Chinas Economic Growth Slows to 5.2%, Marking Its Weakest Pace in Over 30 Years
China economic growth achieving 52 facing slowest pace in over 30 years – China’s economic growth achieving 5.2% facing slowest pace in over 30 years, a stark departure from the rapid expansion that propelled the nation to global prominence. This slowdown, a culmination of various factors, has sent ripples throughout the world, raising concerns about China’s future trajectory and its impact on the global economy.
The slowdown is a complex issue with multiple contributing factors. The COVID-19 pandemic, with its disruptions to supply chains and consumer demand, played a significant role. Government policies, including the zero-COVID approach and property market regulations, further dampened economic activity.
Global economic headwinds, such as rising inflation and interest rates, added to the challenges. Furthermore, demographic changes, including an aging population and declining birth rates, are creating long-term economic pressures.
China’s Economic Slowdown: China Economic Growth Achieving 52 Facing Slowest Pace In Over 30 Years
China’s economic growth has been a defining feature of the global economy for the past three decades. The country’s rapid rise from a developing nation to a global economic powerhouse has been a remarkable feat, transforming the lives of millions of Chinese citizens and reshaping the global economic landscape.
However, in recent years, China’s economic growth has begun to slow, raising concerns about the future trajectory of the world’s second-largest economy.
Historical Trajectory of China’s Economic Growth
China’s economic growth has been nothing short of phenomenal. After the implementation of economic reforms in the late 1970s, the country embarked on a path of rapid industrialization and urbanization. This transformation was driven by a combination of factors, including:
- Open-door policy:China’s opening up to the global economy facilitated trade and investment, attracting foreign capital and technology. This allowed the country to integrate into the global supply chains, leveraging its low-cost labor and abundant resources to manufacture goods for export.
- Market-oriented reforms:The shift towards a more market-based economy provided incentives for businesses to innovate and invest, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
- Investment in infrastructure:China invested heavily in infrastructure projects, including roads, railways, and ports, which improved connectivity and facilitated trade and transportation.
- Human capital development:The country invested in education and training, creating a skilled workforce that could support the burgeoning industries.
These factors combined to drive China’s average annual GDP growth to over 10% for several decades, making it the fastest-growing major economy in the world.
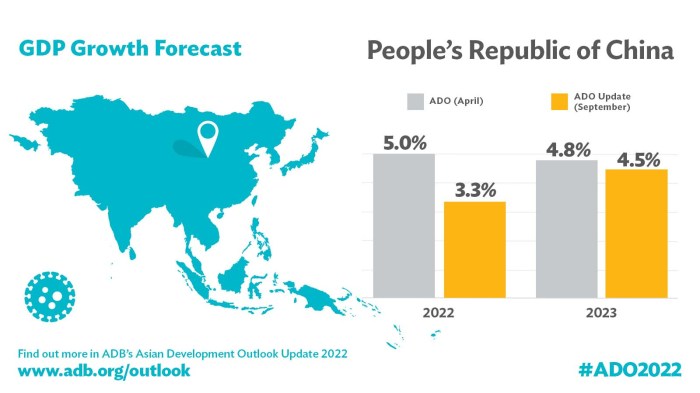
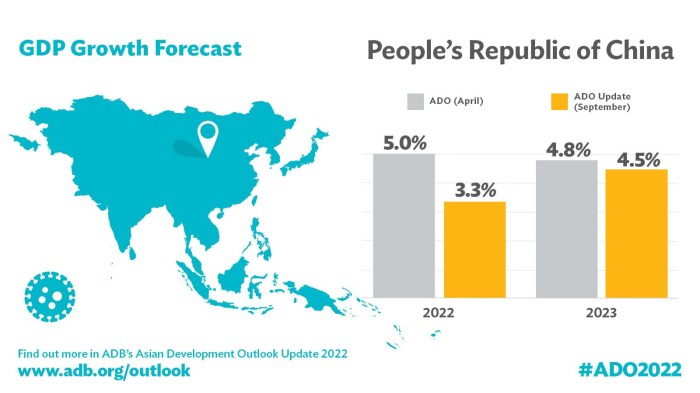
China’s economic growth slowed to 5.2% in the second quarter, its weakest pace in over 30 years. This sluggish growth, fueled by weakening domestic demand and global uncertainties, has investors looking for insights into the potential impact on their portfolios.
Understanding the role of credit rating agencies like Fitch, Moody’s, and S&P is crucial for making informed investment decisions, as they provide valuable assessments of the financial health of countries and companies. Know all about credit rating agencies, a closer look at Fitch, Moody’s, and S&P for smart investments to navigate the complex landscape of global economic trends and make strategic investment choices.
While China faces economic challenges, the insights gleaned from these agencies can help investors stay ahead of the curve and make informed decisions about their portfolios.
Key Economic Indicators Reflecting the Slowdown
China’s economic slowdown is evident in several key economic indicators:
- GDP growth:China’s GDP growth has been steadily declining since 2010. In 2022, the country’s GDP grew by 3%, the slowest pace in over 30 years.
- Industrial production:Industrial production, a key driver of China’s economic growth, has also slowed down. In 2022, industrial production grew by 3.6%, a significant decline from the double-digit growth rates seen in the past.
- Investment:Investment in fixed assets, a measure of capital spending, has also weakened. In 2022, fixed asset investment grew by 5.1%, the lowest level in several years.
Factors Contributing to the Slowdown
China’s economic growth has slowed considerably in recent years, reaching its slowest pace in over three decades. Several factors have contributed to this slowdown, ranging from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic to domestic policy choices and global economic headwinds.
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on China’s economy, disrupting supply chains and dampening consumer demand. The strict “zero-COVID” policy, while initially effective in controlling the spread of the virus, also led to widespread lockdowns and disruptions to businesses and industries.
China’s economic growth reaching 5.2% may be the slowest pace in over 30 years, but it’s not all doom and gloom. While the world grapples with inflation and uncertainty, the US housing market is experiencing a rebound with record-high home prices, as seen in this recent article us housing market rebounds with record high home prices.
This disparity highlights the complex and interconnected nature of global economies, and it’s crucial to remember that even with slowing growth, China still holds significant economic power.
These disruptions caused significant supply chain bottlenecks, particularly in the manufacturing sector, impacting global production and trade. Moreover, the pandemic has also weighed heavily on consumer sentiment, leading to a decline in spending and investment.
Government Policies
China’s government policies, particularly the “zero-COVID” strategy and property market regulations, have played a significant role in the economic slowdown. The “zero-COVID” policy, while aimed at containing the virus, has imposed significant costs on the economy, including production disruptions, reduced consumer spending, and hampered economic activity.
China’s economic growth reaching 5.2% is the slowest pace in over 30 years, a stark contrast to the roaring bull markets we’ve seen in the past. This slowdown comes as Wall Street braces for a slow start to the year, amid lingering concerns over interest rates , which are expected to continue rising.
These global economic headwinds are likely to weigh on China’s growth prospects in the coming months.
The government’s efforts to cool the property market, aimed at preventing a housing bubble, have also had a dampening effect on investment and economic growth. These regulations have led to a decline in property prices and a slowdown in construction activity, impacting related industries and overall economic growth.
Global Economic Headwinds
China’s economy has also been impacted by global economic headwinds, such as rising inflation and interest rates. The war in Ukraine has exacerbated global inflation, leading to higher energy and commodity prices, impacting China’s manufacturing costs and consumer prices. Rising interest rates in major economies have also made it more expensive for Chinese companies to borrow money, slowing down investment and economic growth.
Demographic Changes
China’s demographic changes, including an aging population and declining birth rates, are posing significant challenges to economic growth. The aging population is leading to a shrinking workforce, putting pressure on social security systems and slowing down economic growth. The declining birth rate is also contributing to a shrinking labor pool, further limiting potential economic growth.
Strategies for Addressing the Slowdown

China’s economic slowdown presents a significant challenge, demanding a multifaceted approach to stimulate growth and ensure long-term prosperity. The government has a range of policy options at its disposal, including fiscal and monetary measures, structural reforms, and targeted interventions.
Fiscal and Monetary Policy
Fiscal and monetary policies play a crucial role in stimulating economic activity. The government can use these tools to boost demand, support businesses, and create jobs.
- Increased Government Spending:Investing in infrastructure projects, public services, and social programs can directly create jobs and stimulate economic activity. This approach has been effective in the past, as seen during the 2008-2009 global financial crisis when China’s massive infrastructure investment helped to maintain growth.
- Tax Cuts:Reducing taxes for businesses and individuals can increase disposable income, boost consumer spending, and encourage investment. The government can also consider targeted tax breaks for specific industries or regions to stimulate growth in specific sectors.
- Lower Interest Rates:Reducing interest rates can make borrowing more affordable for businesses and consumers, encouraging investment and spending. However, this approach needs to be carefully managed to avoid excessive inflation.
Effectiveness of Past Interventions
Past government interventions have had mixed results. While some measures, such as infrastructure investment, have been effective in stimulating short-term growth, others, such as tax cuts, have had less impact. The effectiveness of any intervention depends on factors such as the specific policy implemented, the economic context, and the government’s ability to implement the policy effectively.
Structural Reforms, China economic growth achieving 52 facing slowest pace in over 30 years
Addressing long-term economic challenges requires structural reforms that enhance productivity, innovation, and income equality. These reforms can create a more sustainable and inclusive growth path for China.
- Promoting Innovation:China needs to invest in research and development, foster a culture of innovation, and create a supportive ecosystem for startups and technology companies. This can involve increasing government funding for R&D, promoting collaboration between universities and businesses, and simplifying regulations for startups.
- Improving Productivity:China can improve productivity by investing in education and training, upgrading infrastructure, and promoting automation and digitalization. This requires a focus on skills development, access to technology, and efficient infrastructure.
- Addressing Income Inequality:China’s widening income gap poses a significant challenge to social stability and economic growth. The government can address this issue by implementing progressive taxation, strengthening social safety nets, and investing in education and healthcare for all.
Outlook for China’s Economy
The recent slowdown in China’s economic growth has raised concerns about the future trajectory of the world’s second-largest economy. While the immediate outlook remains uncertain, various forecasts and analyses offer insights into potential scenarios for China’s economic performance in the coming years.
Forecasts for China’s Economic Growth
Forecasts for China’s economic growth vary widely, reflecting the complexity of the economic landscape and the numerous factors at play.
- Optimistic Scenario:Some economists predict that China’s economy will rebound in the coming years, driven by government stimulus measures, continued technological advancements, and a gradual recovery in global demand. They anticipate a return to growth rates of around 5-6% by 2025, fueled by robust domestic consumption and investments in infrastructure and green technologies.
For instance, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) projects China’s GDP growth to reach 5.2% in 2023 and 4.5% in 2024, driven by a gradual recovery in domestic demand and a rebound in global trade. This optimistic outlook relies on the assumption that the government will effectively manage its economic policies, stimulate domestic consumption, and promote innovation to drive sustainable growth.
- Pessimistic Scenario:Others are more cautious, citing persistent structural challenges, such as an aging population, rising debt levels, and geopolitical tensions. They predict a slower pace of growth, potentially below 4% in the coming years. This pessimistic outlook highlights the need for China to address these structural issues and implement comprehensive reforms to ensure long-term economic stability and inclusivity.
For example, the World Bank predicts China’s GDP growth to slow down to 4.3% in 2023 and 4.0% in 2024, citing the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, global economic uncertainty, and structural challenges related to demographics and debt. This scenario emphasizes the need for China to focus on structural reforms, enhance productivity, and promote innovation to maintain a healthy growth trajectory.
Potential for Sustainable and Inclusive Economic Growth
China’s ability to achieve sustainable and inclusive economic growth in the long term depends on its capacity to address several key challenges:
- Demographic Transition:China is facing a rapidly aging population, which is putting pressure on its social security system and labor market. The government needs to implement policies that support an aging workforce, encourage innovation, and promote a more inclusive and sustainable economic model.
- Debt Management:China’s high level of debt, particularly in the corporate and local government sectors, poses a significant risk to financial stability. The government must prioritize debt reduction, improve financial regulation, and promote a more sustainable financial system.
- Income Inequality:While China has made significant progress in reducing poverty, income inequality remains a persistent challenge. The government needs to implement policies that promote equitable access to education, healthcare, and employment opportunities, ensuring that the benefits of economic growth are shared more widely.
- Environmental Sustainability:China’s rapid economic growth has come at a significant environmental cost. The government must prioritize environmental protection, invest in renewable energy, and promote sustainable consumption patterns to ensure a healthy and livable environment for future generations.
Challenges and Opportunities for China’s Economic Development
China is navigating a new era of economic development, characterized by increasing global competition, technological advancements, and geopolitical shifts. The country faces both challenges and opportunities in this new landscape.
- Technological Competition:China is striving to become a global leader in technology, particularly in areas such as artificial intelligence, 5G, and quantum computing. However, it faces fierce competition from the United States and other advanced economies.
- Geopolitical Tensions:The trade war with the United States and other geopolitical tensions have created uncertainty and disruption for Chinese businesses. The government must navigate these challenges strategically to protect its economic interests and foster a more stable global environment.
- Domestic Reforms:China needs to continue implementing reforms to improve its economic governance, enhance market efficiency, and promote innovation. These reforms are essential for unlocking the country’s full economic potential and ensuring sustainable and inclusive growth.
- Global Cooperation:China can leverage its economic strength and growing influence to promote global cooperation on issues such as climate change, trade, and development. By working with other countries, China can contribute to a more stable and prosperous world.






