Central Banks Signal Rate Hikes, Challenging Wall Street
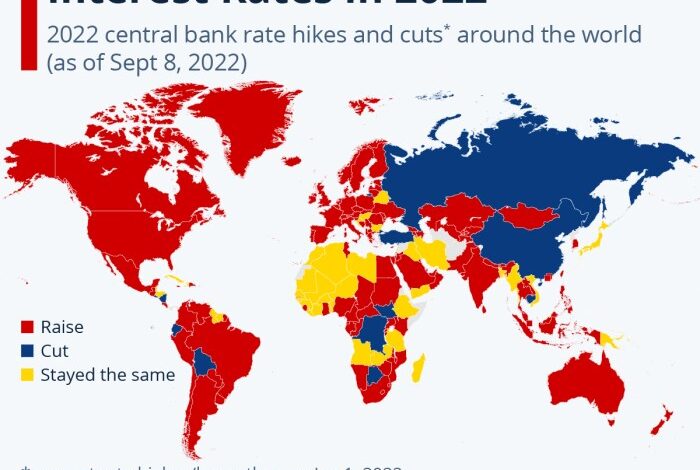
Central banks signal continued rate hikes challenging wall streets sentiment – Central banks signal continued rate hikes challenging Wall Street sentiment sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Central banks across the globe are tightening their monetary policies, signaling continued rate hikes in the face of persistent inflation.
This move, while aimed at curbing price pressures, has sent ripples through financial markets, leaving investors and economists alike pondering the potential implications for economic growth and asset prices.
The decision to raise interest rates is a complex one, driven by a delicate balancing act between managing inflation and supporting economic growth. Central bankers are navigating a challenging landscape, where the specter of a recession looms while inflation remains stubbornly high.
The impact of these rate hikes is far-reaching, affecting everything from housing markets to consumer spending and business investment. As central banks continue to raise rates, the question on everyone’s mind is whether these actions will be enough to tame inflation without triggering a recession.
The answer remains uncertain, but the implications for the global economy are significant.
Central Bank Actions and Rate Hikes
Central banks around the world are currently engaged in a coordinated effort to combat inflation by raising interest rates. This strategy aims to cool down economic activity and curb price increases. The rationale behind these rate hikes is multifaceted, driven by a combination of factors, including persistently high inflation, strong economic growth, and a robust labor market.
Rationale for Continued Rate Increases
The primary objective of central banks in raising interest rates is to tame inflation. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of consumers and businesses, leading to economic uncertainty and instability. By increasing borrowing costs, central banks aim to discourage spending and investment, thereby reducing demand and putting downward pressure on prices.Another factor influencing rate hikes is strong economic growth.
Central banks are sending a clear message: interest rates are going up, and Wall Street is feeling the pressure. This kind of environment can make investors nervous, but it’s also creating opportunities. For example, KKR recently announced the acquisition of PayPal’s buy now, pay later loans, valued at nearly $44 billion kkr announces acquisition of paypal buy now pay later loans valued at nearly 44 billion.
This kind of deal shows that some investors are seeing value in these uncertain times, and that might be a sign that the market is starting to find its footing.
When the economy is expanding rapidly, it can lead to increased demand for goods and services, which can fuel inflation. Central banks use rate increases to moderate economic growth and prevent it from overheating.The strength of the labor market is also a significant consideration for central banks.
A tight labor market, characterized by low unemployment and high job openings, can lead to upward pressure on wages. As wages rise, businesses may pass these costs onto consumers through higher prices, further contributing to inflation.
Impact of Rate Hikes on the Economy
Rate hikes can have a ripple effect throughout the economy, influencing various sectors.
Impact on Housing
Higher interest rates can make it more expensive for individuals to purchase homes. This can lead to a slowdown in home sales and price growth, as buyers become more hesitant to take on larger mortgage payments.
Impact on Consumer Spending
Rising interest rates can also affect consumer spending. As borrowing costs increase, consumers may become more cautious about making large purchases, such as cars or appliances. This can lead to a decline in overall consumer spending, which can have a negative impact on businesses.
Impact on Business Investment
Businesses may also be less likely to invest in new projects or expansions when interest rates are high. This is because the cost of borrowing money to fund these ventures increases, making them less attractive. A decline in business investment can hinder economic growth and job creation.
While central banks continue to signal further rate hikes, challenging Wall Street’s sentiment, a glimmer of hope emerged in the Canadian market. Canadian stocks surged as speculation grew that the Fed might pause its rate hikes, potentially easing the pressure on global markets.
This suggests that despite the ongoing uncertainty, investors are still looking for opportunities to capitalize on potential shifts in monetary policy.
Wall Street Sentiment and Market Reactions: Central Banks Signal Continued Rate Hikes Challenging Wall Streets Sentiment

Wall Street’s sentiment is currently cautious, with investors closely monitoring central bank signals and their potential impact on the economy and financial markets. Recent rate hike announcements have triggered significant market reactions, highlighting the sensitivity of investors to monetary policy shifts.
Impact of Rate Hikes on Financial Indicators
Rate hikes influence various financial indicators, impacting investor behavior and market dynamics. Recent announcements have led to notable changes in:
- Stock Prices:Rate hikes typically increase borrowing costs for businesses, potentially slowing economic growth and reducing corporate earnings. Consequently, stock prices tend to decline in response to rate hike announcements. For instance, the S&P 500 index experienced a dip following the Federal Reserve’s recent rate hike, reflecting investor concerns about potential economic slowdown.
- Bond Yields:As interest rates rise, bond yields generally increase. This is because investors demand higher returns on fixed-income securities to compensate for the increased opportunity cost of holding them. Recent rate hikes have pushed bond yields upward, leading to a decline in bond prices.
- Currency Exchange Rates:Rate hikes can strengthen a country’s currency. This is because higher interest rates make the currency more attractive to foreign investors seeking higher returns. For example, the US dollar has appreciated against other currencies following the Federal Reserve’s rate hikes, reflecting investor confidence in the US economy.
The central banks’ hawkish stance on interest rates continues to send ripples through Wall Street, but amidst the uncertainty, there’s a valuable lesson to be learned from Netflix’s success in navigating social and political issues. As explored in this insightful article , their adaptability and strategic approach can offer valuable insights for businesses facing volatile market conditions.
Ultimately, navigating these turbulent waters requires a blend of financial prudence and a keen understanding of the evolving cultural landscape, just like Netflix has demonstrated.
Implications of Continued Rate Hikes on Investor Confidence and Market Volatility
Continued rate hikes can significantly impact investor confidence and market volatility. As interest rates rise, investors may become more risk-averse, leading to:
- Reduced Investment Activity:Higher borrowing costs can deter businesses from investing, potentially slowing economic growth and dampening investor enthusiasm.
- Increased Market Volatility:Uncertainty about the economic outlook and the potential impact of rate hikes can lead to increased market volatility. Investors may engage in more frequent trading and adjust their portfolios based on perceived risks, contributing to heightened market fluctuations.
- Potential for a Recession:Aggressive rate hikes can potentially trigger a recession by slowing economic growth too rapidly. While central banks aim to control inflation, their actions can have unintended consequences if they overtighten monetary policy.
Economic Outlook and Growth Prospects

The aggressive rate hike strategy adopted by central banks to combat inflation presents a complex economic landscape. While aiming to cool down the economy and curb price increases, these actions also carry the risk of unintended consequences. Understanding the potential economic impact of sustained rate hikes is crucial for navigating this challenging environment.
Impact on Inflation
Sustained rate hikes aim to curb inflation by making borrowing more expensive, thus reducing consumer spending and slowing down economic activity. This can lead to a decrease in demand for goods and services, which, in turn, can put downward pressure on prices.
However, the effectiveness of rate hikes in controlling inflation depends on various factors, including the underlying causes of inflation, the responsiveness of consumers and businesses to higher interest rates, and the overall state of the economy. For instance, if inflation is driven by supply chain disruptions or geopolitical events, rate hikes might have a limited impact on price levels.
Additionally, if consumers and businesses are less sensitive to interest rate changes, the desired cooling effect on the economy might be delayed or muted.
Impact on Economic Growth
Higher interest rates can negatively impact economic growth by discouraging investment and consumer spending. Businesses may be less inclined to borrow money for expansion or new projects, and consumers may postpone major purchases like homes or cars due to higher borrowing costs.
This can lead to a slowdown in economic activity and potentially even a recession.However, it’s important to note that the relationship between interest rates and economic growth is not always straightforward. In some cases, moderate rate hikes can actually stimulate growth by providing businesses with greater certainty about future economic conditions and encouraging investment.
The impact on economic growth also depends on the starting point of the economy and the specific economic conditions prevailing at the time.
Impact on Employment Levels
Sustained rate hikes can lead to job losses as businesses reduce their operations and hiring in response to slowing economic activity. This can particularly affect industries sensitive to interest rate changes, such as construction, real estate, and manufacturing. However, the impact on employment levels is also influenced by factors like the pace of rate hikes, the overall strength of the labor market, and the availability of alternative job opportunities.
In some cases, moderate rate hikes can actually lead to a stronger labor market by promoting long-term economic stability and encouraging investment in areas with high demand for skilled workers.
Potential for a Recession
The possibility of a recession increases as central banks aggressively raise interest rates. A recession is typically defined as a period of significant decline in economic activity, characterized by factors like negative GDP growth, rising unemployment, and declining consumer spending.The risk of a recession is particularly elevated when interest rates rise rapidly, catching businesses and consumers off guard.
However, it’s crucial to note that the timing and severity of a potential recession are difficult to predict and depend on a multitude of factors, including the starting point of the economy, the pace of rate hikes, and the effectiveness of government policies in mitigating economic shocks.
The risk of a recession is not inevitable, and central banks are closely monitoring economic indicators and adjusting their policies accordingly to minimize the risk of a downturn.
Investment Strategies and Market Opportunities
The continued rise in interest rates presents a significant challenge for investors. As central banks tighten monetary policy, asset prices may experience volatility, and traditional investment strategies may need to be adjusted. To navigate this environment, investors should consider a range of strategies designed to mitigate risk and potentially capture opportunities in a higher interest rate environment.
Investment Strategies in a Rising Rate Environment, Central banks signal continued rate hikes challenging wall streets sentiment
Investors should carefully consider the potential impact of rate hikes on different asset classes and adjust their portfolios accordingly.
| Asset Class | Potential Impact of Rate Hikes | Investment Strategy | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Equities | Higher interest rates can increase borrowing costs for companies, potentially leading to lower earnings and reduced valuations. | Focus on companies with strong balance sheets, consistent earnings growth, and a history of dividend payments. | Consider investing in large-cap companies with stable earnings, such as consumer staples or healthcare, which tend to be less sensitive to economic cycles. |
| Fixed Income | Rising interest rates generally lead to declining bond prices. | Shorten the duration of bond holdings to reduce interest rate risk. Consider investment-grade corporate bonds or high-yield bonds for potential higher returns. | Invest in short-term bonds, such as Treasury bills or commercial paper, which are less sensitive to interest rate changes. |
| Real Estate | Higher interest rates can make mortgage financing more expensive, potentially slowing down real estate appreciation. | Focus on properties with strong fundamentals, such as rental income, and consider value-oriented investments in markets with robust demand. | Invest in rental properties in areas with high population growth and limited housing supply. |
| Commodities | Commodities prices can be influenced by interest rate changes, but the relationship is not always straightforward. | Consider investing in commodities with strong underlying fundamentals, such as gold, which can serve as a hedge against inflation. | Invest in gold bullion or gold exchange-traded funds (ETFs) as a potential inflation hedge. |
For example, in a rising rate environment, investors may consider reducing their exposure to long-duration bonds, which are more sensitive to interest rate changes. Instead, they might allocate more capital to short-term bonds, such as Treasury bills, which have a lower duration and are less susceptible to interest rate risk.