7 Best Commodities to Trade for Easy Success? Think Again!
7 Best Commodities to Trade for Easy Success? While the allure of quick riches in commodity markets is tempting, the reality is far more complex. Trading commodities is not a get-rich-quick scheme, but a challenging endeavor that requires careful planning, deep understanding, and a healthy dose of risk management.
This article will delve into the intricacies of commodity markets, debunking the myth of “easy success” and providing a realistic perspective on what it takes to navigate this volatile world.
From understanding the nature of commodity markets and their unique characteristics to exploring different trading strategies and techniques, we will cover the essential aspects of successful commodity trading. We will also examine the factors to consider when choosing commodities, emphasizing the importance of diversification and risk management.
Finally, we will analyze real-world examples and case studies to illustrate the lessons learned and their implications for future trading decisions.
Understanding Commodity Markets
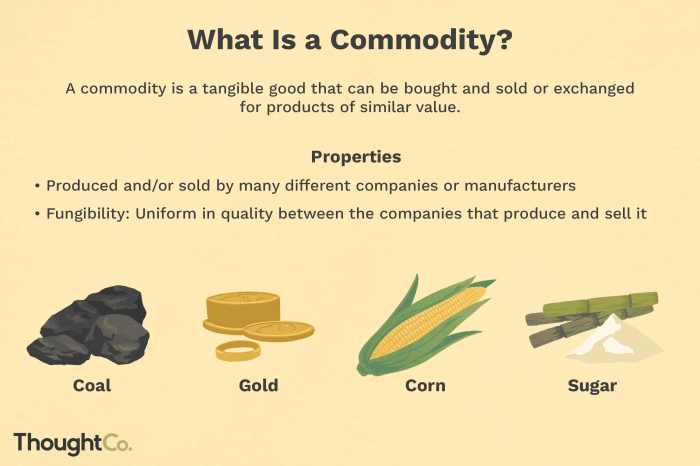
Commodity markets are a fascinating and complex part of the global economy. They are marketplaces where raw materials, such as oil, gold, and agricultural products, are bought and sold. Unlike stocks or bonds, commodities are physical assets with tangible value.
Understanding these markets is crucial for investors, traders, and anyone interested in the global economy.
Characteristics of Commodity Markets
Commodity markets are distinguished by several unique characteristics:
- Standardization:Commodities are traded in standardized units, ensuring consistency and facilitating trading. For example, a barrel of oil is always a specific volume and quality, regardless of the source.
- Global Market:Commodity trading is conducted on a global scale, with prices determined by supply and demand from around the world.
- Price Volatility:Commodity prices can fluctuate significantly due to factors such as weather, geopolitical events, and economic conditions.
- Physical Delivery:While most commodity trading is done electronically, physical delivery of the commodity can occur at some point in the process.
Factors Influencing Commodity Prices
Numerous factors contribute to the ebb and flow of commodity prices:
- Supply and Demand:The fundamental driver of commodity prices is the balance between supply and demand. If demand exceeds supply, prices rise. Conversely, if supply outpaces demand, prices tend to fall.
- Economic Growth:Global economic growth often drives demand for commodities, particularly industrial metals and energy sources. A strong economy typically translates to higher commodity prices.
- Weather Patterns:Weather events can significantly impact agricultural commodity prices. Droughts, floods, and other extreme weather can reduce crop yields, leading to higher prices.
- Geopolitical Events:Political instability, conflicts, and sanctions can disrupt commodity production and supply chains, impacting prices.
- Government Policies:Government policies, such as subsidies, tariffs, and environmental regulations, can influence commodity markets. For example, subsidies for agricultural products can affect supply and prices.
- Technological Advancements:Technological innovations can impact commodity production and consumption patterns. For instance, advancements in energy efficiency can reduce demand for fossil fuels.
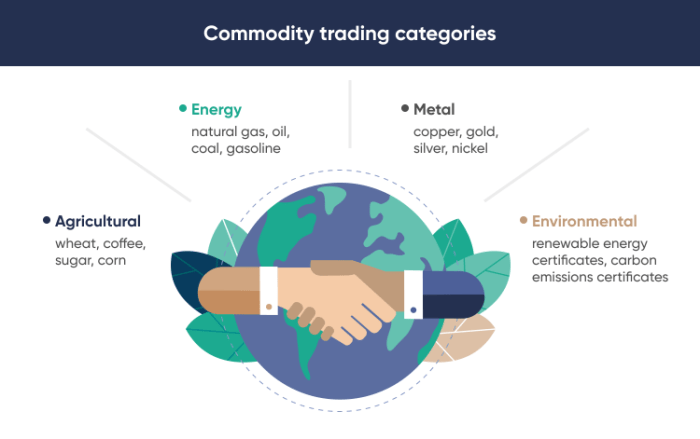
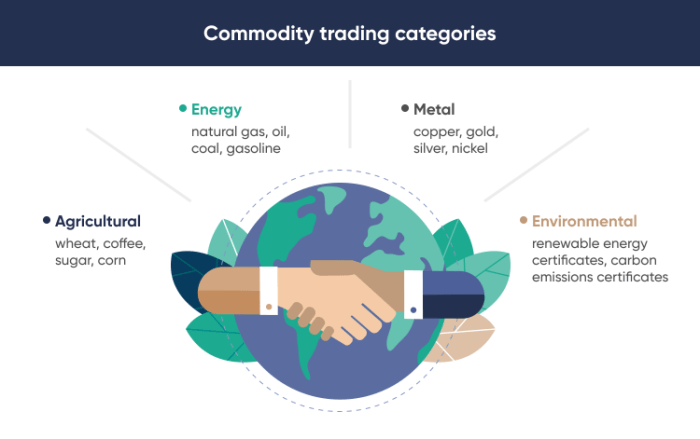
Types of Commodities
Commodities are broadly categorized into three main types:
- Energy:This category includes oil, natural gas, coal, and renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. Energy commodities are essential for transportation, power generation, and industrial processes.
- Metals:Metals, such as gold, silver, copper, aluminum, and iron ore, are used in various industries, from construction and manufacturing to electronics and jewelry. Precious metals like gold and silver are also considered safe-haven assets during times of economic uncertainty.
- Agricultural Products:This category encompasses a wide range of crops, including grains (wheat, corn, rice), oilseeds (soybeans, canola), livestock (cattle, hogs, poultry), and soft commodities (coffee, sugar, cotton). Agricultural commodities are essential for food production, textiles, and biofuels.
Commodity Markets: A Global Network
Commodity markets are interconnected, with prices often influencing each other. For example, rising oil prices can impact the cost of transportation, affecting prices of agricultural products. The global nature of these markets means that events in one region can have ripple effects worldwide.
Understanding Commodity Markets: A Foundation for Success
Understanding the fundamentals of commodity markets is crucial for investors, traders, and anyone seeking to navigate the global economy. By comprehending the factors that drive prices, the different types of commodities, and the interconnectedness of these markets, individuals can make informed decisions and potentially achieve success in this dynamic and ever-evolving landscape.
The Concept of “Easy Success” in Trading
The allure of “easy success” in trading is a persistent myth that attracts many individuals seeking quick riches. While the potential for profits in commodity markets exists, the reality is far more complex and fraught with risks. This section delves into the challenges and risks associated with commodity trading, exposing the myth of “easy success” and highlighting the crucial role of research, risk management, and a sound trading strategy.
The Challenges and Risks of Commodity Trading
Commodity trading involves buying and selling raw materials like oil, gold, wheat, and others. These markets are volatile, influenced by factors like global economic conditions, weather patterns, and geopolitical events. Understanding the intricacies of these markets is essential for navigating their complexities and mitigating potential losses.
- Market Volatility:Commodity prices fluctuate significantly, driven by supply and demand dynamics, economic events, and other factors. This volatility creates opportunities for profit but also exposes traders to substantial losses.
- Economic Factors:Global economic conditions, including interest rates, inflation, and economic growth, impact commodity prices. Recessions, for instance, can lead to lower demand for commodities, resulting in price declines.
- Geopolitical Events:Political instability, wars, and sanctions can disrupt supply chains, leading to price spikes. The 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, for example, significantly impacted global energy markets, driving up oil prices.
- Weather Patterns:Extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, and hurricanes, can affect agricultural commodity production, leading to price fluctuations. A severe drought, for instance, could reduce wheat production, driving up prices.
- Regulatory Changes:Government regulations and policies can impact commodity markets. For example, environmental regulations aimed at reducing carbon emissions could influence the demand for fossil fuels.
- Leverage and Margin Calls:Commodity trading often involves leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with smaller amounts of capital. However, leverage can amplify both profits and losses. Margin calls, where traders are required to deposit additional funds to maintain their positions, can occur if prices move against them, potentially leading to significant losses.
The Myth of “Easy Success” in Trading
The notion of “easy success” in commodity trading is misleading and often perpetuated by individuals promoting get-rich-quick schemes. While some traders may experience short-term gains, consistent success in commodity markets requires a deep understanding of market dynamics, disciplined risk management, and a well-defined trading strategy.
“The market can stay irrational longer than you can stay solvent.”
John Maynard Keynes
Importance of Research, Risk Management, and a Sound Trading Strategy
To navigate the complexities of commodity trading, traders must prioritize research, risk management, and a sound trading strategy.
- Thorough Research:Understanding the fundamentals of the commodity market, including supply and demand dynamics, economic factors, geopolitical events, and regulatory changes, is crucial for making informed trading decisions.
- Risk Management:Defining a clear risk tolerance level and implementing strategies to manage potential losses is essential. Stop-loss orders, for example, can automatically exit a trade when prices move against a trader’s position, limiting potential losses.
- Sound Trading Strategy:Developing a well-defined trading plan that Artikels entry and exit points, position sizing, and risk management strategies is crucial for success. Backtesting the strategy on historical data can help evaluate its effectiveness before deploying it in live markets.
Identifying Potential Commodities for Trading
The key to successful commodity trading lies in identifying promising commodities with potential for growth. This involves understanding current market trends, analyzing historical price movements, and considering the future outlook of various commodities. By combining these elements, you can make informed decisions about which commodities to include in your trading portfolio.
Analyzing Commodity Market Trends
Understanding current market trends is crucial for identifying potential trading opportunities. The global commodity market is influenced by a multitude of factors, including economic growth, geopolitical events, technological advancements, and environmental regulations.
- Energy:The global energy market is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the transition to renewable energy sources and the growing demand for cleaner fuels. This shift has led to increased investments in renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, and a growing focus on energy efficiency.
As a result, the prices of traditional fossil fuels, such as oil and natural gas, have been fluctuating in recent years. However, the demand for oil and gas remains strong, particularly in emerging markets, making them potential trading opportunities.
- Metals:The demand for industrial metals, such as copper, aluminum, and zinc, is closely tied to global economic growth. As emerging markets continue to develop, the demand for these metals is expected to rise. The increasing adoption of electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies is also driving demand for specific metals, such as lithium and cobalt.
These factors have contributed to recent price increases in certain industrial metals, making them attractive trading opportunities.
- Agriculture:The agricultural commodity market is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including weather patterns, global food demand, and government policies. The global population is growing, leading to an increasing demand for food and agricultural products. However, climate change and extreme weather events are posing challenges to agricultural production, potentially leading to price volatility.
The demand for sustainable agricultural practices and organic products is also growing, presenting potential opportunities for trading in specific agricultural commodities.
Examining Historical Price Movements
Historical price data can provide valuable insights into the past performance of different commodities and help identify potential patterns and trends. By analyzing historical price movements, you can gain a better understanding of the factors that have influenced commodity prices in the past and make more informed predictions about future price movements.
- Trend Analysis:Identifying long-term trends in commodity prices can be helpful in determining the overall direction of the market. For example, the price of oil has been on an upward trend in recent years, driven by factors such as increasing global demand and geopolitical tensions.
This trend suggests that oil could continue to be a profitable commodity to trade in the near future.
- Seasonality:Many commodities exhibit seasonal price patterns due to factors such as weather conditions and harvest cycles. For example, the price of coffee tends to rise during the harvest season due to increased supply, while the price of wheat tends to fall during the harvest season due to increased availability.
Understanding these seasonal patterns can help traders identify potential trading opportunities.
- Cyclical Patterns:Some commodities exhibit cyclical price patterns, which can be identified by analyzing historical price data. For example, the price of gold tends to rise during periods of economic uncertainty or inflation, while the price of oil tends to fall during economic recessions.
Understanding these cyclical patterns can help traders identify potential trading opportunities.
Identifying High-Performing Commodities
Several commodities have demonstrated strong performance in recent years, making them potential trading opportunities.
- Lithium:The increasing demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy technologies has driven a surge in the price of lithium, a key component in lithium-ion batteries. As the demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy continues to grow, the price of lithium is expected to remain elevated in the coming years.
- Copper:Copper is an essential component in many industrial applications, including construction, electrical wiring, and plumbing. The increasing demand for copper from emerging markets and the growth of renewable energy technologies have contributed to recent price increases. The future outlook for copper remains positive, with continued demand growth expected in the coming years.
- Natural Gas:The demand for natural gas has been rising in recent years, driven by factors such as its relative affordability compared to other energy sources and its role in the transition to cleaner energy. The development of new natural gas reserves and the growing use of natural gas for electricity generation have also contributed to increased demand.
The future outlook for natural gas remains positive, with continued growth expected in the coming years.
Essential Trading Strategies and Techniques
Successful commodity trading requires a well-defined strategy that incorporates fundamental and technical analysis, risk management, and disciplined execution. This section delves into various strategies and techniques that can enhance your trading decisions and contribute to your overall success in the commodity markets.
Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis focuses on the underlying economic factors that influence commodity prices. It involves evaluating factors such as supply and demand, government policies, global economic conditions, and weather patterns. By understanding these factors, traders can anticipate price movements and make informed trading decisions.For example, a trader might use fundamental analysis to predict an increase in the price of coffee due to a shortage of coffee beans caused by adverse weather conditions in major coffee-producing regions.
While the idea of finding “7 best commodities to trade for easy success” might seem appealing, it’s important to remember that the financial world is complex and unpredictable. The recent federal reserve report on svb collapse highlights mismanagement and supervisory failures is a stark reminder that even seemingly stable institutions can falter.
Understanding the risks and doing thorough research are crucial before entering any market, especially when it comes to commodities trading.
This analysis would consider factors like the extent of the crop failure, the impact on global coffee production, and the potential for price increases in the coffee market.
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis involves studying historical price and volume data to identify patterns and trends that can predict future price movements. It utilizes various technical indicators and chart patterns to identify entry and exit points for trades.Technical analysts might use moving averages to identify trends, Bollinger Bands to measure volatility, or candlestick patterns to predict price reversals.
For instance, a trader might use a moving average crossover to identify a potential buy signal when a short-term moving average crosses above a long-term moving average.
Arbitrage
Arbitrage involves exploiting price discrepancies between different markets. Traders can profit by simultaneously buying a commodity in one market and selling it in another market where it is priced higher.For example, a trader might identify a price difference between the gold price in the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) and the London Bullion Market Association (LBMA).
By buying gold on the NYMEX and simultaneously selling it on the LBMA, the trader can profit from the price difference, assuming transaction costs are lower than the price discrepancy.
Setting Clear Trading Goals
Having clear trading goals is crucial for success. Define your objectives, whether it’s generating a specific return on investment, building a long-term portfolio, or simply learning about the market. This clarity helps you focus your trading efforts and evaluate your performance effectively.For instance, a trader might set a goal of generating a 10% annual return on their investment in gold futures.
This goal would guide their trading decisions and help them measure their success.
Managing Risk
Managing risk is paramount in commodity trading. Identify and quantify your potential losses, and implement strategies to mitigate them. This includes setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on individual trades, diversifying your portfolio across different commodities, and avoiding excessive leverage.For example, a trader might set a stop-loss order to limit their losses on a trade in crude oil futures to 5% of their total capital.
This would ensure that their losses are contained even if the market moves against them.
Utilizing Stop-Loss Orders
Stop-loss orders are essential tools for managing risk. They are pre-programmed orders that automatically exit a trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses. By setting stop-loss orders, traders can minimize the impact of adverse market movements.For instance, a trader might set a stop-loss order for a long position in wheat futures at a price 5% below the current market price.
If the price of wheat falls below this level, the stop-loss order will be triggered, automatically selling the wheat futures and limiting the trader’s losses.
Developing a Trading Plan
A comprehensive trading plan is crucial for disciplined execution and long-term success. This plan should Artikel your trading goals, strategies, risk management approach, and trading rules. By following a well-defined plan, you can make consistent trading decisions and avoid emotional biases.For example, a trader’s trading plan might include:* Trading Goals:Generate a 10% annual return on investment in gold futures.
Trading Strategies Utilize both fundamental and technical analysis to identify trading opportunities.
Risk Management Limit losses to 5% of total capital per trade using stop-loss orders.
Trading Rules
Finding the “7 best commodities to trade for easy success” is a bit of a myth, but understanding market trends is key. One trend worth considering is the shift towards electric vehicles, which could impact the future of oil and gas.
To get a better understanding of the pros and cons of both options, check out this article on gas vs electric vehicles. By staying informed about evolving technologies and their impact on traditional industries, you can make more informed decisions when choosing commodities to trade.
Trading Journal Record all trades, including entry and exit points, reasons for the trades, and results.By adhering to a comprehensive trading plan, traders can increase their chances of achieving their trading goals and mitigating risk.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Commodities
Selecting the right commodities to trade is crucial for success in the market. While “easy success” is a relative term, understanding the key factors that influence commodity performance can help you make informed decisions.
Market Volatility
Volatility refers to the degree of price fluctuation in a commodity market. Highly volatile commodities, like crude oil or natural gas, can offer significant profit potential but also carry a higher risk of losses. Less volatile commodities, like gold or silver, might provide more stable returns but may offer lower potential gains.
Liquidity
Liquidity refers to the ease with which a commodity can be bought or sold in the market. Highly liquid commodities, such as gold or silver, are traded in large volumes and have a readily available market. Less liquid commodities, like agricultural products or industrial metals, might have lower trading volumes and could experience price fluctuations due to limited buying or selling interest.
While there’s no such thing as “easy success” in trading, some commodities are generally considered less volatile and easier to understand than others. Gold, silver, and oil are classic choices, but keep in mind that even the most stable markets can be affected by unforeseen events, like the recent news of genesis crypto lending filing for bankruptcy protection.
This highlights the importance of thorough research and risk management, no matter what commodity you choose to trade.
Storage Costs
Storage costs are incurred when holding physical commodities, such as oil or agricultural products. These costs can vary depending on factors like storage facilities, insurance, and transportation. Commodities with high storage costs, like agricultural products, might be less attractive for long-term trading, as the costs can eat into potential profits.
Correlation with Other Markets
Commodities can be influenced by other markets, such as the stock market or currency markets. For example, the price of oil can be affected by global economic growth, which can influence demand for energy. Understanding the correlation between different markets can help you identify potential trading opportunities.
Supply and Demand Dynamics
The fundamental principle of supply and demand plays a significant role in commodity pricing. Factors like weather conditions, geopolitical events, and technological advancements can influence the supply and demand dynamics of commodities. For example, a drought in a major agricultural region could lead to a decrease in supply and an increase in prices.
Trading Strategies
Different commodities are suitable for different trading strategies. For example, highly volatile commodities like crude oil might be suitable for short-term trading strategies, while less volatile commodities like gold might be more suitable for long-term investments.
Pros and Cons of Different Commodities
| Commodity | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Gold | Safe-haven asset, low correlation with other markets, high liquidity | Low potential returns, subject to central bank intervention |
| Crude Oil | High potential returns, significant global demand | High volatility, subject to geopolitical risks, storage costs |
| Natural Gas | Growing demand, potential for price spikes | High volatility, seasonal price fluctuations |
| Copper | Essential for infrastructure development, high demand from emerging markets | Subject to global economic conditions, cyclical price movements |
| Soybeans | High global demand, potential for price spikes due to weather events | High storage costs, subject to agricultural policies |
Importance of Diversification and Risk Management
In the dynamic world of commodity trading, where prices fluctuate constantly, the importance of diversification and risk management cannot be overstated. These strategies are crucial for mitigating potential losses and enhancing the overall profitability of your trading portfolio.
Diversification in Commodity Trading
Diversification in commodity trading involves spreading investments across different asset classes or commodity sectors to reduce overall portfolio risk. By investing in a variety of commodities, traders can minimize the impact of adverse price movements in any single commodity. This approach helps to smooth out returns and reduce volatility, making the portfolio more resilient to market fluctuations.
- Allocating Investments Across Different Commodity Sectors:Diversifying across various commodity sectors, such as energy, metals, agriculture, and livestock, can help mitigate risk. For example, investing in both oil and gold can offer protection against inflation and economic uncertainty, as these commodities tend to perform differently under varying market conditions.
- Investing in Different Geographic Locations:Diversifying geographically by investing in commodities produced in different regions can further reduce risk. This strategy helps to mitigate the impact of localized events, such as weather disruptions or political instability, that could affect the price of a specific commodity in a particular region.
Setting Realistic Risk Tolerance Levels, 7 best commodities to trade for easy success
Setting realistic risk tolerance levels is a fundamental aspect of risk management in commodity trading. Risk tolerance refers to an individual’s capacity and willingness to accept potential losses in pursuit of higher returns. It is essential to determine your risk tolerance before entering any trades and to avoid taking on more risk than you can comfortably handle.
Implementing Risk Management Strategies
Implementing effective risk management strategies is crucial for protecting your trading capital and maximizing profits. These strategies can include:
- Stop-Loss Orders:Stop-loss orders are pre-set instructions to automatically exit a trade when a specific price level is reached. This strategy helps to limit potential losses by preventing further price declines from eroding your capital.
- Position Sizing:Position sizing refers to determining the appropriate amount of capital to allocate to each trade. By carefully managing position size, traders can limit the potential impact of adverse price movements on their overall portfolio.
- Hedging Strategies:Hedging involves using financial instruments to offset potential losses from adverse price movements in a particular commodity. For example, a trader who is long in oil futures could hedge their position by buying put options on oil, which would provide protection against a decline in oil prices.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies: 7 Best Commodities To Trade For Easy Success
Understanding the intricacies of commodity trading requires more than just theoretical knowledge. It’s essential to analyze real-world examples of successful traders and their strategies, as well as examining case studies of specific trades. These insights provide valuable lessons that can be applied to future trading decisions, helping you navigate the complexities of the commodity market.
Successful Commodity Traders and Their Strategies
The world of commodity trading is filled with individuals who have achieved remarkable success through their expertise and strategic approaches. Examining their methods can provide valuable insights for aspiring traders.
- George Soros:Renowned for his successful short-selling of the British pound in 1992, Soros is known for his astute analysis of global economic trends and his ability to capitalize on market volatility. He utilizes a combination of fundamental and technical analysis to identify trading opportunities.
- Jim Rogers:A prominent investor and commodity trader, Rogers is famous for his long-term bullish outlook on commodities. He emphasizes the importance of diversification and investing in undervalued assets. His strategies focus on identifying long-term trends and holding positions for extended periods.
- Paul Tudor Jones:A hedge fund manager known for his success in commodity trading, Jones is recognized for his expertise in using technical analysis and his ability to predict market turning points. He utilizes a combination of trend-following and contrarian strategies, adapting his approach based on market conditions.
Case Studies of Specific Commodity Trades
Analyzing specific commodity trades, both profitable and unsuccessful, provides valuable insights into the dynamics of the market and the factors that influence trading outcomes.
Case Study 1: Profitable Oil Trade
In 2020, as the COVID-19 pandemic caused a significant drop in global oil demand, a trader recognized the potential for a rebound in oil prices. They purchased oil futures contracts at a low price, anticipating that demand would eventually recover.
As the global economy began to reopen, oil prices rose, leading to substantial profits for the trader.
Case Study 2: Unsuccessful Gold Trade
In 2011, a trader believed that gold prices would continue to rise due to economic uncertainty and inflation. They purchased gold futures contracts at a high price. However, the market did not move as expected, and gold prices declined, resulting in significant losses for the trader.
Lessons Learned from Real-World Examples
The examples and case studies discussed above highlight several key lessons for commodity traders:
- Importance of Fundamental Analysis:Understanding the underlying economic factors that influence commodity prices is crucial for making informed trading decisions.
- Strategic Use of Technical Analysis:Technical analysis can be used to identify trends, support and resistance levels, and potential entry and exit points.
- Risk Management is Essential:Implementing effective risk management strategies, such as stop-loss orders and position sizing, is crucial to protect profits and minimize losses.
- Adaptability is Key:The commodity market is dynamic and constantly changing. Traders must be adaptable and adjust their strategies based on market conditions.