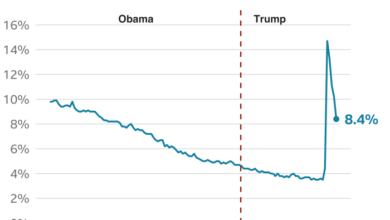
Bidens Factory Boom: Sustaining Growth Amidst Challenges
Biden administrations push to sustain factory boom amidst challenges an inclusive economic vision – Biden’s administration push to sustain factory boom amidst challenges an inclusive economic vision, is a bold initiative aimed at revitalizing American manufacturing. This strategy, built on the foundation of economic growth and national security, seeks to create jobs, stimulate innovation, and bolster the domestic economy.
The Biden administration’s vision goes beyond mere factory construction, aiming for an inclusive approach that benefits workers, communities, and businesses across all sectors.
The initiative, however, faces formidable obstacles. Supply chain disruptions, labor shortages, and rising inflation present significant hurdles. Global competition and the potential for reshoring manufacturing operations add further complexity. Despite these challenges, the Biden administration remains committed to its vision of a thriving manufacturing sector, one that contributes to a more equitable and prosperous nation.
Challenges Facing the Factory Boom: Biden Administrations Push To Sustain Factory Boom Amidst Challenges An Inclusive Economic Vision

The Biden administration’s push to revitalize American manufacturing faces significant obstacles, threatening to dampen the factory boom’s momentum. While the initiative aims to create jobs and boost domestic production, various challenges, including supply chain disruptions, labor shortages, and rising inflation, pose substantial hurdles.
The Biden administration’s push to sustain a factory boom amidst challenges is fueled by an inclusive economic vision. This vision aims to create a more equitable and prosperous society, and it’s encouraging to see that the US dollar is holding steady in the forex market, as reported in this recent article , amid Fed rate hike expectations and debt ceiling optimism.
This stability provides a solid foundation for continued economic growth and progress towards the administration’s goals.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions have become a major bottleneck for manufacturers, particularly in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. These disruptions have led to delays in the delivery of raw materials, components, and finished goods, increasing costs and impacting production schedules.
The Biden administration’s push to sustain the factory boom amidst challenges is a complex undertaking, aiming for an inclusive economic vision. While some focus on traditional manufacturing, a different kind of boom is brewing in the digital realm. The Senate’s most prominent advocate for cryptocurrency, known as the “Crypto Queen,” has unveiled a far-reaching new bill focused on Bitcoin, raising questions about its potential impact on the future of finance and its integration with traditional economic models.
This shift towards digital assets adds another layer to the Biden administration’s economic agenda, forcing them to navigate the evolving landscape of innovation and regulation.
- Global Shipping Congestion:Port congestion and shipping delays have hampered the flow of goods, leading to longer lead times and higher transportation costs. For instance, the average time for a container ship to unload at the Port of Los Angeles in 2022 was nearly double the pre-pandemic levels.
The Biden administration’s push to sustain the factory boom amidst challenges is driven by an inclusive economic vision, one that aims to uplift communities and create opportunities for all. This vision is echoed in the booming success of the Indian Premier League (IPL), where the money game of Indian cricket how IPL scores big in finances fuels a massive industry, generating jobs and enriching local economies.
Just as the IPL demonstrates the power of investment in a shared vision, the Biden administration hopes to unlock similar potential in American manufacturing, building a future where prosperity is accessible to all.
- Microchip Shortage:The ongoing shortage of semiconductors, crucial components in electronics and automobiles, has crippled production lines across industries. The global chip shortage has been attributed to factors such as increased demand, factory closures due to the pandemic, and geopolitical tensions.
- Supply Chain Diversification:The Biden administration’s focus on reshoring manufacturing has led to a shift in sourcing strategies, requiring companies to identify new suppliers and establish new supply chains, a process that takes time and investment.
Labor Shortages
The manufacturing sector faces a growing challenge in attracting and retaining skilled workers. This labor shortage is driven by several factors:
- Aging Workforce:A significant portion of the manufacturing workforce is nearing retirement, creating a gap in experienced personnel.
- Perception of Manufacturing Jobs:The perception of manufacturing jobs as low-paying and physically demanding has deterred younger generations from entering the field.
- Skills Gap:The rapid evolution of manufacturing technologies has created a skills gap, making it difficult for companies to find workers with the necessary qualifications.
Rising Inflation
Soaring inflation has added another layer of complexity to the factory boom. Higher prices for raw materials, energy, and transportation have squeezed profit margins and increased the cost of production.
- Raw Material Costs:The price of key raw materials, such as steel, aluminum, and copper, has risen significantly in recent years, driven by factors such as increased demand and supply chain disruptions.
- Energy Costs:The rising cost of energy, particularly natural gas and oil, has increased manufacturing costs and reduced competitiveness.
- Transportation Costs:Fuel price increases and shipping delays have driven up transportation costs, adding to the overall cost of production.
Global Competition
The US manufacturing sector faces intense competition from global players, particularly from China, which has become a manufacturing powerhouse.
- Lower Labor Costs:China’s lower labor costs give it a competitive advantage in manufacturing, making it challenging for US companies to compete on price.
- Government Support:The Chinese government provides significant support to its manufacturing sector through subsidies, tax breaks, and other incentives.
- Technological Advancement:China has made significant investments in research and development, enabling it to produce high-quality goods at competitive prices.
An Inclusive Economic Vision
The Biden administration’s push for a factory boom is not just about creating jobs and boosting the economy. It’s also about ensuring that the benefits of economic growth are shared broadly and equitably. This “inclusive economic vision” aims to create a more prosperous and just society by tackling systemic inequalities and empowering workers, communities, and businesses across various sectors.
Strategies for Inclusive Economic Growth
The Biden administration’s approach to economic growth is fundamentally different from that of previous administrations. It focuses on creating a more equitable and sustainable economy by prioritizing investments in infrastructure, clean energy, and workforce development. The administration’s approach seeks to ensure that the benefits of economic growth are shared broadly and equitably.
Here are some key strategies:
- Investing in Infrastructure:The Biden administration’s infrastructure plan aims to create millions of jobs while modernizing roads, bridges, airports, and broadband internet access. This investment is expected to benefit workers in construction, manufacturing, and other sectors, while also improving the quality of life for communities across the country.
- Promoting Clean Energy:The administration’s commitment to combating climate change includes substantial investments in clean energy technologies, such as solar and wind power. This will create new jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance, while also reducing reliance on fossil fuels and promoting environmental sustainability.
- Strengthening Labor Unions:The Biden administration supports labor unions and their role in negotiating fair wages and benefits for workers. The administration has also taken steps to protect workers’ rights to organize and bargain collectively, aiming to improve working conditions and empower workers to advocate for their interests.
- Investing in Workforce Development:The administration’s focus on workforce development includes programs that provide training and education for workers, helping them acquire the skills needed for in-demand jobs. This initiative aims to equip workers with the skills necessary to participate in the modern economy and compete for well-paying jobs.
- Promoting Small Business Growth:The Biden administration recognizes the importance of small businesses to the economy. The administration’s policies aim to support small business growth by providing access to capital, technical assistance, and mentorship programs. This focus on small business development fosters entrepreneurship and innovation, contributing to economic growth and job creation.
Case Studies and Examples
The Biden administration’s factory boom initiative has resulted in a number of successful projects across various industries, demonstrating the potential for revitalizing American manufacturing and creating jobs. These projects serve as compelling case studies, highlighting the positive impact of targeted investments and policy changes on local communities and the broader economy.
Examples of Successful Factory Projects
The following table showcases specific examples of successful factory projects or initiatives implemented under the Biden administration’s factory boom initiative:
| Industry | Location | Investment Amount | Job Creation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Vehicle Battery Production | Lordstown, Ohio | $2.3 billion | 1,100 |
| Semiconductor Manufacturing | Phoenix, Arizona | $12 billion | 3,000 |
| Solar Panel Manufacturing | Atlanta, Georgia | $1.7 billion | 2,000 |
Impact on Local Communities and the Broader Economy
These projects have had a significant impact on local communities, revitalizing economies and creating new opportunities for residents. For example, the electric vehicle battery production facility in Lordstown, Ohio, has brought new jobs and investment to a community that had been struggling after the closure of a General Motors plant.
The semiconductor manufacturing facility in Phoenix, Arizona, has boosted the local economy and helped to address the global chip shortage.
Challenges and Opportunities
While these projects have been successful, they have also faced challenges, such as the need for a skilled workforce and the potential for environmental impact. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration. For instance, the semiconductor manufacturing facility in Phoenix, Arizona, has partnered with local educational institutions to train workers in the skills needed for this industry.
“These projects demonstrate the potential for revitalizing American manufacturing and creating jobs, but it’s important to address the challenges and opportunities that come with them.”
President Joe Biden
Future Outlook and Sustainability

The Biden administration’s factory boom initiative, aimed at revitalizing American manufacturing, faces a complex landscape of potential challenges and opportunities. While the initiative has shown initial promise, its long-term sustainability hinges on addressing several critical factors, including evolving economic trends, technological advancements, and global events.
Assessing the Long-Term Impact
To gauge the long-term effectiveness of the factory boom initiative, a comprehensive framework is needed that considers its economic, social, and environmental impact. This framework should encompass the following key aspects:
- Economic Performance: Evaluating the initiative’s contribution to job creation, GDP growth, and overall economic competitiveness. Tracking metrics like manufacturing output, investment in research and development, and worker productivity is crucial.
- Social Equity: Assessing the initiative’s impact on income inequality, access to quality jobs, and community development. Examining the distribution of benefits across different regions and demographics is essential.
- Environmental Sustainability: Evaluating the initiative’s impact on environmental pollution, resource consumption, and climate change. Assessing the adoption of green manufacturing practices, renewable energy sources, and sustainable supply chains is crucial.
Impact of Future Economic Trends
The initiative’s success is intertwined with the trajectory of future economic trends. The potential impact of these trends on the factory boom initiative should be carefully considered:
- Global Economic Slowdown: A global economic downturn could significantly impact demand for manufactured goods, potentially hindering the growth of the factory boom initiative. The initiative’s success would rely on its ability to adapt to changing market conditions and maintain competitiveness in a challenging global environment.
- Inflation and Rising Costs: Persistent inflation and rising input costs could erode the profitability of manufacturing businesses, potentially hindering the initiative’s growth. The initiative would need to explore strategies to mitigate these challenges, such as investing in automation and efficiency improvements.
- Shifting Consumer Preferences: Evolving consumer preferences towards sustainable products and services could present both opportunities and challenges for the factory boom initiative. Adapting to these trends and investing in green manufacturing technologies would be crucial for long-term success.
Impact of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements will play a significant role in shaping the future of manufacturing and the factory boom initiative. The following technological trends should be considered:
- Automation and Robotics: The increasing adoption of automation and robotics could lead to significant job displacement in manufacturing. The initiative would need to invest in worker training and retraining programs to ensure a skilled workforce capable of operating and maintaining advanced technologies.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered technologies could revolutionize manufacturing processes, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. The initiative would need to support research and development in AI and explore its potential applications in manufacturing.
- 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing: Advances in 3D printing and additive manufacturing could enable decentralized production and customized manufacturing. The initiative could explore opportunities to leverage these technologies for on-demand production and localized manufacturing.
Impact of Global Events, Biden administrations push to sustain factory boom amidst challenges an inclusive economic vision
Global events can have a significant impact on the factory boom initiative. The following potential events should be considered:
- Geopolitical Tensions: Escalating geopolitical tensions, such as trade wars or conflicts, could disrupt global supply chains and hinder the growth of the factory boom initiative. The initiative would need to prioritize domestic supply chains and explore strategies to mitigate the impact of global disruptions.
- Climate Change: The effects of climate change, such as extreme weather events and resource scarcity, could pose significant challenges to manufacturing operations. The initiative would need to prioritize sustainable manufacturing practices and invest in climate-resilient infrastructure.
- Pandemics: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the vulnerability of global supply chains. The initiative would need to consider strategies to enhance supply chain resilience and ensure access to critical resources in the event of future pandemics.