seeding research in the western United States, focusing on increasing snowfall in the Sierra Nevada mountains to enhance water resources.
Cloud Seeding and Water Resource Management

Cloud seeding is a technique used to enhance precipitation by dispersing substances into the atmosphere that can serve as condensation nuclei, encouraging the formation of rain or snow. In drought-prone areas, where water scarcity is a major concern, cloud seeding can play a crucial role in managing water resources.
Benefits of Cloud Seeding for Water Management
Cloud seeding offers a potential solution for augmenting water supplies in regions facing water scarcity. It can benefit various aspects of water resource management, including:
- Increased Water Supply:By enhancing precipitation, cloud seeding can directly contribute to increased water availability in reservoirs, rivers, and groundwater aquifers, mitigating water shortages. For example, in the United States, cloud seeding programs in states like Wyoming and Texas have reported increases in precipitation, leading to improved water storage in reservoirs.
Cloud seeding, a technique used to enhance rainfall, has become increasingly important in managing water resources, especially in drought-stricken areas. The ability to influence precipitation patterns is a critical tool in mitigating water scarcity. This reminds me of how Netflix has successfully adapted to social and political issues, drawing valuable insights from a corporate board veteran, as discussed in this insightful article: netflix success in adapting to social and political issues insights from a corporate board veteran.
Just like Netflix, innovative solutions like cloud seeding can help us navigate complex challenges, like water scarcity, by adapting to changing circumstances and embracing new technologies.
- Agricultural Benefits:Increased rainfall from cloud seeding can directly benefit agriculture by providing much-needed water for irrigation, improving crop yields, and enhancing overall agricultural productivity. For instance, in China, cloud seeding has been used to increase rainfall in agricultural areas, leading to improved crop yields and economic benefits for farmers.
- Ecosystem Health:Cloud seeding can contribute to the health of ecosystems by replenishing water sources, supporting biodiversity, and promoting the growth of vegetation. For example, cloud seeding programs in arid regions can help to revitalize ecosystems by increasing water availability, leading to the recovery of vegetation and the return of wildlife.
Comparison with Other Water Management Strategies
Cloud seeding is one of several strategies employed for water resource management. It can be compared to other approaches, such as:
- Water Conservation:This involves reducing water consumption through efficient irrigation techniques, water-saving appliances, and public awareness campaigns. While cloud seeding focuses on increasing water supply, water conservation aims to reduce demand, offering a complementary approach to water management.
- Water Desalination:This process involves removing salt from seawater to produce freshwater. While effective in coastal areas, desalination is energy-intensive and can be costly. Cloud seeding, on the other hand, offers a more natural and potentially less expensive method for increasing water availability.
- Water Transfer:This involves moving water from water-rich areas to water-scarce regions through pipelines or canals. While effective in some cases, water transfer projects can be complex and expensive, with potential environmental impacts. Cloud seeding provides a more localized and potentially less disruptive approach to water management.
Challenges and Concerns of Cloud Seeding
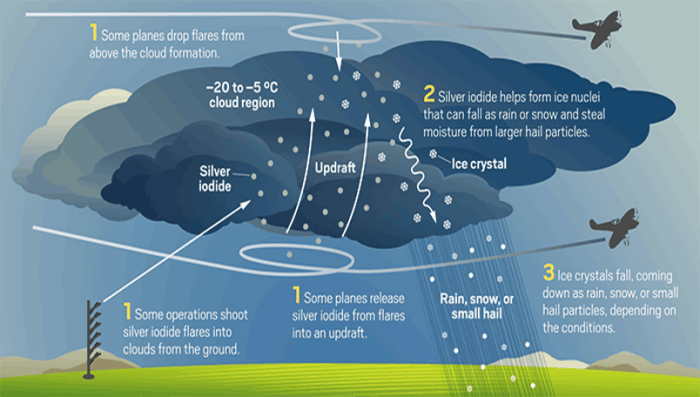
While cloud seeding holds promise for augmenting water resources, it’s not without its challenges and concerns. These stem from potential environmental impacts, ethical considerations, and the need for further research to optimize its effectiveness.
Potential Risks and Environmental Impacts
It’s crucial to acknowledge the potential risks and environmental impacts associated with cloud seeding. While the technology itself is relatively benign, the substances used and the potential consequences need careful consideration.
- Inadvertent Weather Modification:Cloud seeding can unintentionally alter weather patterns in surrounding areas, potentially causing unintended consequences such as increased precipitation in one region while decreasing it in another.
- Impact on Air Quality:The use of seeding agents, particularly silver iodide, can contribute to air pollution, especially in areas with high seeding activity.
- Effects on Ecosystems:The potential impact of cloud seeding on ecosystems, including aquatic life, vegetation, and wildlife, needs further investigation.
- Long-Term Consequences:The long-term consequences of cloud seeding, such as changes in cloud formation and precipitation patterns, are still being studied.
Ethical Considerations and Concerns
Cloud seeding raises ethical questions about the manipulation of natural processes and the potential for unintended consequences.
- Distribution of Water Resources:The potential for cloud seeding to shift rainfall patterns raises ethical concerns about the equitable distribution of water resources among different regions.
- Equity and Access:The cost of cloud seeding technology can be prohibitive for some regions, raising concerns about equitable access to this water management tool.
- International Cooperation:Cloud seeding activities that affect transboundary water resources require international cooperation and agreement to avoid disputes and ensure equitable outcomes.
Need for Further Research and Development
To mitigate risks and maximize the benefits of cloud seeding, ongoing research and development are essential.
- Optimization of Techniques:Research is needed to refine cloud seeding techniques, improving their effectiveness and minimizing unintended consequences.
- Environmental Monitoring:Comprehensive environmental monitoring is crucial to assess the short-term and long-term impacts of cloud seeding on ecosystems and weather patterns.
- Public Engagement:Open and transparent communication with the public is essential to address concerns, build trust, and ensure informed decision-making regarding cloud seeding.
Future Directions in Cloud Seeding Research
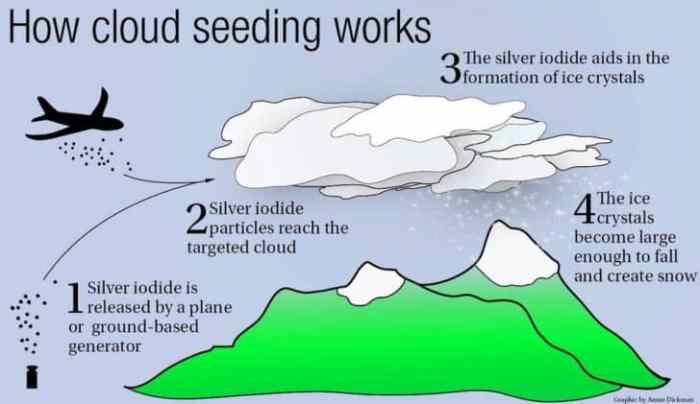
Cloud seeding, a technique to enhance precipitation, has evolved over decades, but its potential remains largely untapped. The future holds exciting possibilities for advancing cloud seeding technology and its applications, particularly in addressing water scarcity challenges exacerbated by climate change.
Advancements in Cloud Seeding Technology
The continuous pursuit of advancements in cloud seeding technology is crucial for maximizing its effectiveness and expanding its applicability.
- Nanotechnology-Enabled Cloud Seeding:Utilizing nanotechnology to create highly efficient seeding agents with enhanced ice nucleation properties could significantly improve cloud seeding efficacy. These nanoparticles could act as more potent ice nuclei, promoting the formation of larger ice crystals and ultimately increasing precipitation.
- Precision Cloud Seeding:Advanced weather forecasting models and real-time cloud monitoring systems can enable more precise targeting of seeding operations, maximizing the impact of seeding agents on specific cloud formations. This precision approach would ensure that seeding occurs in the most conducive cloud environments, optimizing precipitation enhancement.
- Drone-Based Cloud Seeding:Integrating drones into cloud seeding operations could revolutionize the delivery of seeding agents. Drones can be deployed to reach remote areas, navigate challenging terrains, and deliver seeding agents directly to targeted cloud formations. This flexibility would allow for more targeted and efficient seeding operations.
- Hybrid Cloud Seeding Techniques:Combining different cloud seeding techniques, such as silver iodide and hygroscopic seeding, could lead to synergistic effects, enhancing precipitation potential. This approach would exploit the strengths of various seeding methods, maximizing their collective impact on precipitation enhancement.
Climate Change and Cloud Seeding Effectiveness
Climate change is altering global precipitation patterns, impacting cloud seeding effectiveness.
- Warmer Temperatures and Cloud Dynamics:Rising global temperatures are influencing cloud dynamics, potentially impacting the effectiveness of cloud seeding. Warmer temperatures could lead to fewer ice-forming clouds, reducing the effectiveness of traditional cloud seeding methods.
- Cloud Seeding in a Changing Climate:Understanding how climate change is affecting cloud formation and precipitation is crucial for optimizing cloud seeding strategies. Adapting cloud seeding techniques to account for changing cloud characteristics will be essential for maximizing its effectiveness in a changing climate.
- Climate Models and Cloud Seeding:Integrating climate models with cloud seeding simulations will be essential for predicting the potential impact of cloud seeding in a changing climate. These models can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of cloud seeding under different climate scenarios.
Areas for Further Research and Collaboration
The field of cloud seeding offers vast potential for scientific exploration and collaboration.
- Improving Ice Nucleation Understanding:Further research into the fundamental processes of ice nucleation, particularly the interaction of seeding agents with cloud particles, is essential for developing more efficient seeding agents.
- Cloud Seeding and Water Resource Management:Research focusing on the integrated impact of cloud seeding on water resource management, including its potential to augment water supplies for agriculture, urban water systems, and hydroelectric power generation, is crucial for maximizing its benefits.
- International Collaboration:Enhancing international collaboration in cloud seeding research is essential for sharing knowledge, best practices, and technological advancements. Joint research projects and data-sharing initiatives will accelerate progress in this field.

