Chinas Foreign Investment Plunges to Four-Year Low
China records steep drop in foreign investment hitting a four year low, a trend that has sent shockwaves through the country’s economic landscape. This decline, marking a significant shift from previous years, raises concerns about the future of China’s growth trajectory.
The recent downturn in foreign investment is a complex issue, intertwined with a multitude of factors that have impacted the global economy, including the lingering effects of the COVID-19 pandemic, heightened geopolitical tensions, and evolving trade dynamics.
The decrease in foreign investment has been particularly pronounced in key sectors like manufacturing and technology, areas that have historically been major recipients of foreign capital. This trend is not just a cause for concern within China but also raises questions about the broader global economic outlook, as China’s economic health has a ripple effect on the rest of the world.
Foreign Investment Trends in China

Foreign investment plays a crucial role in China’s economic growth, driving technological advancement, creating jobs, and bolstering its global competitiveness. However, recent data reveals a significant decline in foreign investment, raising concerns about the future of China’s economic trajectory.
Recent Decline in Foreign Investment
The recent decline in foreign investment is a concerning trend, reflecting various challenges faced by China’s economy. According to the National Bureau of Statistics, foreign direct investment (FDI) into China fell by 2.5% in the first half of 2023, marking the lowest level in four years.
This decline can be attributed to several factors, including:
- Geopolitical tensions:The ongoing trade war with the United States and rising geopolitical tensions have created uncertainty and discouraged foreign investors.
- Economic slowdown:China’s economic growth has slowed in recent years, impacting investor confidence and making the country less attractive for foreign investment.
- Regulatory challenges:China’s regulatory environment has become more complex and unpredictable, creating hurdles for foreign businesses.
- Competition from other emerging markets:Other emerging markets, such as Vietnam and India, are becoming increasingly competitive, attracting foreign investment away from China.
Comparison to Previous Years
Comparing the current situation to previous years highlights the severity of the decline. In 2019, FDI into China reached a record high of $142 billion. However, this figure has been steadily declining since then, reaching $123 billion in 2022. The decline in 2023 suggests a continuation of this trend, raising concerns about the long-term outlook for foreign investment in China.
Notable Trends
Despite the overall decline, there are some notable trends in foreign investment patterns. One notable trend is the increasing importance of technology-related investments. While traditional manufacturing sectors have seen a decline in foreign investment, investments in areas such as artificial intelligence, electric vehicles, and renewable energy have remained strong.
This suggests that foreign investors are seeking opportunities in sectors with long-term growth potential.Another notable trend is the shift in investment sources. While traditional investors from developed countries, such as the United States and Europe, have reduced their investments in China, investors from emerging markets, such as South Korea and Singapore, have increased their investments.
This shift reflects the changing global economic landscape and the increasing importance of emerging markets as sources of capital.
Factors Contributing to the Decline
The sharp decrease in foreign investment in China, reaching a four-year low, is a complex issue with several contributing factors. While the pandemic’s impact is undeniable, other forces like geopolitical tensions, trade disputes, and China’s regulatory environment play a significant role.
Understanding these factors is crucial for comprehending the current state of foreign investment in China and predicting future trends.
China’s recent record low in foreign investment, hitting a four-year low, raises concerns about the country’s economic stability. This decline could be partially attributed to global uncertainties, but it also highlights the growing influence of alternative financial systems, like cryptocurrencies.
Understanding the impact of Bitcoin on the global economy, as explored in this insightful article on bitcoins impact on the global economy dissecting the influence of cryptocurrency , is crucial for navigating the evolving landscape of international finance. As China seeks to attract foreign investment, its ability to adapt to these changes will be key to its economic future.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on China’s economy and foreign investment. The pandemic’s disruption to global supply chains, coupled with lockdowns and travel restrictions, created significant uncertainty and slowed economic activity. This uncertainty has discouraged foreign investors, who are wary of investing in a volatile market.
China’s economic woes continue to deepen, with foreign investment plummeting to a four-year low. This decline, likely driven by global uncertainties and a cooling Chinese economy, is amplified by the current geopolitical climate. The recent escalation of tensions in the Middle East, as reported in this article , is adding to the overall market nervousness, further discouraging investors from committing to China’s market.
It remains to be seen how long these factors will continue to weigh down China’s economic outlook.
Geopolitical Tensions and Trade Disputes, China records steep drop in foreign investment hitting a four year low
Escalating geopolitical tensions and trade disputes between China and the United States, particularly during the Trump administration, have created a climate of uncertainty and distrust. The trade war, characterized by tariffs and restrictions, has deterred foreign investment and led some companies to reconsider their China strategy.
These tensions have also fueled concerns about intellectual property protection and forced technology transfer, further discouraging foreign investment.
China’s economic woes continue to deepen as foreign investment plummets to a four-year low. This trend, coupled with the recent global economic uncertainty, paints a bleak picture for the country’s future. Meanwhile, across the globe, the EU has launched a formal investigation into Elon Musk’s X, formerly Twitter, regarding its content moderation practices.
This investigation highlights the growing concern over the potential for social media platforms to be used for the spread of misinformation and hate speech. It remains to be seen how these events will impact China’s economic recovery and the global landscape of social media regulation.
China’s Regulatory Environment and Economic Policies
China’s regulatory environment has also played a role in the decline of foreign investment. Increased scrutiny of foreign companies, stricter regulations on data privacy and cybersecurity, and a crackdown on technology giants have raised concerns among foreign investors. Some investors perceive these measures as hindering their operations and creating an unpredictable business environment.Additionally, China’s economic policies, including its focus on self-reliance and the promotion of domestic companies, have contributed to the decline in foreign investment.
These policies, while aimed at bolstering China’s economic independence, can sometimes be perceived as discriminatory by foreign investors, who may feel their access to the Chinese market is being restricted.
Impact on Chinese Economy: China Records Steep Drop In Foreign Investment Hitting A Four Year Low
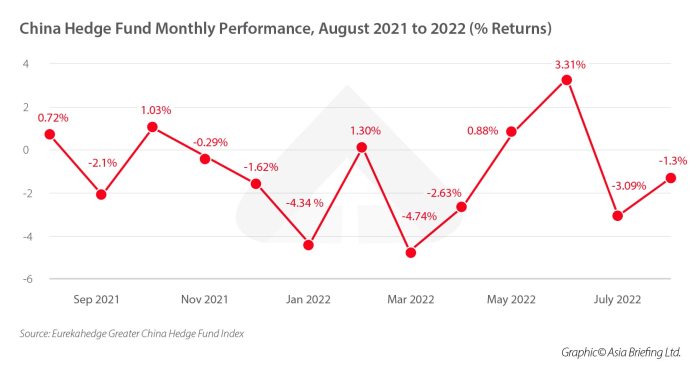
The sharp decline in foreign investment in China has significant implications for the country’s economic growth and stability. While China has long relied on domestic demand to drive its economy, foreign investment plays a crucial role in supporting innovation, technology transfer, and job creation.
The reduction in foreign investment could hinder China’s efforts to achieve its economic goals and could have ripple effects across various sectors.
Economic Growth and Development
The decrease in foreign investment can negatively impact China’s economic growth trajectory. Foreign investment often brings in capital, technology, and expertise, which can stimulate innovation and create new industries. Reduced foreign investment could lead to slower economic growth, particularly in sectors that rely heavily on foreign capital.
For instance, the technology sector, which has traditionally attracted significant foreign investment, could face challenges in attracting funding for research and development, potentially hindering its growth and competitiveness.
Government Response and Future Outlook
The Chinese government has recognized the decline in foreign investment as a significant concern and has taken various steps to address the issue. These initiatives aim to bolster investor confidence and attract more foreign capital.
Government Initiatives to Attract Foreign Investment
The government has implemented several measures to address the declining foreign investment. These initiatives aim to create a more favorable business environment and enhance investor confidence.
- Easing Market Access:The government has further opened up sectors previously restricted to foreign investment, including finance, healthcare, and technology. This move aims to create more opportunities for foreign companies to participate in the Chinese market.
- Improving Regulatory Environment:The government has focused on simplifying regulatory procedures, streamlining approval processes, and enhancing transparency in regulations. These efforts aim to reduce bureaucratic hurdles and create a more predictable business environment for foreign investors.
- Strengthening Intellectual Property Protection:China has intensified its efforts to combat intellectual property theft and enhance protection mechanisms. This move aims to address a major concern for foreign investors and build confidence in the legal framework.
- Promoting Innovation and Technology Transfer:The government has implemented policies to encourage foreign companies to transfer technology and collaborate with Chinese counterparts. This initiative aims to foster innovation and enhance China’s technological capabilities.
Effectiveness of Current Policies
The effectiveness of the government’s initiatives in reversing the decline in foreign investment remains to be seen. While some positive signs have emerged, such as increased investment in certain sectors, the overall trend still needs to be closely monitored.
- Challenges Remain:Despite the efforts, challenges remain in attracting foreign investment. These include concerns over geopolitical tensions, the evolving regulatory landscape, and competition from other emerging markets.
- Long-Term Impact:The long-term impact of these initiatives will depend on the government’s ability to maintain a stable and predictable business environment, address investor concerns, and effectively implement policies that promote sustainable growth.
Future Outlook
The future of foreign investment in China is uncertain. While the government’s initiatives offer potential for attracting more foreign capital, several factors will influence the overall outlook.
- Geopolitical Tensions:Ongoing geopolitical tensions between China and other countries, particularly the United States, could negatively impact foreign investment. Investors may be hesitant to commit capital in an environment characterized by uncertainty and potential trade conflicts.
- Domestic Economic Conditions:The performance of the Chinese economy will be a crucial factor in attracting foreign investment. If the economy continues to slow down or faces significant challenges, investors may become more cautious.
- Competitive Landscape:China faces increasing competition from other emerging markets that are also attracting foreign investment. These markets offer attractive investment opportunities, posing a challenge to China’s efforts to attract foreign capital.
Comparative Analysis
While China’s recent dip in foreign investment is concerning, it’s crucial to compare it to other major economies to understand its significance. Examining global trends and factors influencing investment decisions can shed light on China’s situation and potential solutions.
Foreign Investment Trends in Other Major Economies
Comparing China’s foreign investment situation to other major economies provides context. For instance, the United States, traditionally a top destination for foreign investment, has also experienced fluctuations in recent years. However, the US remains a significant draw for global investors due to its robust economy, stable political system, and established legal framework.
Similarly, the European Union, despite its economic challenges, remains attractive to foreign investors, particularly in sectors like manufacturing, technology, and renewable energy. However, the EU faces challenges like bureaucratic complexities and economic disparities across member states, impacting investment decisions.
Emerging economies like India and Indonesia have witnessed a surge in foreign investment in recent years, driven by factors like rapid economic growth, a large consumer market, and government initiatives to attract foreign capital. However, these countries also face challenges like infrastructure bottlenecks, regulatory hurdles, and political uncertainties.
Factors Influencing Foreign Investment Decisions
Understanding the factors that influence foreign investment decisions across different countries is essential to assess China’s situation accurately. Some key factors include:
- Economic Growth and Stability:Investors seek economies with consistent growth and stability, offering a secure environment for their investments.
- Political Stability and Transparency:A stable political system with transparent governance and predictable policies is crucial for attracting long-term investments.
- Market Size and Access:Large and growing markets with easy access to consumers and resources are attractive to investors seeking to expand their operations.
- Infrastructure and Logistics:Well-developed infrastructure, including transportation, communication, and energy, is essential for businesses to operate efficiently and attract foreign investors.
- Regulatory Environment:Clear and consistent regulations, fair competition, and protection of intellectual property rights are critical for attracting and retaining foreign investment.
- Talent Pool and Skills:Access to a skilled workforce with relevant expertise is crucial for businesses to operate effectively and achieve success.
- Taxation and Incentives:Competitive tax rates and incentives for foreign investors can encourage investment and attract businesses to specific locations.
Best Practices and Lessons Learned from Other Countries
Several countries have successfully attracted and retained foreign investment by adopting best practices. China can learn from these experiences to improve its investment climate and attract more foreign capital.
- Singapore:Singapore’s success in attracting foreign investment can be attributed to its pro-business environment, transparent regulations, efficient bureaucracy, and a skilled workforce. China can learn from Singapore’s experience in simplifying its regulatory framework, fostering a culture of transparency, and investing in human capital development.
- United Arab Emirates (UAE):The UAE’s strategic location, world-class infrastructure, and business-friendly policies have attracted significant foreign investment. China can learn from the UAE’s experience in developing its infrastructure, promoting free trade zones, and creating a conducive environment for foreign businesses.
- Ireland:Ireland’s success in attracting foreign investment in technology and pharmaceuticals is attributed to its skilled workforce, competitive tax rates, and pro-business policies. China can learn from Ireland’s experience in developing its human capital, providing tax incentives, and creating a favorable regulatory environment for foreign investors.