US Housing Market Sees Relief as Mortgage Rates Dip
Us housing market sees marginal relief as mortgage rates inch down from 22 year high – US Housing Market Sees Relief as Mortgage Rates Dip from 22-year highs, offering a glimmer of hope for buyers weary of sky-high rates. This recent dip, while modest, has stirred a sense of optimism, potentially easing some of the pressure on affordability and sparking renewed interest in the market.
The recent decline in mortgage rates, driven by a combination of factors, including economic indicators and Federal Reserve policy, has brought some much-needed relief to the housing market. While rates remain elevated compared to historical averages, this downward trend has spurred a wave of activity among buyers, creating a more competitive landscape for sellers.
This shift in market dynamics presents a unique opportunity for both buyers and sellers to navigate the current housing climate.
Current Housing Market Conditions

The recent decline in mortgage rates has brought some much-needed relief to the housing market, which had been grappling with affordability challenges brought on by soaring rates. While rates are still higher than they were a year ago, the downward trend has provided a glimmer of hope for potential homebuyers.
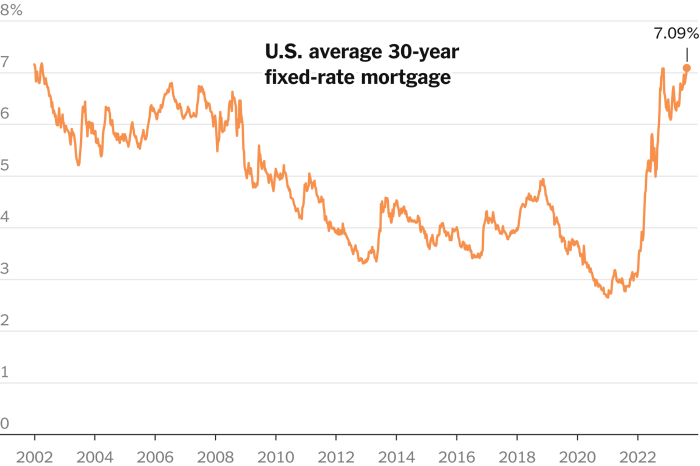
The Significance of the 22-Year High in Mortgage Rates, Us housing market sees marginal relief as mortgage rates inch down from 22 year high
The 22-year high in mortgage rates reached in late 2022 had a profound impact on the housing market. The sharp increase in borrowing costs made homeownership less attainable for many, leading to a slowdown in demand and a cooling of the market.
This period was characterized by:* Reduced Buyer Demand:As mortgage rates climbed, the affordability of homes decreased significantly. This discouraged many potential buyers from entering the market, leading to a decline in demand.
While the US housing market sees marginal relief as mortgage rates inch down from their 22-year high, it’s a good time to revisit your personal finances and make sure you’re on track. If you’re carrying credit card debt, now’s the perfect time to implement some credit debt management tips and strategies to free up more cash flow for a potential future home purchase.
Remember, even small changes can make a big difference in the long run, especially when it comes to your financial well-being and your ability to navigate the fluctuating housing market.
Increased Inventory With fewer buyers competing for homes, inventory levels rose, giving sellers more leverage in negotiations. This shift in market dynamics gave buyers more options and a better chance to secure favorable deals.
Slower Home Price Growth The combination of reduced demand and increased inventory led to a slowdown in home price growth. In some markets, prices even began to decline as sellers adjusted their expectations to attract buyers in a more competitive environment.
The Impact of the Recent Decline in Mortgage Rates
The recent decline in mortgage rates has brought some positive changes to the housing market. As borrowing costs become more manageable, buyer demand is gradually increasing. This has led to:* Increased Buyer Activity:As mortgage rates have eased, more buyers are entering the market, seeking to capitalize on the opportunity to secure financing at more favorable rates.
Competition for Homes With increased buyer activity, competition for available homes has intensified in some areas. This can lead to multiple offers and bidding wars, potentially pushing prices upward.
While the US housing market sees marginal relief as mortgage rates inch down from their 22-year high, Wall Street anticipates a positive start to the week, with the Jackson Hole Symposium and Nvidia earnings taking center stage. The Jackson Hole event is expected to offer insights into the Fed’s future monetary policy, while Nvidia’s results will provide a gauge of the tech sector’s performance.
This week’s economic events could further influence the housing market’s trajectory, as investors seek clarity on inflation and interest rate trends.
Stabilization of Home Prices The increased demand has helped stabilize home prices in many markets, preventing further declines and potentially leading to modest growth in some areas.
Current State of the Housing Market
The housing market is currently in a state of flux, with a delicate balance between buyer demand and affordability. The recent decline in mortgage rates has provided some relief, but the market is still facing challenges:* Inventory Levels:Inventory levels remain relatively low compared to historical averages, which can create competition among buyers and push prices upward.
Affordability While mortgage rates have declined, they are still significantly higher than they were a few years ago. This continues to present affordability challenges for many potential homebuyers, particularly those with limited financial resources.
Economic Uncertainty The current economic climate, with inflation and rising interest rates, creates uncertainty for both buyers and sellers. This can lead to hesitation in the market and affect buying and selling decisions.
Impact of Rate Decline on Buyers and Sellers: Us Housing Market Sees Marginal Relief As Mortgage Rates Inch Down From 22 Year High

The recent decline in mortgage rates, though marginal, has injected a glimmer of hope into the housing market. While rates remain elevated compared to historical lows, this shift has sparked a renewed sense of optimism among both buyers and sellers.
It’s a bit of a mixed bag for the US housing market right now. While mortgage rates have finally dipped from their 22-year high, offering some relief to potential buyers, the rising cost of living is still a concern. This is especially true with the recent news that Saudi Arabia has extended its oil production cuts, sparking a price surge and market speculations , which will likely impact fuel costs and, in turn, inflation.
So, while the housing market might be seeing a slight improvement, it remains to be seen how these global events will ultimately affect affordability and consumer confidence.
Impact on Buyers
The decrease in mortgage rates translates to lower monthly payments for homebuyers. This means that potential homebuyers can now afford to purchase a larger or more expensive property than they could have just a few months ago. For example, a buyer with a $300,000 mortgage at a 7% interest rate would pay approximately $2,000 per month.
If rates were to drop to 6.5%, their monthly payment would decrease to about $1,850, freeing up more cash flow for other expenses.
Impact on Sellers
While the rate decline benefits buyers, it also presents a challenge for sellers. As buyers become more confident in the market, they may be less willing to accept inflated asking prices. Sellers may need to adjust their pricing strategies to reflect the changing market dynamics.
In some cases, sellers may find themselves in a position where they need to offer concessions or incentives to attract buyers.
Economic Factors Influencing the Market
The housing market is a complex ecosystem influenced by a myriad of economic factors, making it susceptible to shifts in the broader economic landscape. Inflation, economic uncertainty, and Federal Reserve monetary policy play a significant role in shaping the housing market’s trajectory.
Inflation and Economic Uncertainty
Inflation, a persistent increase in the general price level of goods and services, can have a profound impact on the housing market. When inflation is high, the cost of building materials and labor rises, leading to higher home prices. Moreover, rising inflation erodes the purchasing power of consumers, making it more challenging for them to afford a home.
Economic uncertainty, characterized by volatility in the stock market, rising unemployment, or geopolitical tensions, can also dampen demand for housing as consumers become more cautious about making significant financial commitments.
Federal Reserve Monetary Policy
The Federal Reserve (Fed) uses monetary policy tools to influence interest rates and the availability of credit in the economy. The Fed’s actions directly impact mortgage rates, which are a key determinant of housing affordability. When the Fed raises interest rates, mortgage rates typically rise, making it more expensive to borrow money for a home purchase.
Conversely, when the Fed lowers interest rates, mortgage rates tend to fall, making homeownership more accessible. The Fed’s decisions are influenced by inflation, economic growth, and unemployment levels. For example, in 2022, the Fed aggressively raised interest rates to combat high inflation, leading to a surge in mortgage rates and a slowdown in the housing market.
Other Macroeconomic Factors
Beyond inflation and monetary policy, other macroeconomic factors influence the housing market. Employment levels play a crucial role in determining consumer confidence and affordability. Strong employment growth often translates into higher wages and greater purchasing power, boosting demand for housing.
Conversely, a decline in employment can lead to job insecurity and reduced consumer confidence, dampening housing demand. Consumer confidence, a measure of consumer optimism about the economy, also affects housing market activity. When consumers are confident about the economy, they are more likely to make significant purchases, such as a home.
Conversely, low consumer confidence can lead to a decline in housing demand.
Future Outlook for the Housing Market
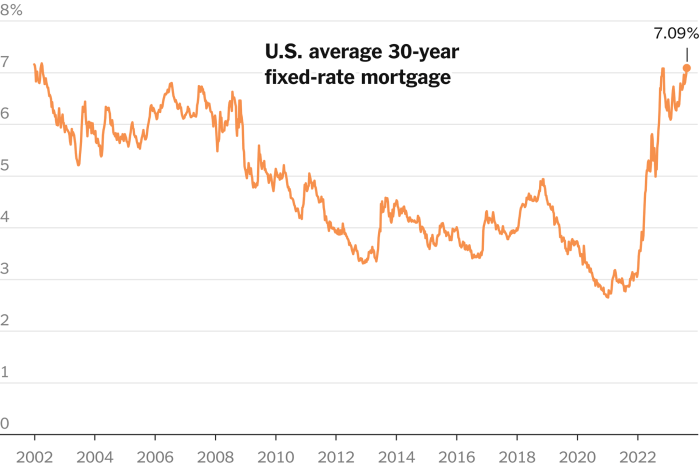
While the recent decline in mortgage rates offers some relief, predicting the future trajectory of the housing market remains complex. Several factors, including economic conditions, inflation, and policy changes, will influence the market’s direction in the coming months and years.
Short-Term and Long-Term Forecasts
The short-term outlook for the housing market hinges on the continued behavior of mortgage rates. If rates remain at their current levels or continue to decline, this could incentivize buyers to re-enter the market, leading to increased demand and potentially stabilizing or even slightly increasing home prices.
However, if rates rise again, this could dampen buyer demand, leading to a continuation of the recent slowdown in price growth. In the long term, the housing market’s trajectory will depend on broader economic conditions. Factors such as inflation, economic growth, and employment trends will play a significant role in shaping buyer sentiment and affordability.
If the economy experiences sustained growth and inflation moderates, the housing market could see a gradual return to normalcy, with steady price appreciation and increased activity. However, if the economy enters a recession or inflation remains high, the housing market could experience a prolonged period of sluggish growth or even a decline in prices.