Bitcoin Hash Rate Dips 34% in Texas Freeze: Impact on Mining Industry
Bitcoin hash rate dips 34 in texas freeze impact on mining industry – Bitcoin hash rate dips 34% in Texas freeze: Impact on mining industry. This event shook the crypto world, exposing the vulnerability of the mining industry to extreme weather conditions. The Texas freeze, a record-breaking cold snap, crippled power grids, leaving millions without electricity, including Bitcoin miners who rely heavily on cheap energy.
This unexpected shutdown had a significant impact on the Bitcoin network’s security and stability, highlighting the need for greater resilience in the face of unpredictable events.
The Texas freeze revealed the fragility of the Bitcoin mining industry’s reliance on a single energy source. Miners, often operating in geographically concentrated locations, faced significant operational disruptions, leading to substantial financial losses. The incident prompted discussions about the long-term sustainability of the Bitcoin mining industry and the need to diversify energy sources to mitigate future disruptions.
The Texas Freeze and its Impact on Bitcoin Mining
The recent severe winter storm that hit Texas in February 2021, known as the Texas Freeze, had a significant impact on the Bitcoin mining industry. The extreme weather conditions and subsequent power outages disrupted operations for many mining facilities, leading to a substantial drop in the Bitcoin hashrate.
Impact of Power Outages
The Texas Freeze caused widespread power outages across the state, including in areas where Bitcoin mining facilities were located. Many miners were forced to shut down their operations due to the lack of electricity, resulting in a significant reduction in the Bitcoin hashrate.
The hashrate is a measure of the total computing power used to process Bitcoin transactions, and a decrease in hashrate indicates a decline in the network’s security and efficiency.
Challenges Faced by Miners, Bitcoin hash rate dips 34 in texas freeze impact on mining industry
Miners faced several challenges during the Texas Freeze, including:
- Power Outages:The most significant challenge was the prolonged power outages, which forced many miners to shut down their operations.
- Extreme Weather Conditions:The extreme cold temperatures also posed a threat to mining equipment, potentially causing damage or malfunction.
- Supply Chain Disruptions:The storm also disrupted supply chains, making it difficult for miners to obtain essential equipment and supplies.
Energy Consumption of Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is an energy-intensive process, relying heavily on electricity to power the computers that solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions. The energy consumption of Bitcoin mining has been a subject of debate, with some arguing that it is unsustainable and contributes to environmental problems.
The recent dip in Bitcoin’s hash rate, attributed to the Texas freeze’s impact on mining operations, highlights the fragility of the industry’s reliance on specific geographic locations. This situation, coupled with the Biden administration’s growing concern over the dominance of tech giants in the stock market, as reported by The Venom Blog , raises questions about the future of decentralized technologies and their potential vulnerability to external factors.
The Texas freeze serves as a stark reminder that even the most robust crypto infrastructure can be susceptible to unforeseen events, emphasizing the need for greater diversification and resilience within the mining industry.
The energy consumption of Bitcoin mining is estimated to be around 130 terawatt-hours per year, which is comparable to the annual energy consumption of a small country.
The Texas Freeze highlighted the vulnerability of the Bitcoin mining industry to power outages and extreme weather events. It also raised concerns about the environmental impact of Bitcoin mining, given its high energy consumption.
Bitcoin Hash Rate Fluctuations
The Bitcoin hash rate is a crucial metric that reflects the computational power dedicated to securing the Bitcoin network. It’s a testament to the collective effort of miners worldwide, who contribute their processing power to solve complex mathematical problems and validate transactions on the blockchain.
A higher hash rate indicates a more robust and secure network, making it harder for malicious actors to manipulate or compromise the system.
Impact of the Texas Freeze on Bitcoin Hash Rate
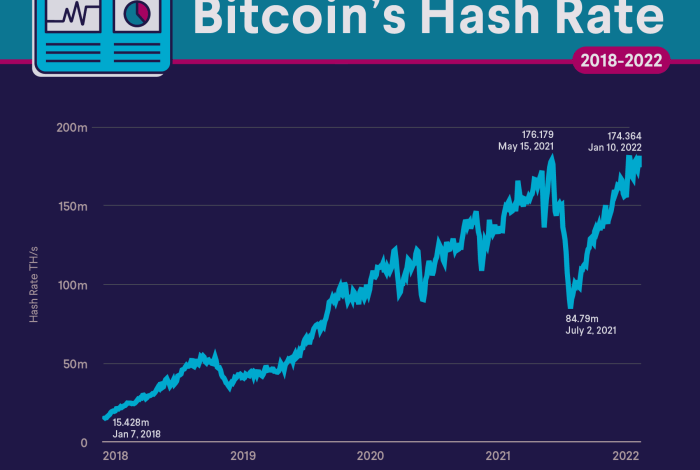
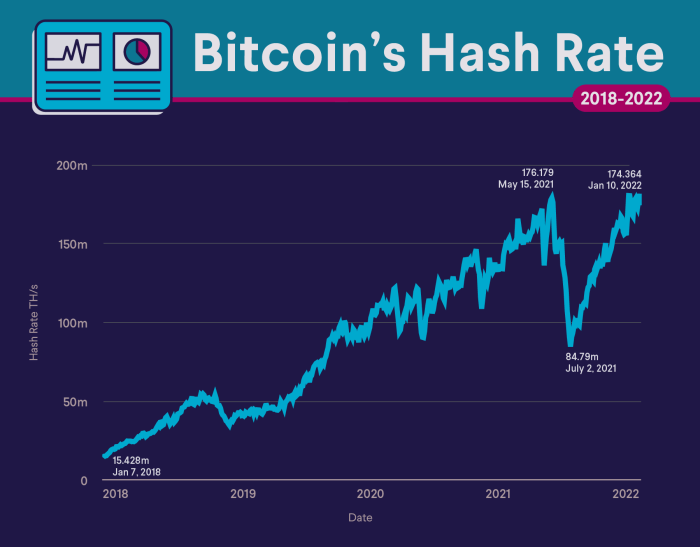
The Texas freeze in February 2021 had a significant impact on the Bitcoin hash rate, leading to a 34% dip. This sharp decline was attributed to the widespread power outages that affected many mining operations in the state. Texas, known for its abundant and affordable energy resources, has become a hub for Bitcoin mining.
However, the extreme weather conditions disrupted the mining infrastructure, forcing many miners to temporarily shut down their operations.
The hash rate drop during the Texas freeze highlights the vulnerability of the Bitcoin network to external factors, especially those related to energy supply.
Hash Rate Fluctuations Before and After the Freeze
The Bitcoin hash rate has historically been subject to fluctuations, influenced by factors such as the price of Bitcoin, the cost of electricity, and the availability of mining hardware. Before the Texas freeze, the hash rate had been steadily increasing, reflecting the growing interest in Bitcoin mining.
However, the freeze caused a sharp decline, with the hash rate dropping from an all-time high of 180 exahashes per second (EH/s) to around 120 EH/s. Following the freeze, the hash rate gradually recovered, although it took several weeks for it to return to pre-freeze levels.
The recent Texas freeze that caused a 34% dip in Bitcoin’s hash rate highlighted the vulnerability of the mining industry to extreme weather events. While this incident has raised concerns about the industry’s resilience, it also underscores the growing demand for data centers, as evidenced by the 3 billion dollar equipment supply deal secured by Schneider Electric with Compass Datacenters.
This deal signifies a commitment to fuel the growth of AI-powered data centers, a sector poised to benefit from the shift towards more distributed and resilient infrastructure solutions. It’s a clear indication that while the Bitcoin mining industry faces challenges, the broader data center market remains robust and is likely to continue attracting significant investments.
This recovery was driven by the resumption of mining operations in Texas, as well as the ongoing expansion of mining activities in other regions.
- Before the Freeze:The hash rate had been steadily increasing, reflecting the growing interest in Bitcoin mining.
- During the Freeze:The hash rate experienced a significant drop due to power outages in Texas.
- After the Freeze:The hash rate gradually recovered as mining operations resumed and expanded in other regions.
The Texas freeze served as a stark reminder of the potential impact of external factors on the Bitcoin network. While the hash rate has since recovered, it highlights the importance of diversifying mining operations and ensuring a resilient energy infrastructure.
Impact on Mining Operations: Bitcoin Hash Rate Dips 34 In Texas Freeze Impact On Mining Industry
The Texas freeze had a significant impact on Bitcoin mining operations, causing widespread disruptions and financial losses for miners. The sudden drop in temperatures and subsequent power outages forced many mining farms to shut down, resulting in a substantial decrease in the Bitcoin hash rate.
Mining Farms Affected
The Texas freeze affected numerous Bitcoin mining farms, particularly those located in the state’s ERCOT (Electric Reliability Council of Texas) grid. Some of the prominent mining farms that experienced disruptions include:
- Riot Blockchain
- Core Scientific
- Whinstone US
- Compute North
These farms, along with many others, were forced to halt operations due to power outages and freezing temperatures.
The recent Texas freeze, which caused a 34% dip in Bitcoin’s hash rate, is a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in the mining industry. While this event highlights the need for diversification and resilience, it’s interesting to note that Gen Z investors, as reported in this article , are increasingly drawn to growth-oriented sectors like technology and housing.
This focus on growth suggests that the long-term potential of Bitcoin, despite its recent setbacks, remains attractive to younger investors who are likely to play a significant role in shaping the future of the cryptocurrency landscape.
Financial Losses
The downtime and operational disruptions caused by the freeze resulted in significant financial losses for miners. The primary sources of these losses include:
- Lost Mining Revenue:Miners lost the opportunity to earn Bitcoin rewards during the downtime, impacting their profitability. For example, Riot Blockchain reported a 30% decrease in its Bitcoin production due to the freeze.
- Operational Costs:Even with operations halted, miners still incurred costs related to facility maintenance, staff salaries, and energy bills.
- Equipment Damage:The extreme cold and power fluctuations could have damaged mining equipment, leading to repair or replacement costs.
The extent of financial losses varied depending on the size and location of the mining farm, as well as the duration of the downtime.
Long-Term Consequences
The Texas freeze highlighted the vulnerabilities of the Bitcoin mining industry to extreme weather events and energy grid instability. This incident has led to concerns about the long-term sustainability of mining operations in regions prone to such disruptions.
- Increased Focus on Energy Resilience:Miners are likely to invest in more resilient energy sources, such as on-site generation and energy storage solutions, to mitigate the impact of future disruptions.
- Diversification of Mining Locations:The industry may see a shift towards mining operations in regions with more stable energy grids and climates. This could lead to a geographical diversification of mining activities.
- Regulatory Scrutiny:The freeze could prompt regulators to scrutinize the energy consumption and environmental impact of Bitcoin mining, potentially leading to stricter regulations.
The Texas freeze served as a wake-up call for the Bitcoin mining industry, emphasizing the need for greater resilience and adaptability in the face of unpredictable events.
Implications for the Bitcoin Network
The significant drop in Bitcoin’s hash rate during the Texas freeze raised concerns about the network’s security and stability. A lower hash rate means fewer miners are actively validating transactions and securing the blockchain, potentially increasing the risk of attacks.
Network Security and Stability
The hash rate is a crucial indicator of the Bitcoin network’s security. It represents the combined computational power of all miners working to solve complex mathematical problems and add new blocks to the blockchain. A higher hash rate makes it more difficult for attackers to double-spend coins or manipulate the network.
During the Texas freeze, the hash rate dipped significantly, potentially exposing the network to vulnerabilities. A lower hash rate could theoretically make it easier for attackers to launch a 51% attack, where a single entity controls more than half of the network’s computational power and could potentially manipulate the blockchain.
Potential Vulnerabilities
While a 51% attack remains highly unlikely, even with a reduced hash rate, the freeze highlighted potential vulnerabilities. A concentrated mining pool in a single region, like Texas, could become a target for malicious actors seeking to exploit a temporary weakness.
Resilience of the Network
Despite the hash rate dip, the Bitcoin network remained largely resilient during the freeze. The network’s decentralized nature and the diverse geographic distribution of miners helped mitigate the impact of the outage in Texas. Miners in other regions were able to compensate for the reduced hash rate, ensuring the network’s continued operation.The Texas freeze serves as a reminder of the importance of geographic diversity and network resilience.
The incident highlighted the need for miners to spread their operations across multiple regions to mitigate the risk of localized outages.
Future Considerations for Bitcoin Mining
The Texas freeze highlighted the vulnerability of Bitcoin mining to extreme weather events. To ensure the long-term sustainability and resilience of the industry, it’s crucial to consider strategies for mitigating future disruptions and explore alternative energy sources and infrastructure.
Strategies for Mitigating Future Weather Events
To reduce the impact of future weather events, Bitcoin mining operations can implement several strategies:
- Diversification of Mining Locations:Expanding mining operations to regions with diverse climates and weather patterns can minimize the impact of localized events. This strategy spreads risk and ensures continued operation even if one location experiences a disruption.
- Enhanced Power Infrastructure:Investing in robust power infrastructure, including backup power sources like generators and batteries, can provide redundancy during outages. This ensures continuous mining operations even during extreme weather events.
- Improved Weather Forecasting and Early Warning Systems:Implementing advanced weather forecasting systems and early warning mechanisms can provide miners with ample time to prepare for potential disruptions. This allows for the timely relocation of mining equipment or the implementation of mitigation measures.
Alternative Energy Sources and Infrastructure
Exploring alternative energy sources and infrastructure can significantly enhance the sustainability and resilience of Bitcoin mining:
- Renewable Energy Sources:Transitioning to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power can reduce reliance on traditional fossil fuels and mitigate the environmental impact of mining. This also provides a more sustainable and cost-effective long-term solution.
- Energy Storage Solutions:Implementing energy storage solutions like battery systems can provide a buffer during periods of low renewable energy generation, ensuring continuous mining operations. This also reduces reliance on the grid and increases energy independence.
- Microgrid Systems:Utilizing microgrid systems can provide a localized and self-sufficient energy source for mining operations. These systems can operate independently from the main grid, providing greater resilience during outages.
Improving Resilience and Sustainability
Several measures can be taken to improve the overall resilience and sustainability of the Bitcoin mining industry:
- Industry-Wide Collaboration:Encouraging collaboration and knowledge sharing among miners can facilitate the development and implementation of best practices for mitigating weather events and enhancing energy efficiency. This can also lead to the creation of industry standards for sustainable mining practices.
- Technological Advancements:Investing in research and development to improve mining hardware efficiency and reduce energy consumption can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of Bitcoin mining. This can also lead to the development of new and innovative mining technologies.
- Regulatory Frameworks:Establishing clear and comprehensive regulatory frameworks that encourage sustainable mining practices and incentivize the adoption of renewable energy sources can promote the long-term growth and resilience of the industry. This can also ensure the responsible use of resources and minimize the environmental impact of mining.






